MVC
MVC含義
一種軟件構(gòu)架,簡(jiǎn)單的說就是在做軟件的時(shí)候,可以將軟件分為不同的模塊,不同的模塊實(shí)現(xiàn)了不同功能。
MVC 組成部分
Model 模型
View 視圖
Controller 控制器
MVC就是三種組成部分的縮寫。
MVC 不同模塊的功能
Model(模型層) 程序員編寫程序應(yīng)用的功能,數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)設(shè)計(jì)等。屬于后臺(tái)操作。
View (視圖層) 前臺(tái)界面,也就是用戶可以看到的圖形見面,一般在web中是一些*.jsp或*.html。
Controller(控制器) 處理前臺(tái)和后臺(tái)請(qǐng)求。
MVC 優(yōu)點(diǎn)
采用MVC的優(yōu)點(diǎn)太多了,說再多不如你在真正的項(xiàng)目中自己體會(huì),在這里不做太多解釋。
MVC 包結(jié)構(gòu)
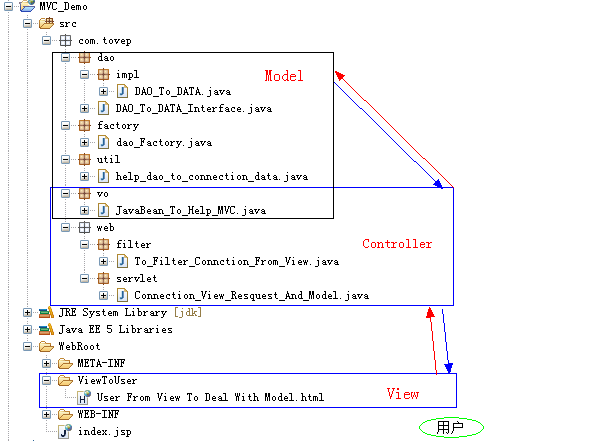
雖然,這并不能說明所有MVC框架所有的包模式,不過我覺得新手對(duì)于這個(gè)包結(jié)構(gòu)還是比較容易接受的。
DAO 模式
在DAO層,最主要的作用是:完成數(shù)據(jù)的操作。在這層,你可以完成對(duì)任何表的數(shù)據(jù)操作,不過個(gè)人認(rèn)為DAO層最大的作用是簡(jiǎn)單了編程人員的編程邏輯,簡(jiǎn)單的說就是將一個(gè)大的問題,分成了幾個(gè)比較小的問題,這樣不管在測(cè)試還是在維護(hù)都起著很大的方便。
Factory 工廠
Factory 工廠在這里也可以說成是DAO的工廠,這里Factory僅僅產(chǎn)生了DAO。那么Factory工廠模式有什么好處呢?
在MVC中的Factory 層,你完全可以把它想象成現(xiàn)實(shí)中的工廠,生產(chǎn)某些東西,如果在程序中使用工廠模式,你可以簡(jiǎn)化編程代碼,相當(dāng)與現(xiàn)實(shí)中你需要某個(gè)產(chǎn)品不需要自己去生產(chǎn),完全可以去工廠“拿”一個(gè),這樣程序的編程更加符合現(xiàn)實(shí)中的邏輯。
MVC 總結(jié)
本節(jié),我僅僅是將MVC的編輯思想簡(jiǎn)單的介紹了一下,我沒有加入一些詳細(xì)的例子,因?yàn)槲矣X得你在接觸MVC的時(shí)候,最好先了解MVC的編程思想,如果你要了解MVC的編程思想之后,你再接觸MVC的編程時(shí),你就會(huì)覺得特別簡(jiǎn)單。
最后,希望我這篇文章可以讓大家簡(jiǎn)單的了解MVC的編程模式。
摘要: ForEach小結(jié)
<c:forEach>標(biāo)簽具有以下一些屬性:
var:迭代參數(shù)的名稱。在迭代體中可以使用...
閱讀全文
通過以下Servlet程序和web.xml來說明web.xml的配置以及過程
創(chuàng)建一個(gè)Login的HTML文件
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<title>login.html</title>
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="this is my page">
<meta http-equiv="content-type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
</head>
<body>
<form action="
test1" method="
post">
<table border="0" width="379" height="79">
<tr>
<td>帳號(hào):</td>
<td><input type="text" name="username"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>密碼:</td>
<td><input type="password" name="password"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td colspan="5" align="center"><input type="submit" value="登錄"></td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
</body>
</html>
以上HTML標(biāo)簽中要說明的是:
<form>標(biāo)簽中的
action="test_Web_xml" 和 method="post" 分別定義了Html將登陸的信息發(fā)送給了誰(shuí),以及發(fā)送信息的方法!
創(chuàng)建一個(gè)Servlet程序
public class LoginServlet extends HttpServlet{
public void
doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
String username = null;
username = request.getParameter("username");
String password = null;
password = request.getParameter("password");
if(username.equals("username")&&password.equals("password")){
request.getRequestDispatcher("成功登陸!!!").forward(request,response);
}else{
request.getRequestDispatcher("登陸失敗!!!").forward(request,response);
}
}
}
web.xml配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app version="2.5"
xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee
http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd">
<servlet>
<servlet-name>
Login
</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>
com.rise.LoginServlet
</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>
Login
</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>
/test1
</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file>
</welcome-file-list>
</web-app>
我理解web.xml的作用就是將頁(yè)面和后臺(tái)程序正確連接!!!
通過一張圖片說明我理解的web.xml的作用
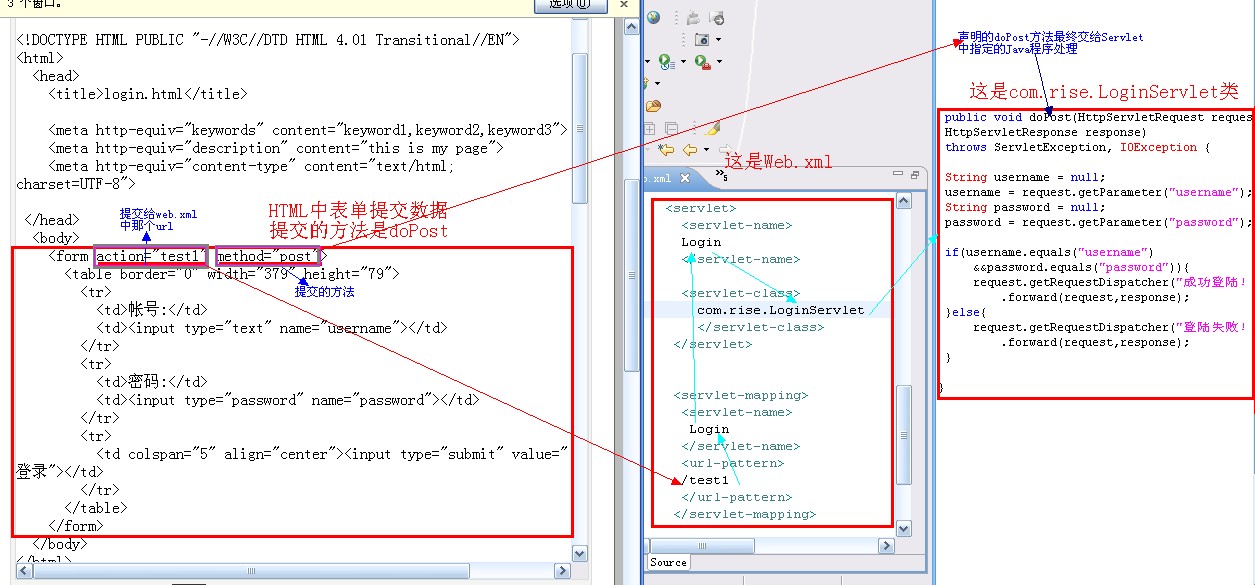
以上的內(nèi)容是我自己對(duì)web.xml的理解,我覺得很簡(jiǎn)單,但真正寫程序的時(shí)候部署程序是非常復(fù)雜的!