Introduction
jPDL是一種直觀的流程語言,用以展現商業邏輯的處理過程。jPDL包含的概念涉及任務、異步通訊狀態、定時器、自動執行的動作等,為此,為了整合上述行為,jPDL提供了強大、可擴展的控制流機制。
graph based execution languages
implementation technique for graph based execution languages:
- based on runtime interpretation of a graph.
- based on message queues
- code generation.
The strategy on how graph execution can be implemented on top of an OO programming language. For those who are familiar with design patterns, it's a combination of the command pattern and the chain of responsibility pattern.
1、Transitions 可以理解為進入和離開節點的箭頭,應該存在多個Transitions 進入一個節點和一個節點有多個離開的Transitions 的情況
the structure of the graph is represented with the classes Node and Transition,而Transition是具有方向性的

transitions are able to pass the execution from a source node to a destination node with the method take.
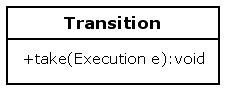
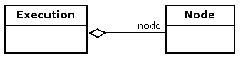
2、execution ,類似petri中的標記,是變遷就緒的前提
An execution (also known as a token) is represented with a class called Execution. An execution has a reference to the current node.
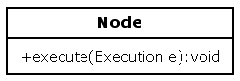
3、Node
A node is a command and has an execute method. Subclasses of Node are supposed to override the execute method to implement some specific behaviour for that node type.
When an execution arrives in a node, that node is executed. The Node's execute method is also responsible for propagating the execution. Propagating the execution means that a node can pass the execution that arrived in the node over one of its leaving transitions to the next node.
When a node's execute method does not propagate the execution, it behaves as a wait state.
Also when a new execution is created, it is initialized in some start node and then waits for an event.
An event is given to an execution and it can trigger the execution to start moving. If the event given to an execution relates to a leaving transition of the current node, the execution takes that transition. The execution then will continue to propagate until it enters another node that behaves as a wait state.
So now we can already see that the two main features are supported : wait states and a graphical representation. During wait states, an Execution just points to a node in the graph
4、Actions
An Action is a command with an execute method. Actions can be associated with events.
Synchronous execution
The default propagation of execution is synchronous.