一.歸并排序的思路
①把 n 個記錄看成 n 個長度為 l 的有序子表;
②進行兩兩歸并使記錄關鍵字有序,得到 n/2 個長度為 2 的有序子表;
③重復第②步直到所有記錄歸并成一個長度為 n 的有序表為止。
二.歸并排序算法實例
對于歸并排序算法這類的分治算法,其核心就是"分解"和"遞歸求解"。對于"分解"實例,會在下面分析msort()方法中給出。我們先看合并的過程。
以下面描述的序列為例,在索引范圍內[first , last)的序列還有九個整數元素,它由索引范圍為[first , mid]的四個元素有序子列表A和索引范圍[mid , last]的五個元素有序子列表B組成。
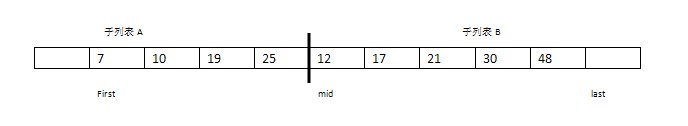
步驟1:比較arr[indexA]=7與arr[indexB]=12。將較小的元素7復制到數組tempArr的索引indexC處。并將indexA和indexC都指向下一個位置。
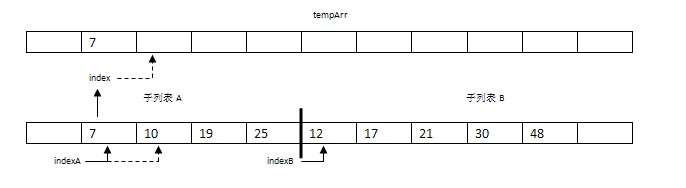
步驟2:比較arr[indexA]=10與arr[indexB]=12。將較小的元素10復制到數組tempArr的索引indexC處。并將indexA和indexC都指向下一個位置。
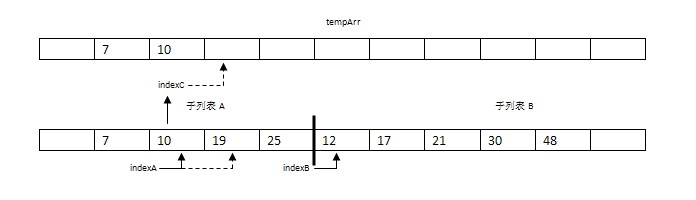
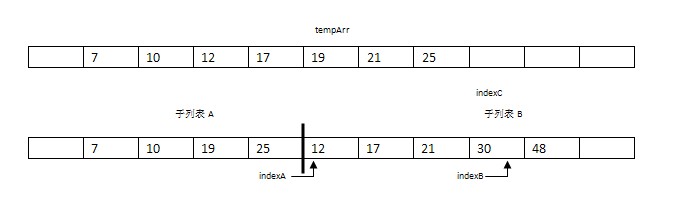
步驟3:比較arr[indexA]=19與arr[indexB]=12。將較小的元素12復制到數組tempArr的索引indexC處。并將indexB和indexC都指向下一個位置。
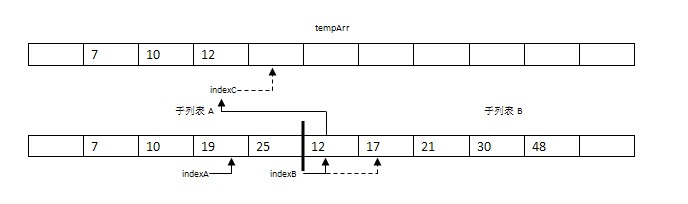
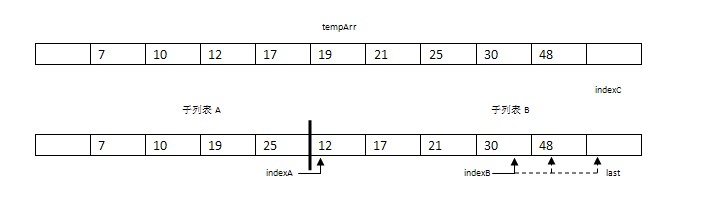
步驟4-7:依次成對比較兩子表的元素將17,19,21,25復制到數組tempArr。此時,indexA到達子表A的未尾(indexA = mid),indexB引用的值為30。
步驟8-9:將未到尾部的子表剩余數據復制到tempArr中。
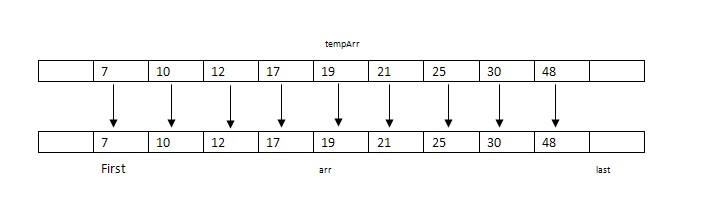
步驟10:將tempArr復制到原始數據arr中。
三.歸并排序算法的實現
了解了合并過程,那么理解下面的代碼并不是一件難事。下面提供了歸并算法的非泛型版本和泛型版本。

 public class MergeSort
public class MergeSort  {
{


 public static void sort(Object[] arr)
public static void sort(Object[] arr)  {
{
 //create a temporary array to store partitioned elements
//create a temporary array to store partitioned elements
 Object[] tempArr = arr.clone();
Object[] tempArr = arr.clone();

 //call msort with arrays arr and tempArr along
//call msort with arrays arr and tempArr along
 //with the index range
//with the index range
 msort(arr, tempArr, 0, arr.length);
msort(arr, tempArr, 0, arr.length);
 }
}


 public static <T extends Comparable<? super T>> void sort(T[] arr)
public static <T extends Comparable<? super T>> void sort(T[] arr)  {
{
 //create a temporary aray to store partitioned elements
//create a temporary aray to store partitioned elements
 T[] tempArr = (T[]) arr.clone();
T[] tempArr = (T[]) arr.clone();

 //call msort with arrays arr and tempArr along
//call msort with arrays arr and tempArr along
 //with the index range
//with the index range
 msort(arr, tempArr, 0, arr.length);
msort(arr, tempArr, 0, arr.length);
 }
}

 private static void msort(Object[] arr, Object[] tempArr, int first,
private static void msort(Object[] arr, Object[] tempArr, int first,

 int last)
int last)  {
{
 //if the sublist has more than 1 element continue
//if the sublist has more than 1 element continue

 if (first + 1 < last)
if (first + 1 < last)  {
{
 //for sublists of size 2 or more, call msort()
//for sublists of size 2 or more, call msort()
 //for the left and right sublists and than
//for the left and right sublists and than
 //merge the sorted sublists using merge()
//merge the sorted sublists using merge()
 int midpt = (last + first) / 2;
int midpt = (last + first) / 2;

 msort(arr, tempArr, first, midpt);
msort(arr, tempArr, first, midpt);
 msort(arr, tempArr, midpt, last);
msort(arr, tempArr, midpt, last);

 //if list is already sorted, just copy src to
//if list is already sorted, just copy src to
 //dest; this is an optimization that results in faster
//dest; this is an optimization that results in faster
 //sorts for nearly ordered lists
//sorts for nearly ordered lists
 if (((Comparable) arr[midpt - 1]).compareTo(arr[midpt]) <= 0)
if (((Comparable) arr[midpt - 1]).compareTo(arr[midpt]) <= 0)
 return;
return;
 //the elements in the ranges [first,mid] and
//the elements in the ranges [first,mid] and
 //[mid,last] are ordered;merge the ordered sublists
//[mid,last] are ordered;merge the ordered sublists
 //into an ordered sequence in the range [first , last]
//into an ordered sequence in the range [first , last]
 //using the temporary array
//using the temporary array
 int indexA, indexB, indexC;
int indexA, indexB, indexC;

 //set indexA to scan sublist A with rang [first , mid]
//set indexA to scan sublist A with rang [first , mid]
 //and indexB to scan sublist B with rang [mid , last]
//and indexB to scan sublist B with rang [mid , last]
 indexA = first;
indexA = first;
 indexB = midpt;
indexB = midpt;
 indexC = first;
indexC = first;

 //while both sublists are not exhausted, compare
//while both sublists are not exhausted, compare
 //arr[indexA] and arr[indexB]; copy the smaller
//arr[indexA] and arr[indexB]; copy the smaller
 //to tempArr
//to tempArr

 while (indexA < midpt && indexB < last)
while (indexA < midpt && indexB < last)  {
{

 if (((Comparable) arr[indexA]).compareTo(arr[indexB]) < 0)
if (((Comparable) arr[indexA]).compareTo(arr[indexB]) < 0)  {
{
 tempArr[indexC] = arr[indexA]; //copyto tempArr
tempArr[indexC] = arr[indexA]; //copyto tempArr
 indexA++; //increment indexA
indexA++; //increment indexA

 } else
} else  {
{
 tempArr[indexC] = arr[indexB]; //copyto tempArr
tempArr[indexC] = arr[indexB]; //copyto tempArr
 indexB++; //increment indexB
indexB++; //increment indexB
 }
}
 indexC++; //increment indexC
indexC++; //increment indexC
 }
}
 //copy the tail of the sublist that is not exhausted
//copy the tail of the sublist that is not exhausted

 while (indexA < midpt)
while (indexA < midpt)  {
{
 tempArr[indexC++] = arr[indexA++]; //copy to tempArr
tempArr[indexC++] = arr[indexA++]; //copy to tempArr

 } while (indexB < last)
} while (indexB < last)  {
{
 tempArr[indexC++] = arr[indexB++]; //copy to tempArr
tempArr[indexC++] = arr[indexB++]; //copy to tempArr
 }
}
 //copy elements form temporary array to original array
//copy elements form temporary array to original array
 for (int i = first; i < last; i++)
for (int i = first; i < last; i++)
 arr[i] = tempArr[i];
arr[i] = tempArr[i];
 }
}
 }
}
 }
}
上述代碼中最核心的msort()方法是一遞歸算法。下圖說明了msort()方法中子列表的分割與合并。
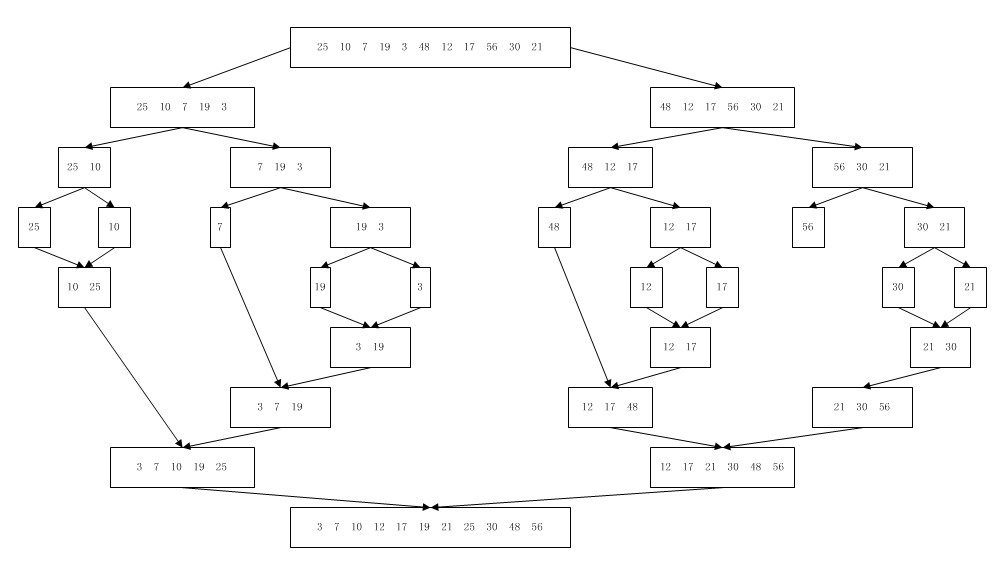
四.歸并排序算法的效率
歸并排序的最壞情況與平均情況運行時間都為O(nlog
2n)。假定數組具有n=2
k個元素。如下圖:
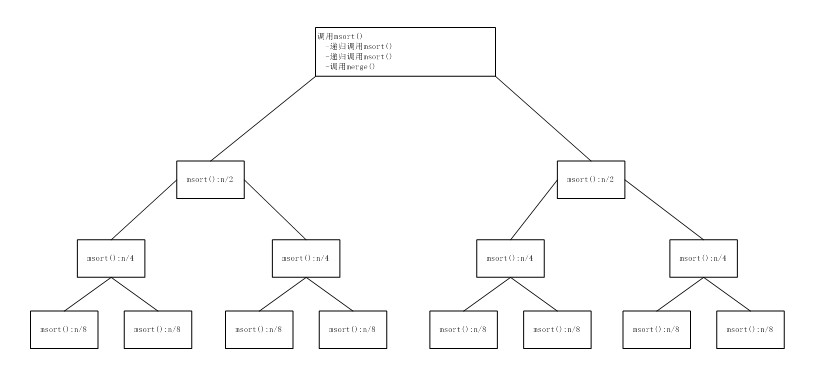
在層數0上對msort()方法的第一個調用會產生兩個遞歸調用,這兩個遞歸調用產生長度為n/2的兩個半部分列表,而merge()方法將上述兩個半部分列表組合的一個有序的n元素列表;在層數1上存在兩個msort()方法的調用,每個調用又會產生另外兩個對長度為n/4的列表的遞歸調用。每個合并會將兩個長度為n/4的子列表連接為一個長度為n/2的有序列表;在層數2上存在對merge()方法的4=2
2個調用,每個調用會創建一個長度為n/4的有序列表。通常,在層數i上存在對merge()方法的2
i個調用,每個調用會創建一個長度為n/2
i的有序子列表。
層數0:存在對merge()方法的1=2
0次調用。這個調用對n個元素排序。
層數1:存在對merge()方法的2=2
1次調用。這個調用對n/2個元素排序。
層數2:存在對merge()方法的4=2
2次調用。這個調用對n/4個元素排序。
......
層數i:存在對merge()方法的2
i次調用。這個調用對n/i個元素排序。
在樹中的每一層,合并涉及具有線性運行時間的n/2
i個元素,這個線性運行時間需要少于n/2
i次的比較。在層數i上組合的2
i個合并操作需要少于2
i*n/2
i=n次的比較。假定n=2
k,分割過程會在n/2
k=1的k層數上終止。那么所有層上完成的工作總量為:k*n = nlog
2n。因此msort()方法的最壞情況效率為O(nlog
2n)。