|
|
Posted on 2009-11-10 14:02 瘋狂 閱讀(4181) 評論(2) 編輯 收藏 所屬分類: android

本文通過一個實例來學習intent的部分功能。
網上也有很多文章講解了intent的用法,自己感覺他的字面意義說到了他的精髓: “目的、意向”,也就是說通過它來告訴應用程序將要做什么,intent正是這樣,android通過Intent機制來協助應用間的交互與通訊,網上的一句話來理解:Intent有兩種基本用法:一種是顯式的Intent,即在構造Intent對象時就指定接收者,這種方式與普通的函數調用類似,只是復用的粒度有所差別;另一種是隱式的Intent,即Intent的發送者在構造Intent對象時,并不知道也不關心接收者是誰,這種方式與函數調用差別比較大,有利于降低發送者和接收者之間的耦合。另外Intent除了發送外,還可用于廣播。本文的例子正式介紹其中的顯示intent,隱式的Intent將在下一篇中學習。
實例要達到大致的效果:一個頁面顯示用戶列表,其中有一個按鈕來添加用戶。
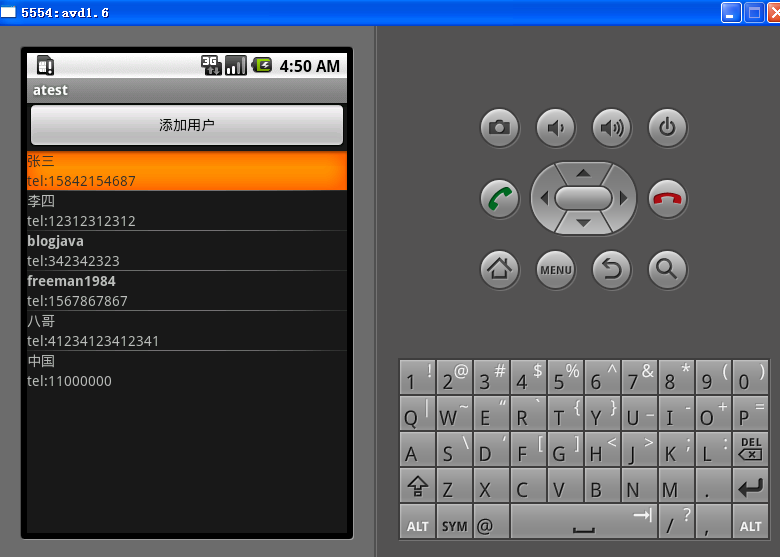
用戶列表界面:
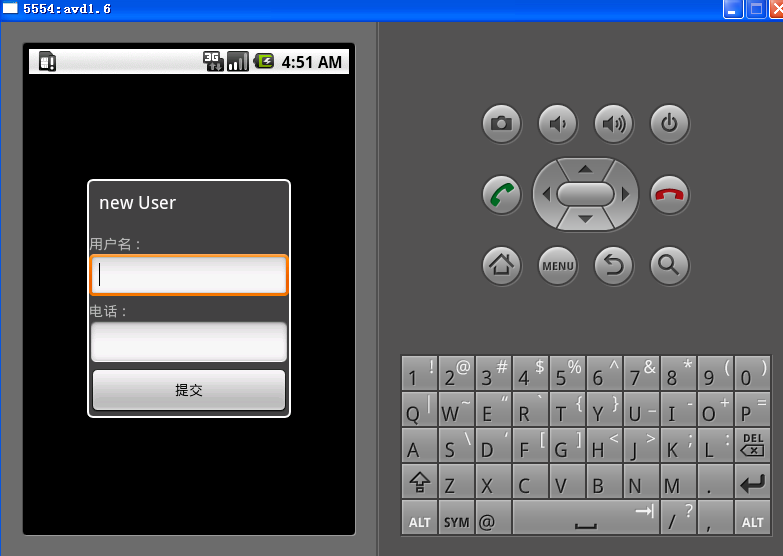
添加用戶界面:
顯示的intent需要明確他的目標Component 也就是intent必須包含具體Component的Name,什么是Component:
大致看下ComponentName源代碼:
  public final class ComponentName implements Parcelable public final class ComponentName implements Parcelable  { {
 private final String mPackage; private final String mPackage;
 private final String mClass; private final String mClass;

 構造方法: 構造方法:
 public ComponentName(String pkg, String cls) public ComponentName(String pkg, String cls)
 public ComponentName(Context pkg, String cls) public ComponentName(Context pkg, String cls)
 public ComponentName(Context pkg, Class<?> cls) public ComponentName(Context pkg, Class<?> cls)
其中有這樣的介紹:
@param pkg The name of the package that the component exists in. Can
* not be null.
* @param cls The name of the class inside of <var>pkg</var> that
* implements the component. Can not be null.
這個成員變量分別為目標的包和class的name
因此可以有三種方法夠造ComponentName 例如
new ComponentName(targetclass.class.getPackage().getName(),targetclass.class.getName()));
new ComponentName(this,targetclass.class.getName()));
new ComponentName(this,targetclass.class));
---------------------------------
這樣就構建了我們的意圖,
但是要通知目標組件實現這個意圖:
可以使用startActivity(intent)方法來啟動,但是本文使用了startActivityForResult方法,因為我們需要新打開的activity返回數據(新添加的用戶數據),
此方法的參數:startActivityForResult(Intent intent, int requestCode),
requestCode是干嘛的呢:文檔是這樣說的:
 requestCode If >= 0, this code will be returned in requestCode If >= 0, this code will be returned in
 * onActivityResult() when the activity exits. * onActivityResult() when the activity exits.
也就是說如果requestCode>0 我們就可以在目標activity返回的時候執行父窗口(官方叫做originating activity)的onActivityResult方法來處理我們的數據,我們可以使用已經定義好的requestCode,也可以自己定義,在代碼中我直接給賦值為1,正如文檔所說的,我們在用戶類表的activity里面重寫onActivityResult方法來刷新界面,以顯示新添加的用戶。
下面來看下我們的本實例的兩個activity:
首先是用戶列表activity:Test1.java:(使用到了simpleAdapter可以見于我的另外一篇文章http://www.tkk7.com/freeman1984/archive/2009/11/06/301475.html)
  public class Test1 extends Activity public class Test1 extends Activity  { {
 ArrayList<HashMap<String, String>> users = new ArrayList<HashMap<String, String>>(); ArrayList<HashMap<String, String>> users = new ArrayList<HashMap<String, String>>();

  /** *//** Called when the activity is first created. */ /** *//** Called when the activity is first created. */
 @Override @Override
  public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)  { {
 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
 setContentView(R.layout.main); setContentView(R.layout.main);
 final Button adduser = (Button)findViewById(R.id.Button01); final Button adduser = (Button)findViewById(R.id.Button01);
  adduser.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() adduser.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() { {

  public void onClick(View v) public void onClick(View v)  { {
 Intent addnew = new Intent(); Intent addnew = new Intent();
 addnew.setComponent(new ComponentName(Test1.this,Test2.class)); addnew.setComponent(new ComponentName(Test1.this,Test2.class));
 startActivityForResult(addnew, 1);//通知打開新建用戶界面 ,requestCode>0就行 startActivityForResult(addnew, 1);//通知打開新建用戶界面 ,requestCode>0就行
 }}); }});
 initUser();//初始化界面上顯示一個用戶 initUser();//初始化界面上顯示一個用戶
 updateList();//顯示列表 updateList();//顯示列表
 } }
  private void initUser() private void initUser()  { {
 HashMap<String, String> user = new HashMap<String, String>(); HashMap<String, String> user = new HashMap<String, String>();
 user.put("name", "張三"); user.put("name", "張三");
 user.put("phonenum", "tel:15842154687"); user.put("phonenum", "tel:15842154687");
 users.add(user); users.add(user);
 } }
  private void updateList() private void updateList()  { {
 SimpleAdapter saImageItems = new SimpleAdapter(this, SimpleAdapter saImageItems = new SimpleAdapter(this,
 users,// 數據來源 users,// 數據來源
 R.layout.user,//每一個user xml 相當ListView的一個組件 R.layout.user,//每一個user xml 相當ListView的一個組件
  new String[] new String[]  {"name", "phonenum" }, {"name", "phonenum" },
 // 分別對應view 的id // 分別對應view 的id
  new int[] new int[]  { R.id.name, R.id.phonenum}); { R.id.name, R.id.phonenum});
 // 獲取listview // 獲取listview
 ((ListView) findViewById(R.id.userlist)).setAdapter(saImageItems); ((ListView) findViewById(R.id.userlist)).setAdapter(saImageItems);
 } }



 @Override @Override
  protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, Intent data) protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, Intent data)  {//重寫回調方法 將新用戶添加到列表中,并刷新界面 {//重寫回調方法 將新用戶添加到列表中,并刷新界面
 // TODO Auto-generated method stub // TODO Auto-generated method stub
 super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data); super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data);
 Bundle newuser = data.getExtras(); Bundle newuser = data.getExtras();
 String name = newuser.getString("name"); String name = newuser.getString("name");
 String phonenum = newuser.getString("phonenum"); String phonenum = newuser.getString("phonenum");
 HashMap<String, String> user = new HashMap<String, String>(); HashMap<String, String> user = new HashMap<String, String>();
 user.put("name", name); user.put("name", name);
 user.put("phonenum", "tel:"+phonenum); user.put("phonenum", "tel:"+phonenum);
 Log.d("Test1", "phonenum:"+phonenum); Log.d("Test1", "phonenum:"+phonenum);
 users.add(user); users.add(user);
 updateList(); updateList();
 } }
 } }
新建用戶activity Test2.java
  public class Test2 extends Activity public class Test2 extends Activity  { {
  /** *//** Called when the activity is first created. */ /** *//** Called when the activity is first created. */
 EditText newname; EditText newname;
 EditText newphone; EditText newphone;
 Button submitbn; Button submitbn;
 @Override @Override
  public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)  { {
 setTheme(android.R.style.Theme_Dialog); setTheme(android.R.style.Theme_Dialog);
 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
 setContentView(R.layout.newuser); setContentView(R.layout.newuser);
 setTitle("new User"); setTitle("new User");
 newname = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.newname); newname = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.newname);
 newphone = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.newphone); newphone = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.newphone);
 submitbn = (Button)findViewById(R.id.submitbn); submitbn = (Button)findViewById(R.id.submitbn);
  submitbn.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() submitbn.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() { {

  public void onClick(View v) public void onClick(View v)  { {
 Intent submiti = new Intent(); Intent submiti = new Intent();
 submiti.setComponent(new ComponentName(Test2.this,Test1.class)); submiti.setComponent(new ComponentName(Test2.this,Test1.class));
 Bundle user = new Bundle(); Bundle user = new Bundle();
 user.putString("name", newname.getText().toString()); user.putString("name", newname.getText().toString());
 user.putString("phonenum", newphone.getText().toString()); user.putString("phonenum", newphone.getText().toString());
 submiti.putExtras(user); submiti.putExtras(user);
 setResult(RESULT_OK, submiti);//返回正確 setResult(RESULT_OK, submiti);//返回正確
 finish();//此方法將會根據resultCode來處理如何關閉acticity finish();//此方法將會根據resultCode來處理如何關閉acticity
 }}); }});


 } }
 } }
本文大致介紹了下顯示的intent 將在下一篇中看看隱式的intent,也就是intent的其他成員變量的使用:intent主要的成員變量如下:
 private String mAction; private String mAction;
 private Uri mData; private Uri mData;
 private String mType; private String mType;
 private ComponentName mComponent; private ComponentName mComponent;
 private int mFlags; private int mFlags;
 private HashSet<String> mCategories; private HashSet<String> mCategories;
 private Bundle mExtras; private Bundle mExtras;
希望高手指點,共同學習~!
評論
# re: android學習之 intent 實例[未登錄] 回復 更多評論
2009-11-10 16:20 by
學習了!
# re: android學習之 intent 實例 回復 更多評論
2010-01-27 16:05 by
LZ通過代碼學習的方面很見功力啊! PFPF.
|