??????網絡的監測是所有 Linux 子系統里面最復雜的,有太多的因素在里面,比如:延遲、阻塞、沖突、丟包等,更糟的是與 Linux 主機相連的路由器、交換機、無線信號都會影響到整體網絡并且很難判斷是因為 Linux 網絡子系統的問題還是別的設備的問題,增加了監測和判斷的復雜度。現在我們使用的所有網卡都稱為自適應網卡,意思是說能根據網絡上的不同網絡設備導致的不同網絡速度和工作模式進行自動調整。我們可以通過 ethtool 工具來查看網卡的配置和工作模式:
# /sbin/ethtool eth0
Settings for eth0:
Supported ports: [ TP ]
Supported link modes: 10baseT/Half 10baseT/Full
100baseT/Half 100baseT/Full
1000baseT/Half 1000baseT/Full
Supports auto-negotiation: Yes
Advertised link modes: 10baseT/Half 10baseT/Full
100baseT/Half 100baseT/Full
1000baseT/Half 1000baseT/Full
Advertised auto-negotiation: Yes
Speed: 100Mb/s
Duplex: Full
Port: Twisted Pair
PHYAD: 1
Transceiver: internal
Auto-negotiation: on
Supports Wake-on: g
Wake-on: g
Current message level: 0x000000ff (255)
Link detected: yes
上面給出的例子說明網卡有 10baseT,100baseT 和 1000baseT 三種選擇,目前正自適應為 100baseT(Speed: 100Mb/s)。可以通過 ethtool 工具強制網卡工作在 1000baseT 下:
# /sbin/ethtool -s eth0 speed 1000 duplex full autoneg off
iptraf
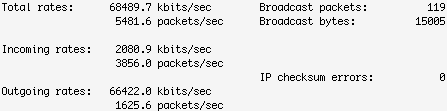
兩臺主機之間有網線(或無線)、路由器、交換機等設備,測試兩臺主機之間的網絡性能的一個辦法就是在這兩個系統之間互發數據并統計結果,看看吞吐量、延遲、速率如何。iptraf 就是一個很好的查看本機網絡吞吐量的好工具,支持文字圖形界面,很直觀。下面圖片顯示在 100 mbps 速率的網絡下這個 Linux 系統的發送傳輸率有點慢,Outgoing rates 只有 66 mbps.
# iptraf -d eth0
netperf
netperf 運行在 client/server 模式下,比 iptraf 能更多樣化的測試終端的吞吐量。先在服務器端啟動 netserver:
# netserver
Starting netserver at port 12865
Starting netserver at hostname 0.0.0.0 port 12865 and family AF_UNSPEC
然后在客戶端測試服務器,執行一次持續10秒的 TCP 測試:
# netperf -H 172.16.38.36 -l 10
TCP STREAM TEST from 0.0.0.0 (0.0.0.0) port 0 AF_INET to 172.16.38.36 (172.16.38.36) port 0 AF_INET
Recv Send Send
Socket Socket Message Elapsed
Size Size Size Time Throughput
bytes bytes bytes secs. 10^6bits/sec
87380 16384 16384 10.32 93.68
從以上輸出可以看出,網絡吞吐量在 94mbps 左右,對于 100mbps 的網絡來說這個性能算的上很不錯。上面的測試是在服務器和客戶端位于同一個局域網,并且局域網是有線網的情況,你也可以試試不同結構、不同速率的網絡,比如:網絡之間中間多幾個路由器、客戶端在 wi-fi、VPN 等情況。
netperf 還可以通過建立一個 TCP 連接并順序地發送數據包來測試每秒有多少 TCP 請求和響應。下面的輸出顯示在 TCP requests 使用 2K 大小,responses 使用 32K 的情況下處理速率為每秒243:
# netperf -t TCP_RR -H 172.16.38.36 -l 10 -- -r 2048,32768
TCP REQUEST/RESPONSE TEST from 0.0.0.0 (0.0.0.0) port 0 AF_INET to 172.16.38.36 (172.16.38.36) port 0 AF_INET
Local /Remote
Socket Size Request Resp. Elapsed Trans.
Send Recv Size Size Time Rate
bytes Bytes bytes bytes secs. per sec
16384 87380 2048 32768 10.00 243.03
16384 87380
iperf
iperf 和 netperf 運行方式類似,也是 server/client 模式,先在服務器端啟動 iperf:
# iperf -s -D
------------------------------------------------------------
Server listening on TCP port 5001
TCP window size: 85.3 KByte (default)
------------------------------------------------------------
Running Iperf Server as a daemon
The Iperf daemon process ID : 5695
然后在客戶端對服務器進行測試,客戶端先連接到服務器端(172.16.38.36),并在30秒內每隔5秒對服務器和客戶端之間的網絡進行一次帶寬測試和采樣:
# iperf -c 172.16.38.36 -t 30 -i 5
------------------------------------------------------------
Client connecting to 172.16.38.36, TCP port 5001
TCP window size: 16.0 KByte (default)
------------------------------------------------------------
[ 3] local 172.16.39.100 port 49515 connected with 172.16.38.36 port 5001
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth
[ 3] 0.0- 5.0 sec 58.8 MBytes 98.6 Mbits/sec
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth
[ 3] 5.0-10.0 sec 55.0 MBytes 92.3 Mbits/sec
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth
[ 3] 10.0-15.0 sec 55.1 MBytes 92.4 Mbits/sec
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth
[ 3] 15.0-20.0 sec 55.9 MBytes 93.8 Mbits/sec
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth
[ 3] 20.0-25.0 sec 55.4 MBytes 92.9 Mbits/sec
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth
[ 3] 25.0-30.0 sec 55.3 MBytes 92.8 Mbits/sec
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth
[ 3] 0.0-30.0 sec 335 MBytes 93.7 Mbits/sec
tcpdump 和 tcptrace
tcmdump 和 tcptrace 提供了一種更細致的分析方法,先用 tcpdump 按要求捕獲數據包把結果輸出到某一文件,然后再用 tcptrace 分析其文件格式。這個工具組合可以提供一些難以用其他工具發現的信息:
# /usr/sbin/tcpdump -w network.dmp
tcpdump: listening on eth0, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), capture size 96 bytes
511942 packets captured
511942 packets received by filter
0 packets dropped by kernel
# tcptrace network.dmp
1 arg remaining, starting with 'network.dmp'
Ostermann's tcptrace -- version 6.6.7 -- Thu Nov 4, 2004
511677 packets seen, 511487 TCP packets traced
elapsed wallclock time: 0:00:00.510291, 1002714 pkts/sec analyzed
trace file elapsed time: 0:02:35.836372
TCP connection info:
1: zaber:54581 - boulder:111 (a2b) 6> 5< (complete)
2: zaber:833 - boulder:32774 (c2d) 6> 5< (complete)
3: zaber:pcanywherestat - 172.16.39.5:53086 (e2f) 2> 3<
4: zaber:716 - boulder:2049 (g2h) 347> 257<
5: 172.16.39.100:58029 - zaber:12865 (i2j) 7> 5< (complete)
6: 172.16.39.100:47592 - zaber:36814 (k2l) 255380> 255378< (reset)
7: breakpoint:45510 - zaber:7012 (m2n) 9> 5< (complete)
8: zaber:35813 - boulder:111 (o2p) 6> 5< (complete)
9: zaber:837 - boulder:32774 (q2r) 6> 5< (complete)
10: breakpoint:45511 - zaber:7012 (s2t) 9> 5< (complete)
11: zaber:59362 - boulder:111 (u2v) 6> 5< (complete)
12: zaber:841 - boulder:32774 (w2x) 6> 5< (complete)
13: breakpoint:45512 - zaber:7012 (y2z) 9> 5< (complete)
tcptrace 功能很強大,還可以通過過濾和布爾表達式來找出有問題的連接,比如,找出轉播大于100 segments 的連接:
# tcptrace -f'rexmit_segs>100' network.dmp
如果發現連接 #10 有問題,可以查看關于這個連接的其他信息:
# tcptrace -o10 network.dmp
下面的命令使用 tcptrace 的 slice 模式,程序自動在當前目錄創建了一個 slice.dat 文件,這個文件包含了每隔15秒的轉播信息:
# tcptrace -xslice network.dmp
# cat slice.dat
date segs bytes rexsegs rexbytes new active
--------------- -------- -------- -------- -------- -------- --------
16:58:50.244708 85055 4513418 0 0 6 6
16:59:05.244708 110921 5882896 0 0 0 2
16:59:20.244708 126107 6697827 0 0 1 3
16:59:35.244708 151719 8043597 0 0 0 2
16:59:50.244708 37296 1980557 0 0 0 3
17:00:05.244708 67 8828 0 0 2 3
17:00:20.244708 149 22053 0 0 1 2
17:00:35.244708 30 4080 0 0 0 1
17:00:50.244708 39 5688 0 0 0 1
17:01:05.244708 67 8828 0 0 2 3
17:01:11.081080 37 4121 0 0 1 3
posted on 2010-10-29 09:17
cssseek 閱讀(1713)
評論(0) 編輯 收藏