2010年1月21日
#
1. Remote
Method Invocation (RMI)
2. Hessian
3. Burlap
4. HTTP invoker
5. EJB
6. JAX-RPC
7. JMX
zz from http://marakana.com/forums/tomcat/general/106.html
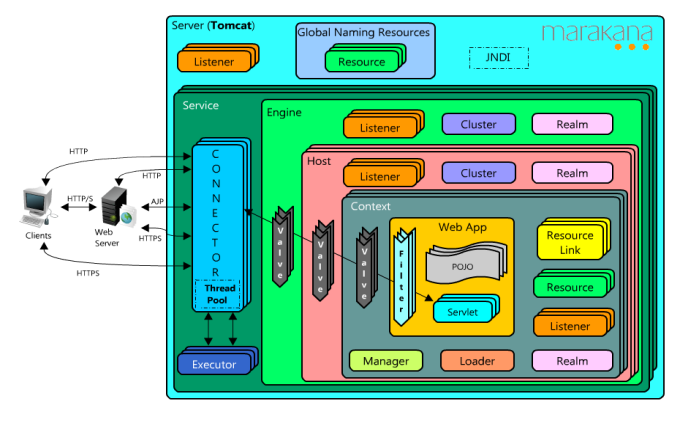
Valve and Filter:
"Valve" is Tomcat
specific notion, and they get applied at a higher level than anything in a specific webapp. Also, they work only in Tomcat.
"Filter" is a Servlet Specification notion and should work in any compliant servlet container. They get applied at a lower level than all of Tomcat's
Valves.
However, consider also the division between your application and the application
server. Think whether the feature you're planning is part of your application, or is it rather a generic feature of the application server, which could have uses in other applications as well. This would be the correct criteria to decide between Valve and Filter.
Order for filter: The order in which they are
defined matters. The container will execute the filters in the order
in which they are defined.
Use one single table "blank_fields" for both A and B. "blank_fields" has fields: 'ref_id', 'blank_field', 'type'. 'type' is used to identify which entity the record belongs to. Use 'type' + 'ref_id' to specify the collection of elements for one entity.
@Entity
@Table(name = "table_a")
public class A {
private Set<BlankField> blankFields = new HashSet<BlankField>();
@CollectionOfElements
@Fetch(FetchMode.SUBSELECT)
@Enumerated(EnumType.ORDINAL)
@JoinTable(name = "blank_fields", joinColumns = { @JoinColumn(name = "ref_id") })
@Cascade(value = org.hibernate.annotations.CascadeType.DELETE_ORPHAN)
@Column(name = "blank_field", nullable = false)
@SQLInsert(sql = "INSERT INTO blank_fields(ref_id, blank_field, type) VALUES(?,?,0)")
@Where(clause = "type=0")
public Set<BlankField> getBlankFields() { // BlankField is an enum
return blankFields;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
private void setBlankFields(Set<BlankField> blankFields) {
this.blankFields = blankFields;
}
} // End B
@Entity
@Table(name = "table_b")
public class B {
private Set<BlankField> blankFields = new HashSet<BlankField>();
@CollectionOfElements
@Fetch(FetchMode.SUBSELECT)
@Enumerated(EnumType.ORDINAL)
@JoinTable(name = "blank_fields", joinColumns = { @JoinColumn(name = "ref_id") })
@Cascade(value = org.hibernate.annotations.CascadeType.DELETE_ORPHAN)
@Column(name = "blank_field", nullable = false)
@SQLInsert(sql = "INSERT INTO blank_fields(ref_id, blank_field, type) VALUES(?,?,1)") // used for insert
@Where(clause = "type=1") // used for query, if not @CollectionOfElements, such as @OneToMany, use @WhereJoinTable instead
public Set<BlankField> getBlankFields() {
return blankFields;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
private void setBlankFields(Set<BlankField> blankFields) {
this.blankFields = blankFields;
}
}
當(dāng)然還有其他的方式來實(shí)現(xiàn)上面的需求,上面采用的單表來記錄不同實(shí)體的associations(這兒是CollectionOfElements,并且返回的是Set<Enum>,不是Set<Embeddable>),然后用'type'來區(qū)分不同的實(shí)體,這樣做的好處是:數(shù)據(jù)庫冗余少,易于擴(kuò)展,對(duì)于新的實(shí)體,只需加一個(gè)type值,而不需更改數(shù)據(jù)庫表結(jié)構(gòu)。另外一種采用單表的方式是為每個(gè)實(shí)體增加新的字段,如"blank_fields": 'a_id', 'b_id', 'blank_field', a_id reference table_a (id), b_id reference table_b (id). 這樣在映射的時(shí)候更簡單,
對(duì)于A,映射為
@JoinTable(name = "blank_fields", joinColumns = { @JoinColumn(name = "a_id") })
對(duì)于B,映射為
@JoinTable(name = "blank_fields", joinColumns = { @JoinColumn(name = "b_id") })
這樣作的缺點(diǎn)是:帶來了數(shù)據(jù)庫冗余,對(duì)于blank_fields來講,任一條記錄,a_id和b_id中只有一個(gè)不為null。當(dāng)多個(gè)實(shí)體共用這個(gè)表時(shí),用上面的方法更合理,如果共用實(shí)體不多時(shí),這種方法更方便。
The case to use One Hibernate Session Multiple Transactions:
each transaction would NOT affect others.
i.e., open multiple transactions on the same session, even though one transaction rolls back, other transactions can be committed. If one action fails, others should fail too, then we should use one transaction for all actions.
Note:
A rollback with a single Session will lead to that Session being cleared (through "Session.clear()").
So do lazy collections still work if the session is cleared? =>Not of any objects that you loaded up until the rollback. Only for new objects loaded afterwards.
We should load necessary objects to session for each transactional action to avoid LazyInitializationException, even if those objects are loaded before other forward transactional actions, since forward action may be rolled back and clear the session.
BTW, Hibernate Session.merge() is different with Session.update() by:
Item item2 = session.merge(item);
item2 == item; // false, item - DETACHED, item2 - PERSIST
session.update(item); // no return value, make item PERSIST
發(fā)生這種異常的case:
@Transactional
public void foo() {
try{
bar();
} catch (RuntimeException re) {
// caught but not throw further

}

}
@Transactional
public void bar() {

}
如果foo在調(diào)用bar的時(shí)候,bar拋出RuntimeException,Spring在bar return時(shí)將Transactional標(biāo)記為Rollback only, 而foo捕獲了bar的RuntimeException,所以Spring將會(huì)commit foo的事務(wù),但是foo和bar使用的是同一事務(wù),因此在commit foo事務(wù)時(shí),將會(huì)拋出UnexpectedRollbackException。注意:如果foo和bar在同一class中,不會(huì)出現(xiàn)這種情況,因?yàn)椋?br />
Since this mechanism is based on proxies, only 'external' method calls coming in through the proxy will be intercepted. This means that 'self-invocation', i.e. a method within the target object calling some other method of the target object, won't lead to an actual transaction at runtime even if the invoked method is marked with @Transactional!
可以通過配置log4j來debug Spring事務(wù)獲取情況:
To delve more into it I would turn up your log4j logging to debug and also look at what ExerciseModuleController is doing at line 91, e.g.: add a logger for org.springframework.transaction
這周被Quartz折騰了一番。
我們知道,Quartz采用JobDataMap實(shí)現(xiàn)向Job實(shí)例傳送配置屬性,正如Quartz官方文檔說的那樣:
How can I provide properties/configuration for a Job instance? The key is the JobDataMap, which is part of the JobDetail object.
The JobDataMap can be used to hold any number of (serializable) objects
which you wish to have made available to the job instance when it
executes.
JobDataMap map = context.getJobDetail().getJobDataMap();
我們通過map向Job實(shí)例傳送多個(gè)objects,其中有一個(gè)是個(gè)bean,一個(gè)是基本類型。對(duì)于scheduled triggers,我們要求bean對(duì)于所有的序列都不變,包括其屬性,而基本類型可以在Job運(yùn)行過程中改變,并影響下一個(gè)序列。實(shí)際情況是,對(duì)于下個(gè)序列,bean的屬性被上次的修改了,而基本類型卻維持第一次put到Map里面的值。正好和我們要求的相反。
受bean的影響,以為map里面包含的都是更新的對(duì)象,即每個(gè)序列里面的JobDetail是同一個(gè)對(duì)象,但是基本類型的結(jié)果否認(rèn)了這一點(diǎn)。回頭重新翻閱了下Quartz的文檔:
Now, some additional notes about a job's state data (aka JobDataMap): A
Job instance can be defined as "stateful" or "non-stateful".
Non-stateful jobs only have their JobDataMap stored at the time they
are added to the scheduler. This means that any changes made to the
contents of the job data map during execution of the job will be lost,
and will not seen by the job the next time it executes.
Job有兩個(gè)子接口:StatefulJob and InterruptableJob,我們繼承的是InterruptableJob,或許Quartz應(yīng)該有個(gè)InterruptableStatefulJob。另外StatefulJob不支持并發(fā)執(zhí)行,和我們的需求不匹配,我們有自己的同步控制,Job必須可以并發(fā)運(yùn)行。
然后查看了Quartz的相關(guān)源碼:
// RAMJobStore.storeJob
public void storeJob(SchedulingContext ctxt, JobDetail newJob,
boolean replaceExisting) throws ObjectAlreadyExistsException {
JobWrapper jw = new JobWrapper((JobDetail)newJob.clone()); // clone a new one

 .
.
jobsByFQN.put(jw.key, jw);


}
也就是說,store里面放的是初始JobDetail的克隆,在序列運(yùn)行完時(shí),只有StatefulJob才會(huì)更新store里面的JobDetail:
// RAMJobStore.triggeredJobComplete
public void triggeredJobComplete(SchedulingContext ctxt, Trigger trigger,
JobDetail jobDetail, int triggerInstCode) {
JobWrapper jw = (JobWrapper) jobsByFQN.get(jobKey);


if (jw != null) {
JobDetail jd = jw.jobDetail;
if (jd.isStateful()) {
JobDataMap newData = jobDetail.getJobDataMap();
if (newData != null) {
newData = (JobDataMap)newData.clone();
newData.clearDirtyFlag();
}
jd.setJobDataMap(newData); // set to new one




}


}
然后,每次序列運(yùn)行時(shí)所用的JobDetail,是存放在Store里面的克隆。
// RAMJobStore.retrieveJob
public JobDetail retrieveJob(SchedulingContext ctxt, String jobName,
String groupName) {
JobWrapper jw = (JobWrapper) jobsByFQN.get(JobWrapper.getJobNameKey(
jobName, groupName));
return (jw != null) ? (JobDetail)jw.jobDetail.clone() : null; // clone a new
}
問題很清楚了,存放在Store里面的JobDetail是初始對(duì)象的克隆,然后每個(gè)序列所用的JobDetail, 是Store里面的克隆,只有Stateful job,Store里面的JobDetail才更新。
最有Quartz里面使用的clone():
// Shallow copy the jobDataMap. Note that this means that if a user
// modifies a value object in this map from the cloned Trigger
// they will also be modifying this Trigger.
if (jobDataMap != null) {
copy.jobDataMap = (JobDataMap)jobDataMap.clone();
}
所以對(duì)于前面所講的,修改bean的屬性,會(huì)影響所有clone的對(duì)象,因此,我們可以將基本類型封裝到一個(gè)bean里面,map里面存放的是bean,然后通過修改bean的屬性,來達(dá)到影響下一個(gè)序列的目的。