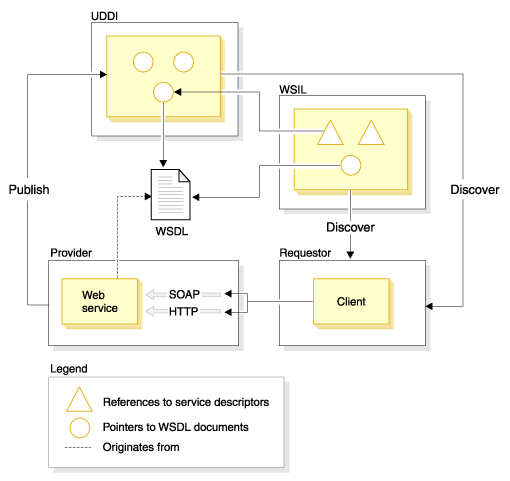
The following standards play key roles in Web services: Universal Description, Discovery and Integration (UDDI), Web Services Description Language (WSDL), Web Services Inspection Language (WSIL), Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP) and Web Services Interoperability (WS-I). The relationship between these standards is described in Figure .
與Web services密切相關的主要標準有以下幾種:
1、UDDI
UDDI是平臺無關的,為業務提供了一個全局的注冊、查找Web Services 的規范。
UDDI has two functions:
- It is a SOAP-based protocol that defines how clients communicate with UDDI registries.
- It is a particular set of global replicated registries.
UDDI includes an XML schema for SOAP messages that defines a set of documents to describe business and services information, a common set of APIs for querying and publishing information to the directories, and an API for replicating directory entries between peer UDDI nodes.
2、WSIL
Web Services Inspection Language (WSIL) is a service discovery mechanism that is an alternative to UDDI as well as complementary to UDDI. When you discover Web services with UDDI, you go to a centralized registry.? WSIL is an alternative approach to Web service discovery.? WSIL allows you to go directly to the service provider and ask for the services it provides.
WSIL也是用于查找Web Services 的機制。它是UDDI的補充。
The Web Services Inspection Language (WSIL) and the Universal Description, Discovery, and Integration (UDDI) specification both address issues related to Web service discovery.? However, each specification takes a different approach to the discovery of Web services.? The two specifications can be used separately or jointly; searching with WSIL can result in finding items in UDDI.
3、WSDL
WSDL is an XML-based open specification that describes the interfaces to and instances of Web services on the network. It is extensible, so endpoints can be described regardless of the message formats or network protocols that are used to communicate.
Relationship between UDDI and WSDL
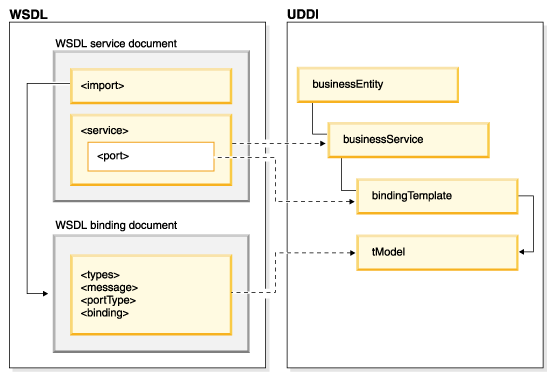
Figure? illustrates the relationship between UDDI and WSDL. The WSDL service element references the WSDL binding element. The URL of the document containing the WSDL binding element is published to the UDDI business registry as a tModel. The URL of the document containing the WSDL service element is published to the UDDI business registry as a businessService and contains information about the bindingTemplate.
4、SOAP
SOAP is an XML-based standard for messaging over HTTP and other Internet protocols. It is a lightweight protocol for the exchange of information in a decentralized, distributed environment. It is based on XML and consists of three parts:
- An envelope that defines a framework for describing what is in a message and how to process it.
- A set of encoding rules for expressing instances of application-defined data types.
- A convention for representing remote procedure calls and responses.
SOAP enables the binding and usage of discovered Web services by defining a message path for routing messages. SOAP may be used to query UDDI for Web services.
簡單對象訪問協議(SOAP)是一種輕量的、簡單的、基于 XML 的協議,它被設計成在 WEB 上交換結構化的和固化的信息。 SOAP 可以和現存的許多因特網協議和格式結合使用,包括超文本傳輸協議( HTTP),簡單郵件傳輸協議(SMTP),多用途網際郵件擴充協議(MIME)。它還支持從消息系統到遠程過程調用(RPC)等大量的應用程序。
SOAP 包括三個部分:
- SOAP 封裝:它定義了一個框架,該框架描述了消息中的內容是什么,誰應當處理它以及它是可選的還是必須的。
- SOAP 編碼規則:它定義了一種序列化的機制,用于交換應用程序所定義的數據類型的實例。
- SOAP RPC 表示:它定義了用于表示遠程過程調用和應答的協定。
SOAP 消息基本上是從發送端到接收端的單向傳輸,但它們常常結合起來執行類似于請求 / 應答的模式。所有的 SOAP 消息都使用 XML 編碼。一條 SOAP 消息就是一個包含有一個必需的 SOAP 的封裝包,一個可選的 SOAP 標頭和一個必需的 SOAP 體塊的 XML 文檔。
SOAP 消息格式:
SOAP 標頭
<SOAP-ENV: Envelope Attributes>
<SOAP-ENV:Body>
Attributes
</SOAP-ENV:Body>
</SOAP-ENV:Envelope>