Enterprise JavaBean(EJB)
a.Enterprise JavaBeans (EJBs) are a part of the Java 2 Enterprise Edition specifications
b.Some Problems Within The Distribution Application
(Distributed, Transactional ,Persistent)


1. Ejb主要包括:Session Bean(業務邏輯),Entity Bean(業務數據),Message Driven Bean
2. Ejb遠程調用的核心:RMI—>Client –(RMI-IIOP)協議—ejb home
3. Ejb的Bean遠程訪問的基礎:Seriliable,因為不同接口繼承了Remote,所以bean要通過網絡傳播只能序列化才行,常見的數據類型如:String,Double都是已經可以序列化的
二.在wsad中ejb實例:
1.新建Enterprise Application Project—>選擇New Module(ejb+client)à創建Stateless SessionBeanà Finish。生成了三個類:Home Object,EJB Object,SessionBean
2.代碼如下:a. Home Object :
public interface SayHelloHome extends javax.ejb.EJBHome {
public mypack.SayHello create()
throws javax.ejb.CreateException, java.rmi.RemoteException; }
b. EJB Object
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
public interface SayHello extends javax.ejb.EJBObject {
public void sayHello()throws RemoteException; }
c. public class SayHelloBean implements javax.ejb.SessionBean {
private javax.ejb.SessionContext mySessionCtx;
public void sayHello(){ System.out.println("nihao"); }
public javax.ejb.SessionContext getSessionContext() {
return mySessionCtx; }
public void setSessionContext(javax.ejb.SessionContext ctx) {
mySessionCtx = ctx; }
public void ejbCreate() throws javax.ejb.CreateException { }
public void ejbActivate() { } //交給緩沖池管理掛起和激活
public void ejbPassivate() { }
public void ejbRemove() { } }
c.Generate部署并生成遠程代碼ejb-jar.xml,主要作用是產生stub和Skeleton,產生的內容:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE ejb-jar PUBLIC "-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Enterprise JavaBeans 2.0//EN" "http://java.sun.com/dtd/ejb-jar_2_0.dtd">
<ejb-jar id="ejb-jar_ID">
<enterprise-beans>
<session id="SayHello">
<ejb-name>SayHello</ejb-name>
<home>mypack.SayHelloHome</home>
<remote>mypack.SayHello</remote>
<ejb-class>mypack.SayHelloBean</ejb-class>
<session-type>Stateless</session-type>
<transaction-type>Container</transaction-type>
</session>
</enterprise-beans>
</ejb-jar>
雙擊ejbModule可以得到jndi地址:ejb/mypack/sayHelloHome-----à運行服務器
3.編寫測試:a.new Client, 將EJB Module加到build path中:
b.編寫測試類:public class HelloTest {
public static void main(String args[])throws Exception{
InitialContext ctx=new InitialContext();
SayHelloHome home=(SayHelloHome) ctx.lookup("ejb/mypack/sayHelloHome");
SayHello hello=home.create(); hello.sayHello(); }}
c. 添加測試類運行期依賴的EJB組件,右擊—>open with jar—>鉤選ejb.jarà找到main class
d.運行測試類(確定你的WebSphere已經啟動):即先要啟動Servers下的服務器后才可以
run as application client,在客戶端看到的是客戶端的內容,服務器斷才能看到服務器結果
(也可以將打包的jar導入到eclipse的進行了封裝,然后調用測試)
三.Entity bean 是RDBMS的視圖,分為CMP和BMP兩種
1.CMP實例:
a.Create ejb to RDB mapping-à加載數據庫的驅動—>根據數據庫表結構生成CMP EntityBeanà選bottom Upà填寫包名就可以自動創建了entity bean
映射方式一共有三種:
bottom-up:通過數據庫表直接生成相應的cmp
top-down:通過已有的entity bean生成相應的數據庫表
meet-in-the-middle:前兩者匯合

b.LocalHome:
public interface AccountLocalHome extends javax.ejb.EJBLocalHome {
public mypack.AccountLocal create(java.lang.String id)
throws javax.ejb.CreateException;
public mypack.AccountLocal findByPrimaryKey(mypack.AccountKey primaryKey)
throws javax.ejb.FinderException;}
c. public interface AccountLocal extends javax.ejb.EJBLocalObject { //業務方法
public java.lang.String getOwername();
public void setOwername(java.lang.String newOwername);
public java.lang.Double getBalance();
public void setBalance(java.lang.Double newBalance); }
d. public abstract class AccountBean implements javax.ejb.EntityBean {
private javax.ejb.EntityContext myEntityCtx;
public void setEntityContext(javax.ejb.EntityContext ctx) {
myEntityCtx = ctx; }
public javax.ejb.EntityContext getEntityContext() {return myEntityCtx; }
public void unsetEntityContext() { myEntityCtx = null; }
public mypack.AccountKey ejbCreate(java.lang.String id)
throws javax.ejb.CreateException { setId(id); return null; }
public void ejbPostCreate(java.lang.String id)
throws javax.ejb.CreateException { }
public void ejbActivate() { }
public void ejbLoad() { }
public void ejbPassivate() { }
public void ejbRemove() throws javax.ejb.RemoveException { }
public void ejbStore() { }
public abstract java.lang.String getOwername();
public abstract void setOwername(java.lang.String newOwername);
public abstract java.lang.Double getBalance();
public abstract void setBalance(java.lang.Double newBalance);
public abstract java.lang.String getId();
public abstract void setId(java.lang.String newId); }
e. public class AccountKey implements java.io.Serializable { //一定要可序列化的
static final long serialVersionUID = 3206093459760846163L;
public java.lang.String id; public AccountKey() { }
public AccountKey(java.lang.String id) { this.id = id; }
public boolean equals(java.lang.Object otherKey) {
if (otherKey instanceof mypack.AccountKey) {
mypack.AccountKey o = (mypack.AccountKey) otherKey;
return ((this.id.equals(o.id))); } return false; }
public int hashCode() { return (id.hashCode()); } }
f.部署generate,生成ejb-jar.xml對主鍵,由容器管理,對應的字段映射進行描述
g. 打開server進行配置security,添加用戶的訪問密碼和用戶名(jaas)
h. 采用數據源的方式和數據庫進行連接(websphere數據源):serveràdate source
àadd listàdb2 jdbc Provideràdefine jdbcà改變數據源jndi地址-à改變databaseName
i. 配置EJB組件訪問DataSource-àcmp open with Deployment Descriptionà改成自設jndi地址
2.CMP方法詳述:
a.context變量:將成員變量,安全信息和環境屬性等放在上下文中
b.跟單行紀錄相關的業務邏輯方法,是abstract的,由容器去生成jdbc代碼,工具生成接口
c.Home接口中的跟整個數據庫有關的業務邏輯方法,findAll不是單條記錄對應的entity
d.entity bean必須的方法,用于管理,load將數據庫中放到內存,store相反
f.容器自動調用的方法,不含jdbc,從entityBean中繼承來的
3.CMP和BMP的比較:
a.cmp是模擬bmp的,cmp沒有持久化字段,沒有get.set方法,都是從ejb-jar.xml中讀取
b.cmp bean class是abstract,標明由容器去實現
c.cmp中對數據庫的操作可以寫成抽象方法,由容器去實現
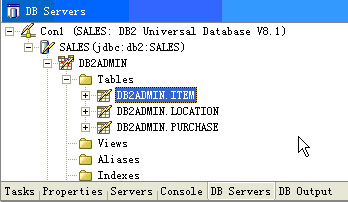
2. 為item添加EJBQL:打開EJB部署描述文件(ejb-jar.xml),找到Bean Item,添加Queriesà
方法名為findAll-à返回為collection 即:select object(o) from item o,
3.為entity bean配置Transaction:切換到“Assembly Descriptor”頁:為Requried
事務:一系列方法的集合,同時成功,不成功可以回滾同時失敗。相當于jdbc時connection的rollback;類型如下:
a. supports:A事務運動,B發現有就加入這一事務中,沒有就算
b. notSupported:A有沒有都不加入,B不一定是事務,B執行,A掛起,B重開啟事務
c. required:上下文中A有就加入,沒有就new一個事務
d. requiresNew:都自己去啟動一個事務, B要執行,A掛起,B不加入別人事務
e. mandatory:強制獨裁,事務A必須有,沒有B就報錯
f. never:有事務在B之前就拋異常,沒有就算
4.修改實體關系:切換到“Overview”頁,找到relationships關聯關系,編輯關系的導航性
一般只是單導航性
5.創建值對象(Value Objects):只要是傳遞entity bean對象,供sessionbean調用
切換到“Project Navigator”頁,新建Java Project:SalesValueObjects
a. ItemVo:Long id;String name; //setter/getter方法 //必須要實現Serialiable接口
b. LocationVo:String city;String state;String zipcode;String areaCode; //setter/getter
6. 將SalesValueObjects project加到sales project中:整個應用中
打開“EAR Deployment Descriptor”(META-INF/application.xml),切換“Module”頁:
--à 選中Project Utility JARs
7.創建業務層 ---- Stateless SessionBean:SalesFacade
8. 下面配置SessionBean訪問EntityBean的本地引用: 是session和entity bean 關聯
打開“EJB Development Descriptor”(META-INF/ejb-jar.xml),切換“References”頁
---àejb local reference,因為entity bean 都是local的
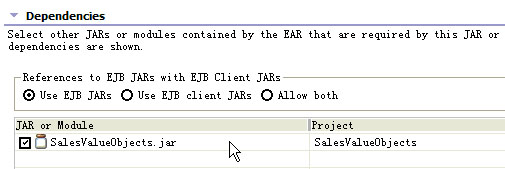
9.在EJB組件中添加對SalesValueObjects project的依賴àopen with jar dependency editor
10. SalesFacade中添加三個業務方法(Remote接口的EJB OBJECT)
public LocationVo getLocation(String zipCode)throws RemoteException;
public ItemVo[] getAllItems()throws RemoteException;
public boolean makePurchase(String zipCode,Long[] itemIds)throws RemoteException;
11.為了業務方法能夠得到EntityBean Item的itemId,在ItemKey中添加get()方法:
12.SalesFacadeBean中實現業務方法:如:
public LocationVo getLocation(String zipCode){
final String locRef="java:comp/env/ejb/Location";
LocationVo locationVo=new LocationVo();
try{ Context ctx=new InitialContext();
LocationLocalHome locationHome=(LocationLocalHome)ctx.lookup(locRef);
LocationLocal location=locationHome.findByPrimaryKey(new LocationKey(zipCode));
locationVo.setAreaCode(location.getAreacode());locationVo.setZipCode(zipCode);
locationVo.setCity(location.getCity());locationVo.setState(location.getState());
}catch(NamingException ne){throw new EJBException(ne);
}catch(FinderException fe){ return locationVo; } return locationVo;}
findByPrimaryKey是home中為entity bean 創建的主鍵查找方法
new LocationKey(zipCode)是key中的一個構造方法
public ItemVo[] getAllItems(){
final String itRef="java:comp/env/ejb/Item"; ItemVo[] itemVos=null;
try{ Context ctx=new InitialContext();
ItemLocalHome itemHome=(ItemLocalHome)ctx.lookup(itRef);
Collection items=itemHome.findAll();//在home中添加查找這個數據庫的方法
if(items!=null){
itemVos=new ItemVo[items.size()];
int i=0;
for(Iterator it=items.iterator();it.hasNext();i++){
ItemLocal item=(ItemLocal)it.next(); ItemVo vo=new ItemVo();
vo.setItemId(((ItemKey)item.getPrimaryKey()).getItemid());
vo.setName(item.getName()); itemVos[i]=vo;} }
}catch(NamingException ne){ throw new EJBException(ne);
}catch(FinderException fe){return new ItemVo[0];} return itemVos; }
13.創建Web層:添加Web Module對SalesValueObjects project和EJB Module的依賴
14.添加Web Module對EJB的引用:
打開“Web Development Descriptor”(WEB-INF/web.xml),切換到“References”
絕大多數情況下web采用了struts,可以在action中lookup homeobject.