我們都知道java面向對象的三大特征是封裝、多態、和繼承。對于一個類來說封裝多態就很簡單了,繼承無非就是多個類之間的父與子的關系。如果我們在做一個項目時把所有的程序都寫到一個文件中是不是太麻煩了,那么我們怎么做呢,那就是分解成多個小程序放在不同的文件中,在一個文件中可以通過導入另一個文件來調用那個文件。這樣做有幾點好處:1.編譯出錯時根據錯誤信息能很快定位到相應的程序中2.可擴展性非常好。這個程序雖然小,但是足可以說明類調用的作用。
這個程序有Main、Menu、Person、PersonOperate、FileOperate和InputData。他們之間的關系如下圖
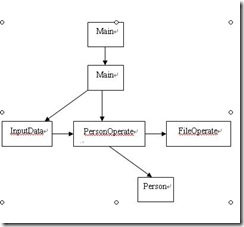
這個程序的運行步驟如下:
運行系統時:它的界面是:

輸入1,就會彈出添加信息的提示,輸入正確的信息:

選擇2,就會將剛添加的信息輸出出來:

選擇3,就是修改信息提示,輸入修改后的信息就會:

選擇4,就退出系統。
程序代碼如下:


 //main類
//main類

 package main;
package main;

 import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.IOException;

 import menu.Menu;
import menu.Menu;


 public class Main
public class Main  {
{
 public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException


 {
{
 new Menu();
new Menu();
 }
}

 }
}



 //menu類
//menu類

 package menu;
package menu;

 import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
 import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.IOException;
 import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;

 import op.PersonOperate;
import op.PersonOperate;
 import util.InputData;
import util.InputData;


 public class Menu
public class Menu  {
{
 BufferedReader input=null;
BufferedReader input=null;
 //創建菜單
//創建菜單
 public Menu() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException
public Menu() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException


 {
{
 this.input=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
this.input=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
 while(true)
while(true)


 {
{
 show();
show();
 }
}
 }
}
 //顯示菜單
//顯示菜單

 private void show() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException
private void show() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException  {
{
 System.out.println("\t\t1.增加人員信息");
System.out.println("\t\t1.增加人員信息");
 System.out.println("\t\t2.瀏覽人員信息");
System.out.println("\t\t2.瀏覽人員信息");
 System.out.println("\t\t3.修改人員信息");
System.out.println("\t\t3.修改人員信息");
 System.out.println("\t\t4.退出系統");
System.out.println("\t\t4.退出系統");
 System.out.println("請選擇:");
System.out.println("請選擇:");
 //根據用戶輸入的信息選擇相應的功能
//根據用戶輸入的信息選擇相應的功能
 int temp=new InputData().getInt();
int temp=new InputData().getInt();
 switch(temp)
switch(temp)


 {
{
 case 1: PersonOperate.add(); break;
case 1: PersonOperate.add(); break;
 case 2: PersonOperate.show();break;
case 2: PersonOperate.show();break;
 case 3: PersonOperate.update();break;
case 3: PersonOperate.update();break;
 case 4: System.out.println("您選擇了退出系統");System.exit(1);break;
case 4: System.out.println("您選擇了退出系統");System.exit(1);break;
 default:System.out.println("輸入內容必須是0-9,請重新輸入:");
default:System.out.println("輸入內容必須是0-9,請重新輸入:");
 }
}
 }
}

 }
}

 //InputData類
//InputData類

 package util;
package util;

 import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
 import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.IOException;
 import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
 import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;


 public class InputData
public class InputData  {
{
 BufferedReader input=null;//創建輸入流
BufferedReader input=null;//創建輸入流
 public InputData()
public InputData()


 {
{
 this.input=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
this.input=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
 }
}
 //得到鍵盤輸入的信息
//得到鍵盤輸入的信息
 public String getString() throws IOException
public String getString() throws IOException


 {
{
 String buf;
String buf;
 buf=input.readLine();
buf=input.readLine();
 return buf;
return buf;
 }
}
 //將從鍵盤讀入的信息轉換成int類型
//將從鍵盤讀入的信息轉換成int類型
 public int getInt() throws IOException
public int getInt() throws IOException


 {
{
 String str=null;
String str=null;
 int temp = 0;
int temp = 0;
 str=this.getString();
str=this.getString();
 while(true)
while(true)


 {
{
 if(str.matches("\\d+"))
if(str.matches("\\d+"))


 {
{
 temp=Integer.parseInt(str);break;
temp=Integer.parseInt(str);break;
 }
}
 else
else


 {
{
 System.out.println("輸入的數必須是整數");
System.out.println("輸入的數必須是整數");
 }
}
 }
}
 return temp;
return temp;
 }
}
 //將從鍵盤讀入的信息轉換成float類型
//將從鍵盤讀入的信息轉換成float類型

 public float getFloat() throws IOException
public float getFloat() throws IOException  {
{
 boolean flag=true;
boolean flag=true;
 String str=null;
String str=null;
 float score = 0;
float score = 0;
 while(true)
while(true)


 {
{
 str=this.getString();
str=this.getString();
 if(str.matches("\\d+?"))
if(str.matches("\\d+?"))


 {
{
 score=Float.parseFloat(str);break;
score=Float.parseFloat(str);break;
 }
}
 else
else


 {
{
 System.out.println("輸入格式不正確");
System.out.println("輸入格式不正確");
 }
}
 }
}
 return score;
return score;
 }
}

 }
}







 //PersonOperate類
//PersonOperate類

 package op;
package op;

 import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
 import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
 import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.IOException;
 import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;

 import util.FileOperate;
import util.FileOperate;
 import util.InputData;
import util.InputData;
 import vo.Person;
import vo.Person;


 public class PersonOperate
public class PersonOperate  {
{
 private static String name;
private static String name;
 private static int age;
private static int age;
 private static float score;
private static float score;
 private static Person per;
private static Person per;
 static BufferedReader input=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
static BufferedReader input=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
 //添加數據
//添加數據

 public static void add() throws IOException
public static void add() throws IOException  {
{
 System.out.println("請輸入姓名:");
System.out.println("請輸入姓名:");
 name=new InputData().getString();
name=new InputData().getString();
 System.out.println("請輸入年齡:");
System.out.println("請輸入年齡:");
 age=new InputData().getInt();
age=new InputData().getInt();
 System.out.println("請輸入成績:");
System.out.println("請輸入成績:");
 score=new InputData().getFloat();
score=new InputData().getFloat();
 per=new Person(name,age,score);
per=new Person(name,age,score);
 new FileOperate().save(per);
new FileOperate().save(per);
 }
}
 //瀏覽數據
//瀏覽數據
 public static void show() throws FileNotFoundException, IOException, ClassNotFoundException
public static void show() throws FileNotFoundException, IOException, ClassNotFoundException


 {
{
 Person p=(Person)(new FileOperate().read());
Person p=(Person)(new FileOperate().read());
 System.out.println(p);
System.out.println(p);
 }
}
 //更新數據
//更新數據

 public static void update() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException
public static void update() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException  {
{
 Person p=(Person)(new FileOperate().read());//讀出原數據
Person p=(Person)(new FileOperate().read());//讀出原數據
 System.out.println("請輸入新的姓名(原姓名:"+p.getName()+"):");
System.out.println("請輸入新的姓名(原姓名:"+p.getName()+"):");
 name=new InputData().getString();
name=new InputData().getString();
 System.out.println("請輸入新的年齡(原年齡:"+p.getAge()+"):");
System.out.println("請輸入新的年齡(原年齡:"+p.getAge()+"):");
 age=new InputData().getInt();
age=new InputData().getInt();
 System.out.println("請輸入新的成績(原成績:"+p.getScore()+"):");
System.out.println("請輸入新的成績(原成績:"+p.getScore()+"):");
 score=new InputData().getFloat();
score=new InputData().getFloat();
 per=new Person(name,age,score);
per=new Person(name,age,score);
 new FileOperate().update(per);
new FileOperate().update(per);
 }
}

 }
}

 //FileOperate類
//FileOperate類

 package util;
package util;

 import java.io.File;
import java.io.File;
 import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
 import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
 import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
 import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.IOException;
 import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
 import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
 import vo.Person;
import vo.Person;


 public class FileOperate
public class FileOperate  {
{
 File f=new File("e:\\guanli.txt");
File f=new File("e:\\guanli.txt");
 ObjectOutputStream out=null;//創建輸出流
ObjectOutputStream out=null;//創建輸出流
 ObjectInputStream input=null;//創建輸入流
ObjectInputStream input=null;//創建輸入流
 //保存數據到文件中
//保存數據到文件中

 public void save(Object per) throws IOException
public void save(Object per) throws IOException  {
{
 out=new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(f));
out=new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(f));
 out.writeObject(per);
out.writeObject(per);
 System.out.println("數據保存成功");
System.out.println("數據保存成功");
 }
}
 //從文件中讀取數據
//從文件中讀取數據

 public Object read() throws FileNotFoundException, IOException, ClassNotFoundException
public Object read() throws FileNotFoundException, IOException, ClassNotFoundException  {
{
 input=new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(f));
input=new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(f));
 return input.readObject();
return input.readObject();
 }
}
 //同樣是將修改后的數據保存到文件中
//同樣是將修改后的數據保存到文件中

 public void update(Object per) throws FileNotFoundException, IOException
public void update(Object per) throws FileNotFoundException, IOException  {
{
 out=new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(f));
out=new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(f));
 out.writeObject(per);
out.writeObject(per);
 System.out.println("數據更新成功");
System.out.println("數據更新成功");
 }
}

 }
}

 //Person類
//Person類

 package vo;
package vo;

 import java.io.Serializable;
import java.io.Serializable;


 public class Person implements Serializable
public class Person implements Serializable {
{
 private String name;
private String name;
 private int age;
private int age;
 private float score;
private float score;

 public String getName()
public String getName()  {
{
 return name;
return name;
 }
}

 public void setName(String name)
public void setName(String name)  {
{
 this.name = name;
this.name = name;
 }
}

 public int getAge()
public int getAge()  {
{
 return age;
return age;
 }
}

 public void setAge(int age)
public void setAge(int age)  {
{
 this.age = age;
this.age = age;
 }
}

 public float getScore()
public float getScore()  {
{
 return score;
return score;
 }
}

 public void setScore(float score)
public void setScore(float score)  {
{
 this.score = score;
this.score = score;
 }
}
 public Person(String name,int age,float score)
public Person(String name,int age,float score)


 {
{
 this.setName(name);
this.setName(name);
 this.setAge(age);
this.setAge(age);
 this.setScore(score);
this.setScore(score);
 }
}
 public String toString()
public String toString()


 {
{
 return "姓名:"+this.name+"年齡"+this.age+"成績"+this.score;
return "姓名:"+this.name+"年齡"+this.age+"成績"+this.score;
 }
}
 }
}


這個程序只是簡單的說明類之間的關系調用,可能許多細節方面沒有注意到,望各位前輩批評指教!