傳統的hash 算法只負責將原始內容盡量均勻隨機地映射為一個簽名值���,原理上相當于偽隨機數產生算法。產生的兩個簽名�����,如果相等��,說明原始內容在一定概 率 下是相等的�����;如果不相等,除了說明原始內容不相等外,不再提供任何信息,因為即使原始內容只相差一個字節,所產生的簽名也很可能差別極大����。從這個意義 上來 說��,要設計一個 hash 算法,對相似的內容產生的簽名也相近,是更為艱難的任務��,因為它的簽名值除了提供原始內容是否相等的信息外�,還能額外提供不相等的 原始內容的差異程度的信息。
而Google 的 simhash 算法產生的簽名,可以用來比較原始內容的相似度時��,便很想了解這種神奇的算法的原理�����。出人意料,這個算法并不深奧����,其思想是非常清澈美妙的�����。
Simhash算法
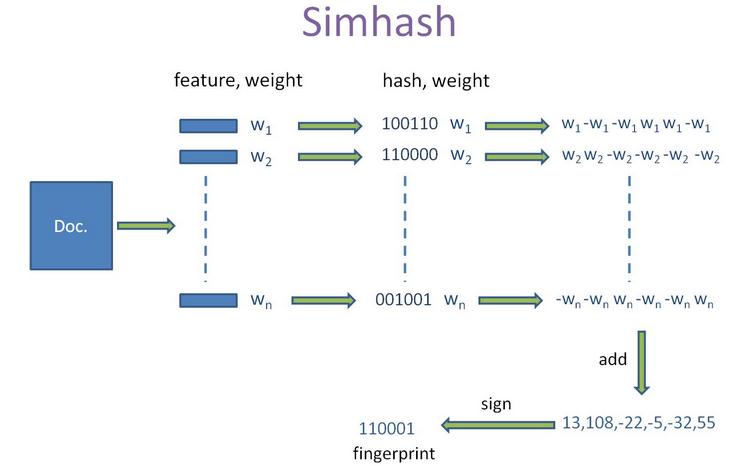
simhash算法的輸入是一個向量�����,輸出是一個 f 位的簽名值。為了陳述方便�,假設輸入的是一個文檔的特征集合����,每個特征有一定的權重��。比如特征可以是文檔中的詞����,其權重可以是這個詞出現的次數���。 simhash 算法如下:
1�����,將一個 f 維的向量 V 初始化為 0 ��; f 位的二進制數 S 初始化為 0 ��;
2����,對每一個特征:用傳統的 hash 算法對該特征產生一個 f 位的簽名 b �。對 i=1 到 f :
如果b 的第 i 位為 1 ,則 V 的第 i 個元素加上該特征的權重�����;
否則��,V 的第 i 個元素減去該特征的權重�。
3�,如果 V 的第 i 個元素大于 0 ,則 S 的第 i 位為 1 ����,否則為 0 ��;
4,輸出 S 作為簽名���。

![]()
![]()
算法幾何意義和原理
這個算法的幾何意義非常明了。它首先將每一個特征映射為f 維空間的一個向量��,這個映射規則具體是怎樣并不重要����,只要對很多不同的特征來說,它們對所對應的 向量是均勻隨機分布的����,并且對相同的特征來說對應的向量是唯一的就行����。比如一個特征的 4 位 hash 簽名的二進制表示為 1010 ��,那么這個特征對應的 4 維向量就是 (1, -1, 1, -1) T ,即hash 簽名的某一位為 1 ,映射到的向量的對應位就為 1 ����,否則為 -1 �����。然后,將一個文檔中所包含的各個特征對應的向量加權求和, 加權的系數等于該特征的權重����。
得到的和向量即表征了這個文檔����,我們可以用向量之間的夾角來衡量對應文檔之間的相似度。最后��,為了得到一個 f 位的簽名�,需要 進一步將其壓縮,如果和向量的某一維大于 0 ��,則最終簽名的對應位為 1 ����,否則為 0 。這樣的壓縮相當于只留下了和向量所在的象限這個信息��,而 64 位的簽名可以 表示多達 2 64 個象限�����,因此只保存所在象限的信息也足夠表征一個文檔了����。
比較相似度
海明距離: 兩個碼字的對應比特取值不同的比特數稱為這兩個碼字的海明距離����。一個有效編碼集中, 任意兩個碼字的海明距離的最小值稱為該編碼集的海明距離��。舉例如下: 10101 和 00110 從第一位開始依次有第一位��、第四、第五位不同�����,則海明距離為 3.
異或: 只有在兩個比較的位不同時其結果是1 ��,否則結果為 0
對每篇文檔根據SimHash 算出簽名后���,再計算兩個簽名的海明距離(兩個二進制異或后 1 的個數)即可����。根據經驗值��,對 64 位的 SimHash �,海明距離在 3 以內的可以認為相似度比較高��。
假設對64 位的 SimHash ���,我們要找海明距離在 3 以內的所有簽名��。我們可以把 64 位的二進制簽名均分成 4 塊,每塊 16 位�����。根據鴿巢原理(也成抽屜原理�,見組合數學),如果兩個簽名的海明距離在 3 以內�����,它們必有一塊完全相同�����。
我們把上面分成的4 塊中的每一個塊分別作為前 16 位來進行查找。 建立倒排索引���。
![]()
![]()
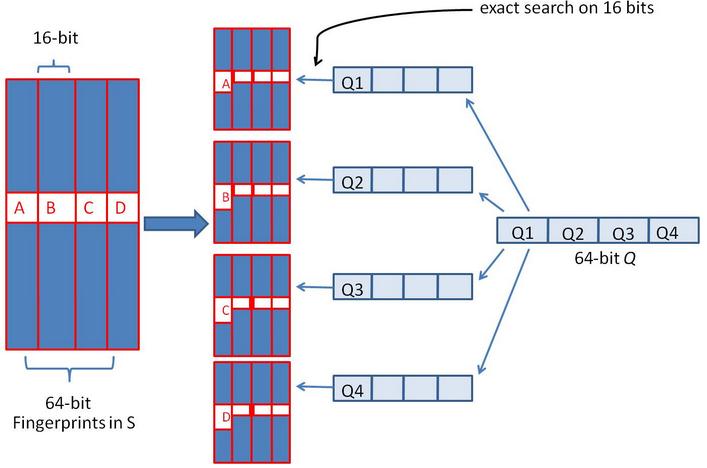
如果庫中有2^34 個(大概 10 億)簽名,那么匹配上每個塊的結果最多有 2^(34-16)=262144 個候選結果 (假設數據是均勻分布��, 16 位的數據��,產生的像限為 2^16 個�����,則平均每個像限分布的文檔數則 2^34/2^16 = 2^(34-16)) ,四個塊返回的總結果數為 4* 262144 (大概 100 萬)��。原本需要比較 10 億次,經過索引�����,大概就只需要處理 100 萬次了����。由此可見,確實大大減少了計算量�����。
Java 代碼實現:
Java代碼

- package com.gemantic.nlp.commons.simhash;
-
- import java.math.BigInteger;
- import java.util.ArrayList;
- import java.util.List;
- import java.util.StringTokenizer;
-
- public class SimHash {
-
- private String tokens;
-
- private BigInteger intSimHash;
-
- private String strSimHash;
-
- private int hashbits = 64;
-
- public SimHash(String tokens) {
- this.tokens = tokens;
- this.intSimHash = this.simHash();
- }
-
- public SimHash(String tokens, int hashbits) {
- this.tokens = tokens;
- this.hashbits = hashbits;
- this.intSimHash = this.simHash();
- }
-
- public BigInteger simHash() {
- int[] v = new int[this.hashbits];
- StringTokenizer stringTokens = new StringTokenizer(this.tokens);
- while (stringTokens.hasMoreTokens()) {
- String temp = stringTokens.nextToken();
- BigInteger t = this.hash(temp);
- for (int i = 0; i < this.hashbits; i++) {
- BigInteger bitmask = new BigInteger("1").shiftLeft(i);
- if (t.and(bitmask).signum() != 0) {
- v[i] += 1;
- } else {
- v[i] -= 1;
- }
- }
- }
- BigInteger fingerprint = new BigInteger("0");
- StringBuffer simHashBuffer = new StringBuffer();
- for (int i = 0; i < this.hashbits; i++) {
- if (v[i] >= 0) {
- fingerprint = fingerprint.add(new BigInteger("1").shiftLeft(i));
- simHashBuffer.append("1");
- }else{
- simHashBuffer.append("0");
- }
- }
- this.strSimHash = simHashBuffer.toString();
- System.out.println(this.strSimHash + " length " + this.strSimHash.length());
- return fingerprint;
- }
-
- private BigInteger hash(String source) {
- if (source == null || source.length() == 0) {
- return new BigInteger("0");
- } else {
- char[] sourceArray = source.toCharArray();
- BigInteger x = BigInteger.valueOf(((long) sourceArray[0]) << 7);
- BigInteger m = new BigInteger("1000003");
- BigInteger mask = new BigInteger("2").pow(this.hashbits).subtract(
- new BigInteger("1"));
- for (char item : sourceArray) {
- BigInteger temp = BigInteger.valueOf((long) item);
- x = x.multiply(m).xor(temp).and(mask);
- }
- x = x.xor(new BigInteger(String.valueOf(source.length())));
- if (x.equals(new BigInteger("-1"))) {
- x = new BigInteger("-2");
- }
- return x;
- }
- }
-
- /**
- * 取兩個二進制的異或��,統計為1的個數,就是海明距離
- * @param other
- * @return
- */
-
- public int hammingDistance(SimHash other) {
-
- BigInteger x = this.intSimHash.xor(other.intSimHash);
- int tot = 0;
-
- //統計x中二進制位數為1的個數
- //我們想想�����,一個二進制數減去1�����,那么���,從最后那個1(包括那個1)后面的數字全都反了����,對吧�����,然后����,n&(n-1)就相當于把后面的數字清0���,
- //我們看n能做多少次這樣的操作就OK了��。
-
- while (x.signum() != 0) {
- tot += 1;
- x = x.and(x.subtract(new BigInteger("1")));
- }
- return tot;
- }
-
- /**
- * calculate Hamming Distance between two strings
- * 二進制怕有錯��,當成字符串,作一個��,比較下結果
- * @author
- * @param str1 the 1st string
- * @param str2 the 2nd string
- * @return Hamming Distance between str1 and str2
- */
- public int getDistance(String str1, String str2) {
- int distance;
- if (str1.length() != str2.length()) {
- distance = -1;
- } else {
- distance = 0;
- for (int i = 0; i < str1.length(); i++) {
- if (str1.charAt(i) != str2.charAt(i)) {
- distance++;
- }
- }
- }
- return distance;
- }
-
- /**
- * 如果海明距離取3����,則分成四塊�,并得到每一塊的bigInteger值 ,作為索引值使用
- * @param simHash
- * @param distance
- * @return
- */
- public List<BigInteger> subByDistance(SimHash simHash, int distance){
- int numEach = this.hashbits/(distance+1);
- List<BigInteger> characters = new ArrayList();
-
- StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer();
-
- int k = 0;
- for( int i = 0; i < this.intSimHash.bitLength(); i++){
- boolean sr = simHash.intSimHash.testBit(i);
-
- if(sr){
- buffer.append("1");
- }
- else{
- buffer.append("0");
- }
-
- if( (i+1)%numEach == 0 ){
- BigInteger eachValue = new BigInteger(buffer.toString(),2);
- System.out.println("----" +eachValue );
- buffer.delete(0, buffer.length());
- characters.add(eachValue);
- }
- }
-
- return characters;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- String s = "This is a test string for testing";
-
- SimHash hash1 = new SimHash(s, 64);
- System.out.println(hash1.intSimHash + " " + hash1.intSimHash.bitLength());
-
- hash1.subByDistance(hash1, 3);
-
- System.out.println("\n");
- s = "This is a test string for testing, This is a test string for testing abcdef";
- SimHash hash2 = new SimHash(s, 64);
- System.out.println(hash2.intSimHash+ " " + hash2.intSimHash.bitCount());
- hash1.subByDistance(hash2, 3);
- s = "This is a test string for testing als";
- SimHash hash3 = new SimHash(s, 64);
- System.out.println(hash3.intSimHash+ " " + hash3.intSimHash.bitCount());
- hash1.subByDistance(hash3, 3);
- System.out.println("============================");
- int dis = hash1.getDistance(hash1.strSimHash,hash2.strSimHash);
-
- System.out.println(hash1.hammingDistance(hash2) + " "+ dis);
-
- int dis2 = hash1.getDistance(hash1.strSimHash,hash3.strSimHash);
-
- System.out.println(hash1.hammingDistance(hash3) + " " + dis2);
-
-
-
- }
- }
參考: http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_72995dcc010145ti.html
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_56d8ea900100y41b.html
http://blog.csdn.net/meijia_tts/article/details/7928579
posted on 2015-04-17 14:43
SIMONE 閱讀(741)
評論(0) 編輯 收藏 所屬分類:
JAVA