2010年10月9日
剛學java流技術IO編程時,一下出來這么多流,很是不敏感,不感冒,在學習了這段時間,發現好多項目中的讀寫數據,輸入輸出用到的都是以前學的最基本的,但是自己卻不是很理解其根本,今天就說幾個流中簡單但又常用的幾個知識點
Java.io包中定義了多個流類型,來實現輸入輸出功能:
- 按數據流的方向不同可以分為輸入流和輸出流。(以程序的角度來考慮)
- 如:輸入流InputStream Reader 輸出流 OutputStream Writer
- 按處理數據單位不同可以分為字節流和字符流。
- 如: 字節流 InputStream OutputStream 字符流 Reader Writer
- 按照功能不同可以分為節點流和處理流。
通俗的說節點流就是一個簡單的輸入輸出流,而處理流是“連接”在已存在的字節流或處理流之上的,通過對數據的處理為程序提供更為強大的讀寫功能。
我們最經常用到的節點流類型是有關文件處理的有FileReader FileWriter FileInputStream FileOutputStream
Ø FileInputSteam 和 FileOutputStream 類支持其父類InputStream 和OutputStream 所提供的數據讀寫方法。
Ø 注意:
§ 在實例化FileInputStream和FileOutputSteam流時要用try-catch語句以處理其可能拋出的FileNotFoundException。
§ 在讀寫數據時也要用try-catch語句以處理可能拋出的 IOException。
§ FileNotFoundException是IOException的子類
FileReader 和 FileWriter 分別繼承自Reader和Writer,FileInputSteam與FileOutputStream類似,所不同的時FileReader和FileWriter向文件輸入和輸出的數據單位為字符。
處理流中常用到的有緩沖流 、轉換流。
l 緩沖流有BufferedReader BufferedWriter BufferedInputStream BufferedOutputStream ,緩沖流要“套接”在相應的節點流之上,對讀寫的數據提供了緩沖的功能,提高了讀寫的效率,同時增加了一些新的方法
l BufferedReader提供了readLine方法用于讀取一行字符串(以"r或"n分 隔)。
l BufferedWriter提供了newLine用于寫入一個行分隔符。
l 對于輸出的緩沖流,寫出的數據會先在內存中緩存,使用flush方法將會使內存中的數據立刻寫出。
在Socket編程中接受信息時,不是直接用InputStream接收,而是把內容放入緩沖之中進行讀取 ,在Socket中的簡單應用如下
 package com.dr.Echo;
package com.dr.Echo;

 import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
 import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.IOException;
 import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
 import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
 import java.io.PrintStream;
import java.io.PrintStream;
 import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
 import java.net.Socket;
import java.net.Socket;


 public class EchoServer
public class EchoServer  {
{


 /** *//**
/** *//**
 * @param args
* @param args
 * @throws IOException
* @throws IOException
 */
*/

 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException  {
{
 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
 ServerSocket server = null;
ServerSocket server = null;
 PrintStream out = null;
PrintStream out = null;
 BufferedReader buf = null;
BufferedReader buf = null;
 server = new ServerSocket(9999);
server = new ServerSocket(9999);
 Socket client = null;
Socket client = null;

 while(true)
while(true) {
{
 //不斷接收數據
//不斷接收數據
 client = server.accept();
client = server.accept();
 //準備好像客戶端輸出內容
//準備好像客戶端輸出內容
 out = new PrintStream(client.getOutputStream());
out = new PrintStream(client.getOutputStream());
 //而且客戶端要有輸入給服務器端
//而且客戶端要有輸入給服務器端
 buf = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(client.getInputStream()));
buf = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(client.getInputStream()));
 //下面先給出一個完整的信息提示
//下面先給出一個完整的信息提示
 out.println("您好!歡迎光臨:http://wwww.tstc.edu.cn");
out.println("您好!歡迎光臨:http://wwww.tstc.edu.cn");
 out.println("輸入bye表示退出哈-");
out.println("輸入bye表示退出哈-");

 while(true)
while(true) {
{
 //接受客戶端發送而來的內容
//接受客戶端發送而來的內容
 String str = buf.readLine();
String str = buf.readLine();
 System.out.println("client's data is "+str);
System.out.println("client's data is "+str);

 if(str == null)
if(str == null) {
{
 //如果str為空就表示退出
//如果str為空就表示退出
 break;
break;

 }else
}else {
{
 //如果輸入的是bye則表示是退出系統
//如果輸入的是bye則表示是退出系統

 if("bye".equals(str))
if("bye".equals(str)) {
{
 break;
break;
 }
}
 out.println("xiaoxiao:"+str);
out.println("xiaoxiao:"+str);
 }
}
 }
}
 out.close();
out.close();
 buf.close();
buf.close();
 client.close();
client.close();
 }
}
 }
}

 }
}

 package com.dr.Echo;
package com.dr.Echo;

 import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
 import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.IOException;
 import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
 import java.io.PrintStream;
import java.io.PrintStream;
 import java.net.Socket;
import java.net.Socket;
 import java.net.UnknownHostException;
import java.net.UnknownHostException;


 public class EchoClient
public class EchoClient  {
{


 /** *//**
/** *//**
 * @param args
* @param args
 * @throws IOException
* @throws IOException
 * @throws UnknownHostException
* @throws UnknownHostException
 */
*/

 public static void main(String[] args) throws UnknownHostException, IOException
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnknownHostException, IOException  {
{
 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
 Socket client = null;
Socket client = null;
 BufferedReader buf = null;
BufferedReader buf = null;
 PrintStream out = null;
PrintStream out = null;
 client = new Socket("127.0.0.1",9999);
client = new Socket("127.0.0.1",9999);
 buf = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(client.getInputStream()));
buf = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(client.getInputStream()));
 System.out.println(buf.readLine());
System.out.println(buf.readLine());
 System.out.println(buf.readLine());
System.out.println(buf.readLine());
 BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));

 String userInput = null;
String userInput = null;
 out = new PrintStream(client.getOutputStream());
out = new PrintStream(client.getOutputStream());

 while((userInput = in.readLine())!=null)
while((userInput = in.readLine())!=null) {
{
 out.println(userInput);
out.println(userInput);
 System.out.println(buf.readLine());
System.out.println(buf.readLine());
 }
}
 out.close();
out.close();
 in.close();
in.close();
 client.close();
client.close();


 }
}

 }
}

轉換流InputStreamReader OutputStreamWriter 用于字節數據到字符數據之間的轉換。其中InputStreamReader 需要和InputStream”套接”,OutputStreamWriter需要和OutputStream套接
數據流DataInputStream DataOutputStream 提供了可以存取與機器無關的java原始數據類型
l Print流:PrintWriter和PrintStream都屬于輸出流,分別針對與字符和字節,PrintWriter和PrintStream提供了重載的print,Println方法用于多種數據類型的輸出。PrintWriter和PrintStream的輸出操作不會拋出異常,用戶通過檢測錯誤狀態獲取錯誤信息。PrintWriter和PrintStream有自動flush功能
l
這幾個流的類型都是在以后的學習中經常用到的。就不一一做例子啦
以后所學到的所有流類型都是繼承 InputStream OutputStream Reader Writer 這四個抽象的流類型
posted @
2011-01-18 22:26 迷人笑笑 閱讀(889) |
評論 (0) |
編輯 收藏
摘要: 我相信大多說人都對構造方法、方法不陌生,而且很了解,但我也相信有很多像我這樣的沒有一個很好很清晰很全面的認識,今天就把它整理如下,希望能給大家帶來點方便與幫助,也希望大家多多討論。
...
閱讀全文
posted @
2010-11-12 16:43 迷人笑笑 閱讀(39170) |
評論 (1) |
編輯 收藏
摘要: 今天我們用實例程序說一下java中常見的生產者與消費者的問題。
首先看一下里面線程間的通信問題:
一個線程向數據存儲空間添加數據(生產者),另一個線程從數據存儲空間去出數據(消費者)。
這個程序中有兩個可能出現的問題需要考慮:
1、 ...
閱讀全文
posted @
2010-11-10 23:07 迷人笑笑 閱讀(2166) |
評論 (1) |
編輯 收藏
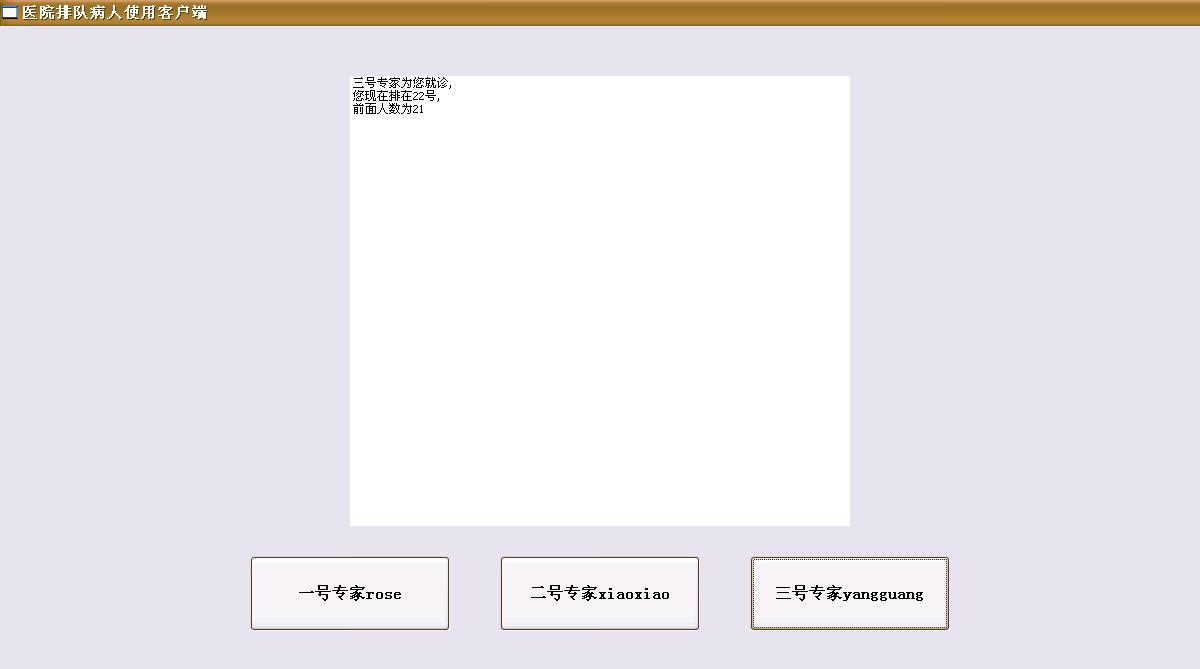
摘要: 項目需求:1.病人來掛號時根據自己想找的醫生掛相應的醫生的號,即加到相應醫生的病人隊列中。
2.醫生看見自己的屏幕,點擊自己的名字,得到自己相應列表的下一位病人
具體代碼如下:
...
閱讀全文
posted @
2010-11-02 16:51 迷人笑笑 閱讀(3472) |
評論 (1) |
編輯 收藏
摘要: 1.當我們去銀行辦理什么業務的時候總會先在一個類似電腦的小系統上去一個號,然后等著,當被叫到時就去相應的窗口辦理業務,這種排隊的小系統主要用到了接口Queue,因為它符合隊列的要求先進先出。
2.還有就是有種特殊情況就是,銀行的金卡用戶,他們的權限較高,總可以在普通用戶的前面辦理業務
相應代碼如下:
package com.dr.queue;
public clas...
閱讀全文
posted @
2010-11-01 13:22 迷人笑笑 閱讀(3776) |
評論 (0) |
編輯 收藏
代碼如下:
 package com.dr.exercise6;
package com.dr.exercise6;

 import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Scanner;


 public class Login
public class Login  {
{

 public static void main(String[] args)
public static void main(String[] args)  {
{
 Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
 System.out.println("請輸入用戶名:");
System.out.println("請輸入用戶名:");
 String name = s.nextLine();
String name = s.nextLine();
 System.out.println("請輸入密碼:");
System.out.println("請輸入密碼:");
 String password = s.nextLine();
String password = s.nextLine();

 if(name.equals("abc")&&password.equals("123"))
if(name.equals("abc")&&password.equals("123")) {
{
 System.out.println("歡迎登入!!");
System.out.println("歡迎登入!!");

 }
}

 else
else {
{
 System.out.println("用戶名或密碼不正確!!");
System.out.println("用戶名或密碼不正確!!");
 }
}

 }
}

 }
}

用戶名密碼輸入正確時:

用戶名或密碼輸入不正確時:

posted @
2010-10-20 16:33 迷人笑笑 閱讀(629) |
評論 (0) |
編輯 收藏
答案是兩個,現在我們具體的說一下:
String s = new String("abc");
首先我們要明白兩個概念,引用變量和對象,對象一般通過new在堆中創建,s只是一個引用變量。
所有的字符串都是String對象,由于字符串文字的大量使用,java中為了節省時間,在編譯階段,會把字符串文字放在文字池中,文字池的一個好處就是可以把相同的字符串合并,占用一個空間,我們可以用==判斷一下兩個引用變量是否指向了一個地址即一個對象

 public class Demo02
public class Demo02  {
{

 public static void main(String[] args)
public static void main(String[] args)  {
{
 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
 String s1 ="abc";
String s1 ="abc";
 String s2 = "abc" ;
String s2 = "abc" ;
 if( s1 == s2 ) System.out.println("s1,s2 refer to the same object");
if( s1 == s2 ) System.out.println("s1,s2 refer to the same object");
 else System.out.println("trouble");
else System.out.println("trouble");
 }
}
 }
}
輸出結果為:
可以看出指向了一個對象,即文字池中保存了一個對象。
二、String s = new String("abc")實際上是"abc"本身就是文字池中的一個對象,在運行 new String()時,把文字池即pool中的字符串"abc"復制到堆中,并把這個對象的應用交給s,所以創建了兩個String對象,一個在pool中,一個在堆中。下面看這個程序,創建了幾個對象。

 public class Demo03
public class Demo03  {
{

 public static void main(String[] args)
public static void main(String[] args)  {
{
 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
 String s1 = new String("abc") ;
String s1 = new String("abc") ;
 String s2 = new String("abc") ;
String s2 = new String("abc") ;

 if( s1 == s2 )
if( s1 == s2 ) { //不會執行的語句}
{ //不會執行的語句}
 System.out.println("在堆中創建了一個對象");
System.out.println("在堆中創建了一個對象");

 }
}

 else
else {
{
 System.out.println("在堆中創建了兩個對象");
System.out.println("在堆中創建了兩個對象");
 }
}
 }
}
 }
}
輸出結果為:

可知在堆中創建了兩個對象,但是在文字池中有一個對象,所以共創建了三個對象。
三、再看下一個例子:

 public class Demo04
public class Demo04  {
{

 public static void main(String[] args)
public static void main(String[] args)  {
{
 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
 String s = new String("abc");
String s = new String("abc");
 s = "cba";
s = "cba";
 System.out.println(s);
System.out.println(s);
 }
}

 }
}
輸出結果為:

String s = new String("abc")并不是給s賦值,而是把字符串"abc"的引用交給s持有,現在把s指向字符串"cba","cba"的引用地址把"abc"的引用地址覆蓋,所以輸出結果為cba
最后這個輸出結果的解釋,希望大家指出不足!!
posted @
2010-10-18 14:32 迷人笑笑 閱讀(10659) |
評論 (0) |
編輯 收藏
要求為:寫一個公司員工類;
數據成員:員工號,姓名,薪水,部門;
方法:
利用構造方法完成設置信息:
A.單參,只傳遞員工號;
B.雙參,只傳遞員工號、姓名;
C.四參,傳遞員工號、姓名、薪水、部門;
D.無參,則均為空值;
main方法中創建兩個對象,分別進行驗證。
 package com.dr.computer;
package com.dr.computer;


 public class Worker
public class Worker  {
{
 private String id;
private String id;
 private String name;
private String name;
 private float salary;
private float salary;
 private String department;
private String department;

 public Worker(String n)
public Worker(String n) {
{
 this.setId(n);
this.setId(n);
 this.setName("無名氏");
this.setName("無名氏");
 this.setSalary(0.0f);
this.setSalary(0.0f);
 this.setDepartment("未定");
this.setDepartment("未定");
 }
}

 public Worker(String n,String na)
public Worker(String n,String na) {
{
 this.setId(n);
this.setId(n);
 this.setName(na);
this.setName(na);
 this.setSalary(1000);
this.setSalary(1000);
 this.setDepartment("后勤");
this.setDepartment("后勤");
 }
}

 public Worker (String n,String na,float sa,String dep)
public Worker (String n,String na,float sa,String dep) {
{
 this.setId(n);
this.setId(n);
 this.setName(na);
this.setName(na);
 this.setSalary(sa);
this.setSalary(sa);
 this.setDepartment(dep);
this.setDepartment(dep);
 }
}

 public Worker()
public Worker() {
{

 }
}

 public String getId()
public String getId()  {
{
 return id;
return id;
 }
}

 public void setId(String n)
public void setId(String n)  {
{
 this.id = n;
this.id = n;
 }
}

 public String getName()
public String getName()  {
{
 return name;
return name;
 }
}

 public void setName(String name)
public void setName(String name)  {
{
 this.name = name;
this.name = name;
 }
}

 public float getSalary()
public float getSalary()  {
{
 return salary;
return salary;
 }
}

 public void setSalary(float f)
public void setSalary(float f)  {
{

 if(f>0.0f)
if(f>0.0f) {
{
 this.salary = f;
this.salary = f;
 }
}
 }
}

 public String getDepartment()
public String getDepartment()  {
{
 return department;
return department;
 }
}

 public void setDepartment(String department)
public void setDepartment(String department)  {
{
 this.department = department;
this.department = department;
 }
}

 public void showWorker()
public void showWorker() {
{
 System.out.println("員工信息為:");
System.out.println("員工信息為:");
 System.out.println("\t+--我的Id號:"+id);
System.out.println("\t+--我的Id號:"+id);
 System.out.println("\t+--我的名字:"+name);
System.out.println("\t+--我的名字:"+name);
 System.out.println("\t+--我的工資:"+salary);
System.out.println("\t+--我的工資:"+salary);
 System.out.println("\t+--我的部門:"+department);
System.out.println("\t+--我的部門:"+department);
 }
}
 }
}

 package com.dr.computer;
package com.dr.computer;


 public class WorkerTest
public class WorkerTest  {
{



 public static void main(String[] args)
public static void main(String[] args)  {
{
 Worker w1 =new Worker("0001","泉水");
Worker w1 =new Worker("0001","泉水");
 Worker w2 =new Worker("0002","陽光",1000.0f,"公關部");
Worker w2 =new Worker("0002","陽光",1000.0f,"公關部");
 w1.showWorker();
w1.showWorker();
 w2.showWorker();
w2.showWorker();
 }
}

 }
}



posted @
2010-10-15 22:47 迷人笑笑 閱讀(443) |
評論 (0) |
編輯 收藏
類是一個抽象的概念,對象則是類的具體實例,是真實的個體,比如人就是一個類,張三、李四等就是一個個真實的
具體的個體對象,人有具備所有人類通用的特征,但不能確定是哪個人,張三、李四等有具體的特征,比如身高性別,即
屬性。類一種看不見摸不著的東西,對象是“有血有肉”的實物。
現實生活中到處皆對象,比如一輛汽車,一棟房子,一臺電腦,一只貓。
面向對象具有封裝、繼承、多態三大特征。封裝,即使屬性用private修飾對外部不可見;繼承,如人,有老人、小孩
、男人、女人,他們都是人的子類。多態包括方法的重載和對象的多態性,方法的重載就是方法名相同,但參數和類型不
同的方法,多態,即人分為老人,小孩,男人,女人等。
posted @
2010-10-15 15:13 迷人笑笑 閱讀(818) |
評論 (0) |
編輯 收藏
java采用堆棧形式對數據進行存取,這樣做的優點是存取速度較快,因為棧的速度比較快,僅次于寄存器的速度,堆棧的模式符合垃圾回收的機制,有利于垃圾的回收,垃圾收集器(GC)自動回收。
現在用一個小實例來感受一下java的堆棧存取,代碼如下:

 public class Person
public class Person  {
{
 String name;
String name;
 int age;
int age;

 public static void main(String[] args)
public static void main(String[] args)  {
{
 Person p1 = new Person();
Person p1 = new Person();
 Person p2 = null;
Person p2 = null;

 p2 = p1;
p2 = p1;
 p1.name = "張三";
p1.name = "張三";
 p1.age = 23;
p1.age = 23;
 p2.name = "李四";
p2.name = "李四";
 p2.age = 24;
p2.age = 24;

 p1.say();
p1.say();
 p2.say();
p2.say();

 }
}

 void say()
void say() {
{
 System.out.println("我的名字是:"+ name +"年齡 :"+age);
System.out.println("我的名字是:"+ name +"年齡 :"+age);
 }
}
運行結果如下:我的名字是:李四年齡 :24
我的名字是:李四年齡 :24
可用畫圖來表示其堆棧的存取:其中李四把張三給覆蓋啦。

修改代碼如下:

 public class Person
public class Person  {
{
 String name;
String name;
 int age;
int age;

 public static void main(String[] args)
public static void main(String[] args)  {
{
 Person p1 = new Person();
Person p1 = new Person();
 Person p2 = new Person();
Person p2 = new Person();

 p2 = p1;
p2 = p1;
 p1.name = "張三";
p1.name = "張三";
 p1.age = 23;
p1.age = 23;
 p2.name = "李四";
p2.name = "李四";
 p2.age = 24;
p2.age = 24;

 p1.say();
p1.say();
 p2.say();
p2.say();

 }
}

 void say()
void say() {
{
 System.out.println("我的名字是:"+ name +"年齡 :"+age);
System.out.println("我的名字是:"+ name +"年齡 :"+age);
 }
}

 }
}
運行結果也是:我的名字是:李四年齡 :24
我的名字是:李四年齡 :24
其堆棧存取用畫圖表示如下:其中李四把張三給覆蓋啦

p2先斷開自己原先的堆指向,再指向p1的指向,原先的堆空間被釋放。
posted @
2010-10-13 08:33 迷人笑笑 閱讀(1001) |
評論 (3) |
編輯 收藏
java API 是應用編程接口,是一種規范,指明編寫應用程序的程序員如何訪問類和行為和狀態。
下面就列舉個API 中string類中的10個方法的小應用:
1. contains:當且僅當此字符串包含指定的char值序列時,返回true

 public class Contains
public class Contains  {
{

 public static void main(String[] args)
public static void main(String[] args)  {
{
 String str ="abcdefg";
String str ="abcdefg";
 boolean i = str.contains("ab");
boolean i = str.contains("ab");
 System.out.print(i);
System.out.print(i);

 }
}

 }
}
2.copyValueOf:通過這個方法把給定數組中的相應的部分copy到字符串中輸出來

 public static void main(String[] args)
public static void main(String[] args)  {
{

 char[] x =
char[] x =  {'a','b','c','d','e'};
{'a','b','c','d','e'};
 String str = null;
String str = null;
 str = String.copyValueOf(x,2,3);
str = String.copyValueOf(x,2,3);
 System.out.print(str);
System.out.print(str);

 }
}

 }
}
str = String.copyValueOf(x,2,3)其中的x表示原數組,2表示偏移量,3表示要輸出的長度。
3.Intern:返回字符串對象的規范化表示形式,遵循以下規則:對于任意兩個字符串s,t,當且僅當s.equals(t) 為true時,s.intern() == t.intern 才為true

 public static void main(String[] args)
public static void main(String[] args)  {
{
 String str1 = "HelloWorld";
String str1 = "HelloWorld";
 String str2 = "Hello"+"World";
String str2 = "Hello"+"World";
 System.out.println(str1 == str2);
System.out.println(str1 == str2);
 System.out.print(str1.intern( ) == str2.intern());
System.out.print(str1.intern( ) == str2.intern());
 }
}

 }
}
4.length:返回此對象的長度

 public class Length
public class Length  {
{



 public static void main(String[] args)
public static void main(String[] args)  {
{
 String str = "abcdefg";
String str = "abcdefg";
 System.out.print(str.length());
System.out.print(str.length());
 }
}

 }
}
5.matches告知此字符串是否匹配指定的正則表達式,當且僅當匹配給定的正則表達式時,輸出true

 public class Matches
public class Matches  {
{



 public static void main(String[] args)
public static void main(String[] args)  {
{
 String str = "abcdefg";
String str = "abcdefg";
 boolean i =str.matches( "abcdefg");
boolean i =str.matches( "abcdefg");
 System.out.println(i);
System.out.println(i);
 }
}

 }
}
6.replaceFirst:用給定的字符串替換正則表達式匹配的字符串

 public class ReplaceFirst
public class ReplaceFirst  {
{

 public static void main(String[] args)
public static void main(String[] args)  {
{
 String str = "abcdefgh";
String str = "abcdefgh";
 String str1 = str.replaceFirst("ef", "k");
String str1 = str.replaceFirst("ef", "k");
 System.out.print(str1);
System.out.print(str1);
 }
}

 }
}

7.subString:返回一個新字符串,他是此字符串的一個字子符串,該子字符串從指定字符串索引處的字符開始,直到指定的索引結束的字符結束

 public class Substring
public class Substring  {
{



 public static void main(String[] args)
public static void main(String[] args)  {
{
 String str = "abcdefgh";
String str = "abcdefgh";
 String str1 = str.substring(2, 4);
String str1 = str.substring(2, 4);
 System.out.print(str1);
System.out.print(str1);
 }
}
 }
}

其中String str = "str.substring(2,4)"中2表示起始索引(包括),4表示結束索引(不包括)
如果把其實索引改為負數或結束索引大于字符串長度,便會出現indexoutBounsException的異常
8.toCharArray:將此字符串轉化為一個新的字符數組

 public class ToCharArray
public class ToCharArray  {
{

 public static void main(String[] args)
public static void main(String[] args)  {
{
 String str1 = "一定要死幸福";
String str1 = "一定要死幸福";
 char[] str2 = str1.toCharArray( );
char[] str2 = str1.toCharArray( );

 for(int i=0;i<str2.length;i++)
for(int i=0;i<str2.length;i++) {
{
 System.out.println(str2[i]);
System.out.println(str2[i]);
 }
}
 }
}
 }
}
9.trim:此方法可用于截去開頭和尾部的空白

 public class Trim
public class Trim  {
{

 public static void main(String[] args)
public static void main(String[] args)  {
{
 String str = " abcd ";
String str = " abcd ";
 String strArr = str.trim();
String strArr = str.trim();
 System.out.println(strArr);
System.out.println(strArr);
 }
}

 }
}
10.valueOf:返回char參數的字符串表示形式

 public class ValueOf
public class ValueOf  {
{

 public static void main(String[] args)
public static void main(String[] args)  {
{

 char[] x =
char[] x =  {'a','b','c','d'};
{'a','b','c','d'};
 String str1 ="null";
String str1 ="null";
 str1 = String.valueOf(x);
str1 = String.valueOf(x);
 System.out.print(str1);
System.out.print(str1);

 }
}

 }
}

posted @
2010-10-09 17:48 迷人笑笑 閱讀(447) |
評論 (0) |
編輯 收藏
摘要: 要求:寫一java小程序,要求輸出姓名,班級、年齡、分數、等級
創建三個類Student,StudentText,Text具體程序為:
package com.dr.student;
public class Student {
private String name;
&nb...
閱讀全文
posted @
2010-10-09 08:38 迷人笑笑 閱讀(171) |
評論 (0) |
編輯 收藏