SpringSide 3.1.4.3是目前SpringSide的最新版本,也是完成度比較高的一個版本,用來做實際項目的開發應該絲毫不成問題。這里寫一下使用該版本開發一個簡單Web項目的全過程,當然,最重要的是我自己的一些心得體會。我的文章很長,只有耐下性子細看,才能體會個中三味。
第一步、下載SpringSide 3.1.4.3 all-in-one版。這個過程太簡單了,SpringSide的官方網站是www.springside.org.cn,去那里就可以下載了,all-in-one版當然是懶人們的不二選擇。這里有一點很搞笑,該版本標的是SpringSide 3.1.4.3,但是下載后解壓縮,解壓縮出來的文件是springside-3.1.4.2,這可能是江南白衣的一點小小的失誤,據我猜測,3.1.4.3較3.1.4.1的進步應該是加入了jsp-api.jar這一個庫,希望白衣這次不要為了更改這個版本號上的失誤而再推出一個新版本,如果真要推出新版本,怎么樣也應該把我最近研究出來的多數據庫的配置加進去。
第二步、安裝SpringSide。如果安裝過SpringSide以前的版本,最好把用戶目錄下的.m2文件夾刪掉,這個文件夾是Maven的本地倉庫所在地,雖說Maven可以有效保證庫文件不會發生版本沖突,但是刪除這個文件夾會使安裝過程加快,否則,SpringSide的安裝過程會不停詢問你是否覆蓋某某文件。刪除.m2文件夾后,運行springside-3.1.4.2目錄下的bin目錄中的quickstart.bat即可(前提條件是已經安裝好了JDK5或以上版本,如果你的電腦中連JDK都沒有,就別來趟SpringSide的渾水了)。 等待這個文件運行完,就可以看到SpringSide 3提供的三個示例項目mini-web、mini-service、showcase都運行起來了,這時你可以細細體會一下SpringSide實現的各種特性。
仔細察看SpringSide的bin目錄,發現該版本提供的腳本更加明確和有用,如start-db.bat可以用來啟動Derby數據庫,start-selenium.bat用來啟動selenium server,而start-tomcat.bat那就別說了,地球人都知道。
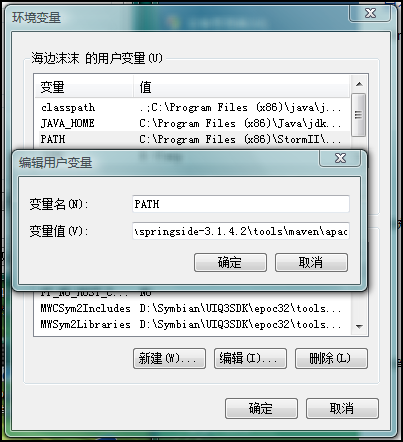
如果要想使用SpringSide來生成項目,還有一點點小工作要做,就是把Maven的bin目錄加入到PATH環境變量中,如下圖:
第三步,使用SpringSide生成項目。運行bin目錄下的new-project.bat即可,如下圖:
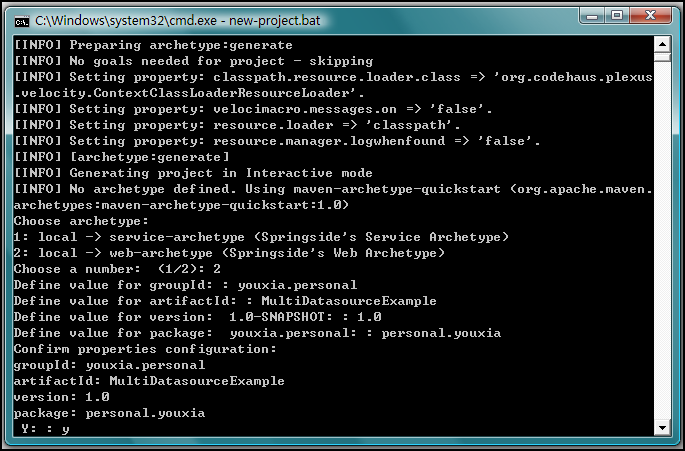
在創建項目的過程中,該腳本會提出一些問題,其中groupId指的是你的組織的名稱,由于該項目由我私人貢獻,純屬示范用,所以我填了youxia.personal,因此,在第5個問題上,我選擇了personal.you作為我項目中的package的名字,這也是符合國際慣例的;artifactId指的是項目的名字,這里為MultiDatasourceExample,名字有點長,從名字就可以看出來我要示范多個數據源的配置。
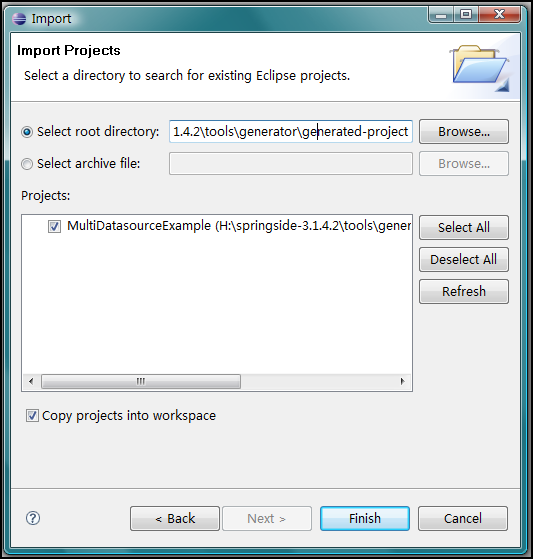
第四步、啟動Eclipse,導入項目。 生成的項目位于SpringSide目錄下的tools\generator\generated-project目錄下,下面是Eclipse的截圖:
項目導入成功后,Eclispe資源管理器的截圖:
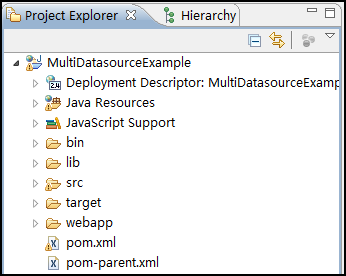
可以看到,該項目一經導入,立即可用,一個煩人的紅叉都沒有,這也正說明了該版本是SpringSide 3的一個革命性版本,從該版本開始,SpringSide 3的易用性提高了不止一個檔次。
Eclipse推薦使用3.4及以上版本,因為在該版本中,對Tomcat服務器的管理更加方便,只需要在項目的快捷菜單中選擇Run On Server,即可自動打開Tomcat服務器并部署項目,如下圖:
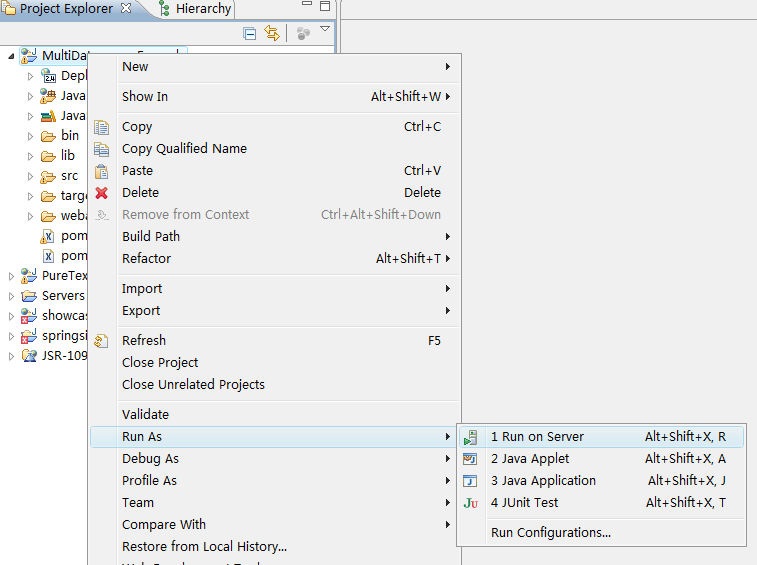
這里有一點一定要注意,由于SpringSide生成的項目默認使用的是Derby數據庫,所以要想成功運行項目,必須先啟動Derby數據庫,還記得前面提到的start-db.bat嗎?運行它!然后運行該項目的bin目錄下的init-db.jar,在數據庫中放入該項目的初始化數據。
然后就可以點Run On Server來啟動項目了,讓大家見識一下Eclipse的嵌入式瀏覽器、Tomcat服務器視圖、Console視圖。真的是太方便了:
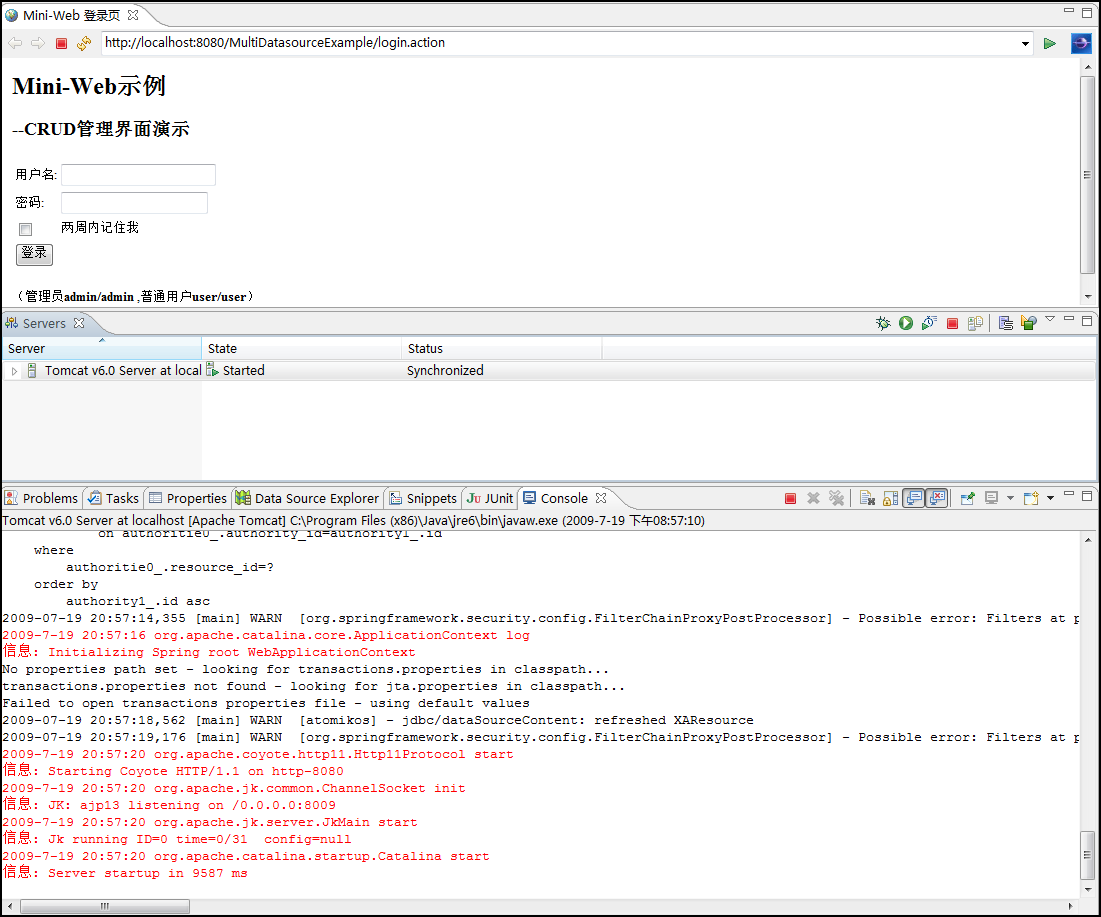
第五步、將數據庫遷移到MySQL中。在項目中,創建數據庫和初始化數據庫的語句都是以SQL文件存在的,如下圖:
但是該語句都是針對Derby的,如果要應用于MySQL,還必須得要做一些修改才行,先修改schema.sql,如下:
 drop table if exists RESOURCES_AUTHORITIES;
drop table if exists RESOURCES_AUTHORITIES;
 drop table if exists ROLES_AUTHORITIES;
drop table if exists ROLES_AUTHORITIES;
 drop table if exists USERS_ROLES;
drop table if exists USERS_ROLES;
 drop table if exists RESOURCES;
drop table if exists RESOURCES;
 drop table if exists AUTHORITIES;
drop table if exists AUTHORITIES;
 drop table if exists USERS;
drop table if exists USERS;
 drop table if exists ROLES;
drop table if exists ROLES;

 create table USERS (
create table USERS (
 ID integer primary key auto_increment,
ID integer primary key auto_increment,
 LOGIN_NAME varchar(20) not null unique,
LOGIN_NAME varchar(20) not null unique,
 PASSWORD varchar(20),
PASSWORD varchar(20),
 NAME varchar(20),
NAME varchar(20),
 EMAIL varchar(30)
EMAIL varchar(30)
 );
);

 create unique index USERS_LOGIN_NAME_INDEX on USERS(LOGIN_NAME);
create unique index USERS_LOGIN_NAME_INDEX on USERS(LOGIN_NAME);

 create table ROLES (
create table ROLES (
 ID integer primary key auto_increment,
ID integer primary key auto_increment,
 NAME varchar(20) not null unique
NAME varchar(20) not null unique
 );
);

 create table USERS_ROLES (
create table USERS_ROLES (
 USER_ID integer not null,
USER_ID integer not null,
 ROLE_ID integer not null,
ROLE_ID integer not null,
 FOREIGN KEY (ROLE_ID) references ROLES(ID),
FOREIGN KEY (ROLE_ID) references ROLES(ID),
 FOREIGN KEY (USER_ID) references USERS(ID)
FOREIGN KEY (USER_ID) references USERS(ID)
 );
);

 CREATE TABLE AUTHORITIES (
CREATE TABLE AUTHORITIES (
 ID integer primary key auto_increment,
ID integer primary key auto_increment,
 NAME varchar(20) not null,
NAME varchar(20) not null,
 DISPLAY_NAME varchar(20) not null
DISPLAY_NAME varchar(20) not null
 );
);

 create table ROLES_AUTHORITIES (
create table ROLES_AUTHORITIES (
 ROLE_ID integer not null,
ROLE_ID integer not null,
 AUTHORITY_ID integer not null,
AUTHORITY_ID integer not null,
 FOREIGN KEY (ROLE_ID) references ROLES(ID),
FOREIGN KEY (ROLE_ID) references ROLES(ID),
 FOREIGN KEY (AUTHORITY_ID) references AUTHORITIES(ID)
FOREIGN KEY (AUTHORITY_ID) references AUTHORITIES(ID)
 );
);

 CREATE TABLE RESOURCES (
CREATE TABLE RESOURCES (
 ID integer primary key auto_increment,
ID integer primary key auto_increment,
 RESOURCE_TYPE varchar(20) not null,
RESOURCE_TYPE varchar(20) not null,
 VALUE varchar(255) not null,
VALUE varchar(255) not null,
 ORDER_NUM float not null
ORDER_NUM float not null
 );
);

 create table RESOURCES_AUTHORITIES (
create table RESOURCES_AUTHORITIES (
 AUTHORITY_ID integer not null,
AUTHORITY_ID integer not null,
 RESOURCE_ID integer not null,
RESOURCE_ID integer not null,
 FOREIGN KEY (AUTHORITY_ID) references AUTHORITIES(ID),
FOREIGN KEY (AUTHORITY_ID) references AUTHORITIES(ID),
 FOREIGN KEY (RESOURCE_ID) references RESOURCES(ID)
FOREIGN KEY (RESOURCE_ID) references RESOURCES(ID)
 );
);
該修改主要包含兩個地方,一個是在drop table后面加上了if exists,一個是把GENERATED ALWAYS as IDENTITY修改為auto_increment。而load-data.sql不需要修改。
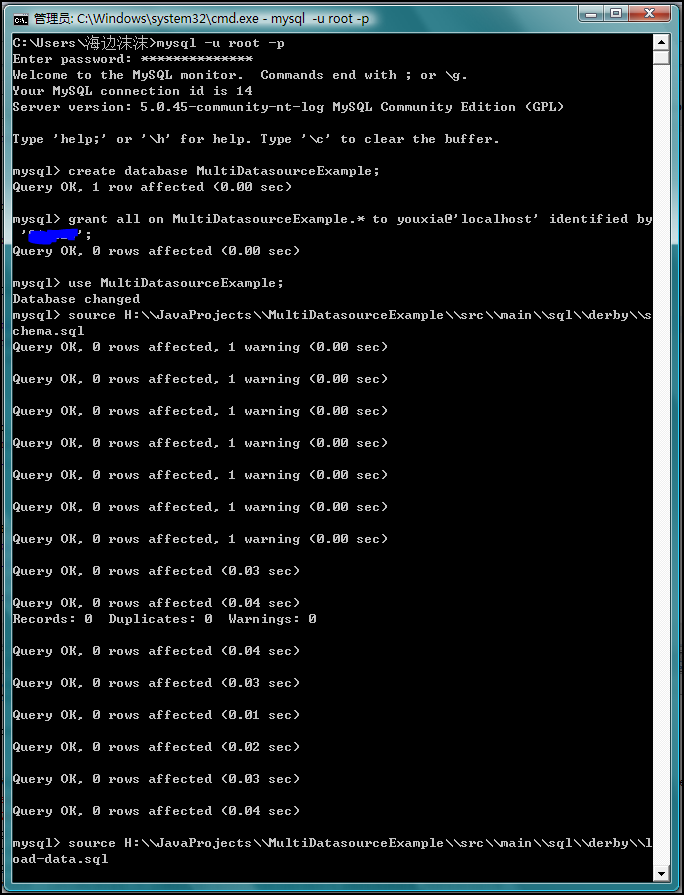
然后,啟動MySQL,在MySQL中使用上面的兩個sql文件創建數據庫和添加初始化數據,如下圖:
然后更改數據庫連接,修改項目的application.properties文件,如下:
 #jdbc settings
#jdbc settings
 jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/MultiDatasourceExample?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/MultiDatasourceExample?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8
 jdbc.username=youxia
jdbc.username=youxia
 jdbc.password=******
jdbc.password=******

 #hibernate settings
#hibernate settings
 hibernate.show_sql=false
hibernate.show_sql=false
 hibernate.format_sql=false
hibernate.format_sql=false
 hibernate.ehcache_config_file=/ehcache/ehcache-hibernate-local.xml
hibernate.ehcache_config_file=/ehcache/ehcache-hibernate-local.xml
修改項目的applicationContext.xml文件,這里要修改兩個地方,一個為DriverClassName,一個為hibernate.dilect,如下:
 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
 xmlns:jee="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:jee="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
 xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee/spring-jee-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-2.5.xsd"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee/spring-jee-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-2.5.xsd"
 default-lazy-init="true">
default-lazy-init="true">

 <description>Spring公共配置文件 </description>
<description>Spring公共配置文件 </description>

 <!-- 定義受環境影響易變的變量 -->
<!-- 定義受環境影響易變的變量 -->
 <bean class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
<bean class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
 <property name="systemPropertiesModeName" value="SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_MODE_OVERRIDE" />
<property name="systemPropertiesModeName" value="SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_MODE_OVERRIDE" />
 <property name="ignoreResourceNotFound" value="true" />
<property name="ignoreResourceNotFound" value="true" />
 <property name="locations">
<property name="locations">
 <list>
<list>
 <!-- 標準配置 -->
<!-- 標準配置 -->
 <value>classpath*:/application.properties</value>
<value>classpath*:/application.properties</value>
 <!-- 本地開發環境配置 -->
<!-- 本地開發環境配置 -->
 <value>classpath*:/application.local.properties</value>
<value>classpath*:/application.local.properties</value>
 <!-- 服務器生產環境配置 -->
<!-- 服務器生產環境配置 -->
 <!-- <value>file:/var/myapp/application.server.properties</value> -->
<!-- <value>file:/var/myapp/application.server.properties</value> -->
 </list>
</list>
 </property>
</property>
 </bean>
</bean>

 <!-- 使用annotation 自動注冊bean,并保證@Required,@Autowired的屬性被注入 -->
<!-- 使用annotation 自動注冊bean,并保證@Required,@Autowired的屬性被注入 -->
 <context:component-scan base-package="personal.youxia" />
<context:component-scan base-package="personal.youxia" />

 <!-- 數據源配置,使用應用內的DBCP數據庫連接池 -->
<!-- 數據源配置,使用應用內的DBCP數據庫連接池 -->
 <bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource" destroy-method="close">
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource" destroy-method="close">
 <!-- Connection Info -->
<!-- Connection Info -->
 <property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" />
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" />
 <property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}" />
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}" />
 <property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}" />
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}" />
 <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" />
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" />

 <!-- Connection Pooling Info -->
<!-- Connection Pooling Info -->
 <property name="initialSize" value="5" />
<property name="initialSize" value="5" />
 <property name="maxActive" value="100" />
<property name="maxActive" value="100" />
 <property name="maxIdle" value="30" />
<property name="maxIdle" value="30" />
 <property name="maxWait" value="1000" />
<property name="maxWait" value="1000" />
 <property name="poolPreparedStatements" value="true" />
<property name="poolPreparedStatements" value="true" />
 <property name="defaultAutoCommit" value="false" />
<property name="defaultAutoCommit" value="false" />
 </bean>
</bean>

 <!-- 數據源配置,使用應用服務器的數據庫連接池 -->
<!-- 數據源配置,使用應用服務器的數據庫連接池 -->
 <!--<jee:jndi-lookup id="dataSource" jndi-name="java:comp/env/jdbc/ExampleDB" />-->
<!--<jee:jndi-lookup id="dataSource" jndi-name="java:comp/env/jdbc/ExampleDB" />-->

 <!-- Hibernate配置 -->
<!-- Hibernate配置 -->
 <bean id="sessionFactory" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.annotation.AnnotationSessionFactoryBean">
<bean id="sessionFactory" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.annotation.AnnotationSessionFactoryBean">
 <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
 <property name="namingStrategy">
<property name="namingStrategy">
 <bean class="org.hibernate.cfg.ImprovedNamingStrategy" />
<bean class="org.hibernate.cfg.ImprovedNamingStrategy" />
 </property>
</property>
 <property name="hibernateProperties">
<property name="hibernateProperties">
 <props>
<props>
 <prop key="hibernate.dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5InnoDBDialect</prop>
<prop key="hibernate.dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5InnoDBDialect</prop>
 <prop key="hibernate.show_sql">${hibernate.show_sql}</prop>
<prop key="hibernate.show_sql">${hibernate.show_sql}</prop>
 <prop key="hibernate.format_sql">${hibernate.format_sql}</prop>
<prop key="hibernate.format_sql">${hibernate.format_sql}</prop>
 <prop key="hibernate.cache.provider_class">org.hibernate.cache.EhCacheProvider
<prop key="hibernate.cache.provider_class">org.hibernate.cache.EhCacheProvider
 </prop>
</prop>
 <prop key="hibernate.cache.provider_configuration_file_resource_path">${hibernate.ehcache_config_file}</prop>
<prop key="hibernate.cache.provider_configuration_file_resource_path">${hibernate.ehcache_config_file}</prop>
 </props>
</props>
 </property>
</property>
 <property name="packagesToScan" value="personal.youxia.entity.*" />
<property name="packagesToScan" value="personal.youxia.entity.*" />
 </bean>
</bean>

 <!-- 事務管理器配置,單數據源事務 -->
<!-- 事務管理器配置,單數據源事務 -->
 <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateTransactionManager">
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateTransactionManager">
 <property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory" />
<property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory" />
 </bean>
</bean>

 <!-- 事務管理器配置,多數據源JTA事務-->
<!-- 事務管理器配置,多數據源JTA事務-->
 <!--
<!--
 <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.transaction.jta.JtaTransactionManager or
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.transaction.jta.JtaTransactionManager or
 WebLogicJtaTransactionManager" />
WebLogicJtaTransactionManager" />
 -->
-->

 <!-- 使用annotation定義事務 -->
<!-- 使用annotation定義事務 -->
 <tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager" />
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager" />
 </beans>
</beans>
由于SpringSide不提供Mysql的jdbc驅動,所以需要自己去MySQL的官方網站下載,將下載到的mysql-connector-5.*.jar復制到項目的WEB-INF中的lib目錄中。然后運行項目,成功。至此,成功將項目遷移到MySQL中。
第六步、添加數據表、編寫Entity類、編寫Dao類、Manager類,并進行單元測試。還是以前幾篇文章中提到的文章發布系統為例,每一篇文章對應多篇評論,所以說據庫中需創建articles和comments兩個數據表,如下:
 create table articles(
create table articles(
 id int primary key auto_increment,
id int primary key auto_increment,
 subject varchar ( 20 ) not null ,
subject varchar ( 20 ) not null ,
 content text );
content text );

 create table comments(
create table comments(
 id int primary key auto_increment,
id int primary key auto_increment,
 content varchar ( 255 ),
content varchar ( 255 ),
 article_id int not null ,
article_id int not null ,
 foreign key (article_id) references articles(id)
foreign key (article_id) references articles(id)
 );
);

在編寫Java代碼之前,我還要做一點小工作,什么工作呢?那就是要為我自己的項目創建一個單獨的源文件夾,因為src\main\java這個文件夾已經被江南白衣放入了太多的package,而且因為涉及到security,所以層次也不明顯,操作起來不方便,找起代碼來也不夠快。下面是我創建了自己的源文件夾后的截圖:
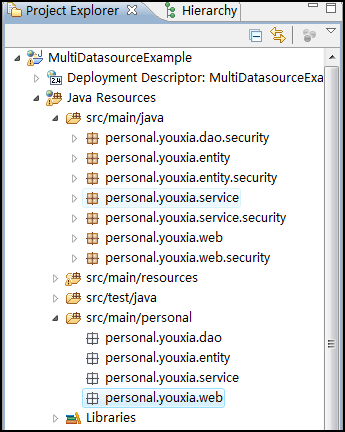
在我自己的源文件夾中,只創建了四個package,剛好代表從底到上的四個層次,這樣,找起代碼來要方便得多。
先來Entity層,Article.java的代碼如下:
 package personal.youxia.entity;
package personal.youxia.entity;

 import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
 import java.util.Set;
import java.util.Set;

 import javax.persistence.CascadeType;
import javax.persistence.CascadeType;
 import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
 import javax.persistence.JoinColumn;
import javax.persistence.JoinColumn;
 import javax.persistence.OneToMany;
import javax.persistence.OneToMany;
 import javax.persistence.OrderBy;
import javax.persistence.OrderBy;
 import javax.persistence.Table;
import javax.persistence.Table;

 import org.hibernate.annotations.Cache;
import org.hibernate.annotations.Cache;
 import org.hibernate.annotations.CacheConcurrencyStrategy;
import org.hibernate.annotations.CacheConcurrencyStrategy;
 import org.hibernate.annotations.Fetch;
import org.hibernate.annotations.Fetch;
 import org.hibernate.annotations.FetchMode;
import org.hibernate.annotations.FetchMode;

 @Entity
@Entity
 // 表名與類名不相同時重新定義表名.
// 表名與類名不相同時重新定義表名.
 @Table(name = "articles")
@Table(name = "articles")
 // 默認的緩存策略.
// 默認的緩存策略.
 @Cache(usage = CacheConcurrencyStrategy.READ_WRITE)
@Cache(usage = CacheConcurrencyStrategy.READ_WRITE)

 public class Article extends IdEntity
public class Article extends IdEntity  {
{
 private String subject;
private String subject;
 private String content;
private String content;
 private Set<Comment> comments = new LinkedHashSet<Comment>();
private Set<Comment> comments = new LinkedHashSet<Comment>();


 public String getSubject()
public String getSubject()  {
{
 return subject;
return subject;
 }
}


 public void setSubject(String subject)
public void setSubject(String subject)  {
{
 this.subject = subject;
this.subject = subject;
 }
}


 public String getContent()
public String getContent()  {
{
 return content;
return content;
 }
}


 public void setContent(String content)
public void setContent(String content)  {
{
 this.content = content;
this.content = content;
 }
}


 @OneToMany(cascade =
@OneToMany(cascade =  { CascadeType.ALL })
{ CascadeType.ALL })
 @JoinColumn(name = "article_id")
@JoinColumn(name = "article_id")
 // Fecth策略定義
// Fecth策略定義
 @Fetch(FetchMode.SUBSELECT)
@Fetch(FetchMode.SUBSELECT)
 // 集合按id排序.
// 集合按id排序.
 @OrderBy("id")
@OrderBy("id")
 // 集合中對象id的緩存.
// 集合中對象id的緩存.
 @Cache(usage = CacheConcurrencyStrategy.READ_WRITE)
@Cache(usage = CacheConcurrencyStrategy.READ_WRITE)

 public Set<Comment> getComments()
public Set<Comment> getComments()  {
{
 return comments;
return comments;
 }
}


 public void setComments(Set<Comment> comments)
public void setComments(Set<Comment> comments)  {
{
 this.comments = comments;
this.comments = comments;
 }
}
 }
}
Comment.java如下:
package personal.youxia.entity.entities;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.Table;
import org.hibernate.annotations.Cache;
import org.hibernate.annotations.CacheConcurrencyStrategy;
import personal.youxia.entity.IdEntity;
@Entity
// 表名與類名不相同時重新定義表名.
@Table(name = "comments")
// 默認的緩存策略.
@Cache(usage = CacheConcurrencyStrategy.READ_WRITE)
public class Comment extends IdEntity {
private String content;
private Long articleId;
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
public void setContent(String content) {
this.content = content;
}
@Column(name = "article_id")
public Long getArticleId() {
return articleId;
}
public void setArticleId(Long articleId) {
this.articleId = articleId;
}
}
編寫Dao層代碼,ArticleDao.java如下:
 package personal.youxia.dao;
package personal.youxia.dao;

 import org.springside.modules.orm.hibernate.HibernateDao;
import org.springside.modules.orm.hibernate.HibernateDao;

 import personal.youxia.entity.Article;
import personal.youxia.entity.Article;


 public class ArticleDao extends HibernateDao<Article, Long>
public class ArticleDao extends HibernateDao<Article, Long>  {
{

 }
}
CommentDao.java如下:
 package personal.youxia.dao;
package personal.youxia.dao;

 import org.springside.modules.orm.hibernate.HibernateDao;
import org.springside.modules.orm.hibernate.HibernateDao;

 import personal.youxia.entity.Comment;
import personal.youxia.entity.Comment;


 public class CommentDao extends HibernateDao<Comment, Long>
public class CommentDao extends HibernateDao<Comment, Long>  {
{

 }
}
可以看出,以上代碼都從HibernateDao繼承,得益于泛型支持,基本不需要編寫一行代碼。
編寫Bussiness層代碼,這一層,白衣使用的包名為service,而類名的后綴都是Manager,我就跟他學算了,懶得改了。
ArticleManager.java如下:
 package personal.youxia.service;
package personal.youxia.service;

 import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
 import org.springside.modules.orm.hibernate.HibernateDao;
import org.springside.modules.orm.hibernate.HibernateDao;

 import personal.youxia.dao.ArticleDao;
import personal.youxia.dao.ArticleDao;
 import personal.youxia.entity.Article;
import personal.youxia.entity.Article;


 public class ArticleManager extends EntityManager<Article, Long>
public class ArticleManager extends EntityManager<Article, Long>  {
{
 @Autowired
@Autowired
 private ArticleDao articleDao;
private ArticleDao articleDao;


 public void setArticleDao(ArticleDao articleDao)
public void setArticleDao(ArticleDao articleDao)  {
{
 this.articleDao = articleDao;
this.articleDao = articleDao;
 }
}

 @Override
@Override

 protected HibernateDao<Article, Long> getEntityDao()
protected HibernateDao<Article, Long> getEntityDao()  {
{
 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
 return articleDao;
return articleDao;
 }
}

 }
}
CommentManager.java如下:
 package personal.youxia.service;
package personal.youxia.service;

 import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
 import org.springside.modules.orm.hibernate.HibernateDao;
import org.springside.modules.orm.hibernate.HibernateDao;

 import personal.youxia.dao.CommentDao;
import personal.youxia.dao.CommentDao;
 import personal.youxia.entity.Comment;
import personal.youxia.entity.Comment;


 public class CommentManager extends EntityManager<Comment, Long>
public class CommentManager extends EntityManager<Comment, Long>  {
{
 @Autowired
@Autowired
 private CommentDao commentDao;
private CommentDao commentDao;


 public void setCommentDao(CommentDao commentDao)
public void setCommentDao(CommentDao commentDao)  {
{
 this.commentDao = commentDao;
this.commentDao = commentDao;
 }
}

 @Override
@Override

 protected HibernateDao<Comment, Long> getEntityDao()
protected HibernateDao<Comment, Long> getEntityDao()  {
{
 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
 return commentDao;
return commentDao;
 }
}

 }
}
以上代碼大同小異,都是從EntityManager繼承,并使用Spring的IoC特性,將Dao類注入到Manager類之中,并重載getEntityDao方法來使用該注入的Dao。這個時候,為了驗證這些數據訪問相關的層能否正常運行,可以編寫單元測試。 代碼如下:
 package personal.youxia.test;
package personal.youxia.test;

 import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.Test;
 import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
 import org.springside.modules.test.junit4.SpringTxTestCase;
import org.springside.modules.test.junit4.SpringTxTestCase;

 import personal.youxia.entity.entities.Article;
import personal.youxia.entity.entities.Article;
 import personal.youxia.entity.entities.Comment;
import personal.youxia.entity.entities.Comment;
 import personal.youxia.service.ArticleManager;
import personal.youxia.service.ArticleManager;
 import personal.youxia.service.CommentManager;
import personal.youxia.service.CommentManager;


 public class DataAccessTest extends SpringTxTestCase
public class DataAccessTest extends SpringTxTestCase  {
{
 @Autowired
@Autowired
 private ArticleManager articleManager;
private ArticleManager articleManager;
 @Autowired
@Autowired
 private CommentManager commentManager;
private CommentManager commentManager;


 public void setArticleManager(ArticleManager articleManager)
public void setArticleManager(ArticleManager articleManager)  {
{
 this.articleManager = articleManager;
this.articleManager = articleManager;
 }
}

 @Test
@Test

 public void addArticle()
public void addArticle()  {
{
 Comment comment = new Comment();
Comment comment = new Comment();
 Article article = new Article();
Article article = new Article();
 article.setSubject("test");
article.setSubject("test");
 article.setContent("test");
article.setContent("test");
 articleManager.save(article);
articleManager.save(article);
 comment.setArticleId(article.getId());
comment.setArticleId(article.getId());
 commentManager.save(comment);
commentManager.save(comment);
 }
}
 }
}
單元測試一運行,發現了三個問題,先是出現Manager類沒有注入成功的錯誤,經檢查發現
所有的Manager類都應該使用@Service注解,再出現的錯誤是提示Dao類沒有注入成功,經檢查發現
所有的Dao類須使用@Repository注解,最后出現的錯誤是找不到Entity類的錯誤,經檢查發現
Entity類不能位于personal.youxia.entity包中,必須位于其子包中,這是由applicationContext.xml文件中的配置決定的,更改包名為personal.youxia.entity.entities后,問題解決。
下一步就應該是編寫Action和JSP了,由于文章太長,在Blogjava的編輯器中編輯已經非常緩慢了,所以只有將該文章分為上中下三部分。且看下回分解!
使用SpringSide 3.1.4.3開發Web項目的全過程(中)