AOP(面向切面)技術: Aspect-Oriented Programming,是對OOP的一種補充。
1.AOP和OOP的主要區別、:OOP針對實體及其屬性和行為進行抽象封裝
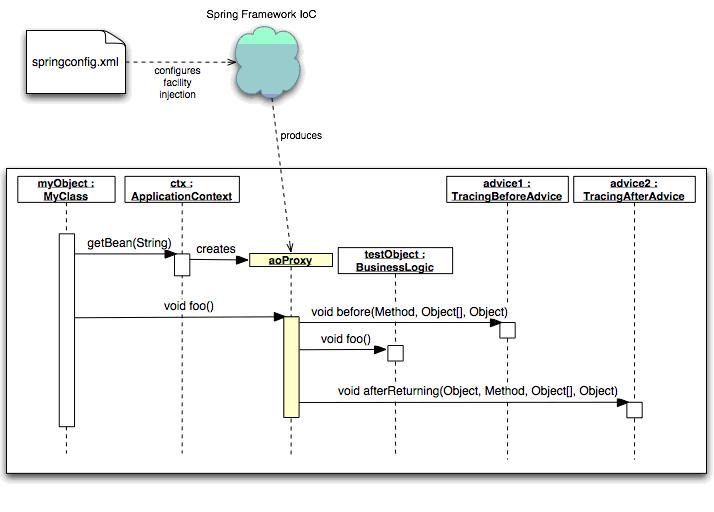
AOP針對業務處理過程中的切面進行提取,它所面對的是處理過程中的某個步驟或階段,比如權限檢查,日志寫入,事務管理,并不需要對OOP采取嵌入式代碼,而是采取在將通知在切點織入的方式。 還是通過容器注入進行管理。
2. AOP常用術語:a.切面(Aspect):是你要實現的交叉功能,是一種描述性的思想。
b.連接點(Joinpoint):應用程序執行過程中插入切面的地點(如方法調用,異常拋出),但連接點不一定要插入切面。
c.通知(Advice):切面的實際實現,是一種邏輯代碼。
d.切入點(Pointcut):定義了通知應用在哪些連接點。e.目標對象(Target):被通知對象
e.代理(Proxy):將通知應用到目標對象后創建的對象。
f.織入:(Weaving):將切面應用到目標對象從而創建一個新的代理對象的過程。
備注:代理模式的優勢:授權機制:不同級別的用戶對同一對象擁有不同的訪問權利
某個客戶端不能直接操作到某個對象,但又必須和那個對象有所互動,可節省內存開銷
客戶端只與接口交互,通過代理模式可以get不同的業務對象。
七:面向切面編程的應用:事務管理(Spring分程序控制和聲明式)
1.描述事務的縮寫詞(ACID)
a.(Atomic):原子性:事務由一個或多個行為綁在一起組成,好像是一個單獨工作單元。
原子性確保在事務中的所有操作要么都發生,要么都不發生。
b.(Consistent):一致性:一旦一個事物結束了(不管成功與否),系統所處的狀態和它的業務規則是一致的。
c.(Isolated):隔離性:事務應該允許多個用戶操作同一個數據,一個用戶的操作不會和其他用戶的操作相混淆。
d.(Durable):一旦事務完成,事務的結果應該持久化。
2.事務屬性:是對事務策略如何應用到方法的描述。
a.傳播行為(Propagation):定義了客戶端和被調用方法的事務邊界,和ejb中傳播規則相同,只是加了前綴PROPAGATION,如:PROPAGATION_REQUIRED
b.隔離級別(Isolation):一般采用數據庫默認行為即可,在理想狀態下,事物要完全相互隔離,然而完全隔離會影響性能,有時需要在事務隔離上有些彈性。
c.只讀(readOnly):如果一個事務只對數據庫執行讀操作,數據庫就可能利用事務只讀的特性,使用某些優化措施。
d.事務超時(timeOut):只對具有啟動新事務的傳播行為的方法的事務設置超時才有意義,即:required,required_new,nested.
3.聲明式事務
a.model:public class User {private Integer id; private String name;
private Integer age; //getter/setter; }
b.Dao: public interface UserDao { public Integer addUser(User user);
public User getUser(Integer userId); public List getUsers(); }
c.DaoImpl: public class UserDaoHibernate extends HibernateDaoSupport implements UserDao { public Integer addUser(User user) {
return (Integer) getHibernateTemplate().save(user); }
public User getUser(Integer userId) {
return (User) getHibernateTemplate().load(User.class, userId); }
public List getUsers() { String hql="from User";
return getHibernateTemplate().find(hql); } }
d.service: public interface UserManager { public Integer addUser(User user);}
e.serviceImpl: public class UserManagerImpl implements UserManager {
private UserDao userDao;
public Integer addUser(User user) {Integer userId=userDao.addUser(user);
return userId; } //對數據庫的操作根本不用代碼嵌入式transaction
public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) { this.userDao = userDao; } }
f.hbm.xml: <hibernate-mapping package="mypack"><class name="User" table="user">
<id name="id" column="id" type="integer"><generator class="identity"/> </id>
<property name="name" column="name" type="string"></property>
<property name="age" column="age" type="integer"></property> </class>
</hibernate-mapping>
g.applicationContext.xml: <bean id="userDao" class="mypack.UserDaoHibernate">
<property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory" /> //為supportDao注入
<bean id="userManagerTarget" class="mypack.UserManagerImpl">
<property name="userDao" ref="userDao"></property> </bean>
<bean id="transactionManager" //真正的事務管理實體對象
class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateTransactionManager">
<property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory"/> </bean>
<bean id="userManager"http://通過代理模式參照一個方法的事務屬性決定如何執行事務策略。
class="org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionProxyFactoryBean">
<property name="transactionManager" ref="transactionManager"></property>//通知
<property name="target" ref="userManagerTarget"></property> //目標
<property name="transactionAttributes">
<props> <prop key="add*">PROPAGATION_REQUIRED</prop> //切點
<prop key="get*">PROPAGATION_REQUIRED,readOnly</prop> </props>
</property> </bean>
h.測試:public void testTransaction(){User user=new User();user.setName("liming");
user.setAge(22); Integer userId=userMgr.addUser(user); }
4.用元數據聲明事務:
a.將service接口加上@ Transactional聲明,當然也可以加在serviceImpl實現類上
@Transactional(propagation=Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW),此處表示聲明該類所有方法
public interface UserManager { public Integer addUser(User user);}
//也可對具體方法聲明
b.applicationContext.xml變成如下形式:使支持對元數據的支持
<bean id="userManager" class="mypack.UserManagerImpl">
<property name="userDao" ref="userDao"></property> </bean>
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateTransactionManager">
<property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory"></property>
</bean>
<bean
class="org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator>
</bean>
<bean id="transactionInterceptor" class="org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionInterceptor">
<property name="transactionManager" ref="transactionManager"></property>
<property name="transactionAttributeSource">
<bean class="org.springframework.transaction.annotation.
AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource"></bean> </property> </bean>
<bean class="org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.
TransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor"> <property name="transactionInterceptor" ref="transactionInterceptor"></property> </bean>