JDOM因其簡潔易用易懂的API而被廣泛的使用。JDOM常用的核心類及它們間的關系如下圖所示:
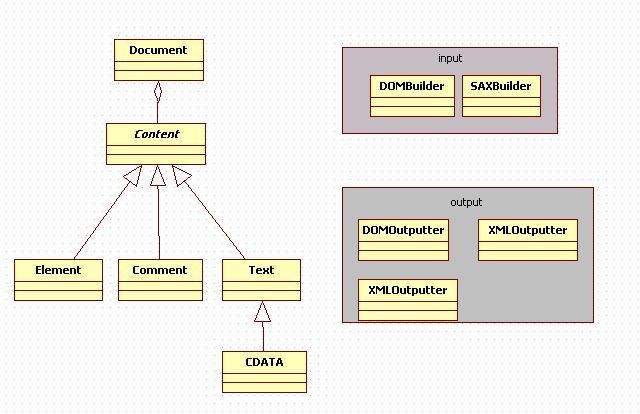
Document代表了文檔對象�����,抽象類Content表示文檔中的內容元素�����,各種內容組成了文檔對象。常用的內容元素有xml元素Element、xml注釋Comment、文本Text��。下面以如下片段來說明各類的含義��。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<customers>
<customer>
<name>徐辛波</name>
<occupation>developer</occupation>
<!-- comment:following is contact info -->
<contact>
<email>sinpo.xu@hotmail.com</email>
<mobile>15029357227</mobile>
<fix-phone>02985457683</fix-phone>
</contact>
</customer>
</customers>
上述文檔用Document來抽象�����;customers為文檔的根元素(root element ),Element即一個封閉起來的元素,element元素可以有子元素��,如<mobile>15029357227</mobile>是一個元素���,而<contact>...</contact>也是一個元素���,甚至<customers>...</customers>也是一個大元素���;<!-- ... -->代表了xml中注釋�����,注釋在JDOM中用Comment類來抽象;Text代表了xml中的文本值�����,如元素屬性的值、元素的值���、注釋的內容等,父元素的Text為子元素和值組成的串,使用Text類可以方便的表示一些特殊字符,如:
Element element = new Element("name");
Text text = new Text("AAA.<�����、BBB/>.<CCC>");
element.addContent(text);
值得一提的是Element的方法addContent(Content content),因參數是抽象父類Content�����,所以可以添加Text�����、Element和Comment等,如果添加的是Text則自動作為element的文本值,如果是Element則作為element的子元素���,如果是Comment則作為element的注釋,使用十分方便。元素的值如<name>徐辛波</name>中的“徐辛波”也是一個和元素平行的Content對象(Text對象),當使用Element的getDescendants()方法時將返回一個該元素所有后代的迭代器,這些后代包括Element�����、Comment��、Text等�����,如元素<contact>的后代包括email�����、mobile���、fix-phone三個元素以及這三個元素的Text共6個后代��,如果計算后代時有父子嵌套則應注意,父元素作為一個后代���,其嵌套的子元素作為另一個后代。
剛才提到核心類都包含在org.jdom包下���,jdom還包含了org.jdom.input和org.jdom.output兩個包分別來處理xml內容的輸入輸出。當要讀取xml資源時我們通常使用input包下的SAXBuilder類從輸入流構建dom對象�����,當資源加載后常用的做法是在內存中緩存��,這樣后續的查找修改等操作就非?����?臁N臋n加載后內存的中各個元素是記錄有各自的位置和關系的���,即保持有上下文環境的。如果想要刪除一段內容(Element Comment Text)��,只用調用該內容的detach方法即可���,這樣元素即和文檔脫離關系了�����,再對文檔進行遍歷或者持久化到磁盤上時游離的元素就不可見了。Jdom的輸出類包括XMLOutputter、DOMOutputter��、SAXOutputter��。最常用的是XMLOutputter���,通過它可以將dom對象輸出到指定的輸出流�����,并且可以指定所輸出xml文件的格式���,比如縮進的樣式等��。DOMOutputter輸出org.w3c.dom.Document對象,用于JDOM對象同w3c dom對象轉換���,SAXOutputter可以注冊回調函數來處理相應的sax事件。
一下示例代碼實現一個常用的讀取配置文件并且允許更改后同步到磁盤的操作:
package sinpo.usagedemo;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.List;
import org.jdom.Document;
import org.jdom.Element;
import org.jdom.input.SAXBuilder;
import org.jdom.output.Format;
import org.jdom.output.XMLOutputter;
/**
* 讀取配置文件�����,并且修改后及時同步到磁盤
* @author 徐辛波(sinpo.xu@hotmail.com)
* Oct 23, 2008
*/
public class Configuration {
private Element root = null;
private Document dom = null;
private static final String resourceName = "/config.xml";
private static Configuration _INSTANCE = null;
public static synchronized Configuration getInstance() {
if (_INSTANCE == null) {
_INSTANCE = new Configuration();
}
return _INSTANCE;
}
private Configuration() {
load();
}
public String getConfig(String configName) {
String configValue = null;
Element found = findRecursively(configName, root);
if (found != null) {
configValue = found.getText();
}
return configValue;
}
public void updateConfig(String configName, String newValue)
throws IOException {
Element found = findRecursively(configName, root);
if (found != null) {
found.setText(newValue);
} else {
Element configNode = new Element(configName);
configNode.addContent(newValue);
// also: configNode.setText(newValue);
root.addContent(configNode);
}
sync();
}
public void deleteConfig(String configName) throws IOException {
Element found = findRecursively(configName, root);
if (found != null) {
found.detach();
}
sync();
}
private void load() {
SAXBuilder builder = new SAXBuilder();
InputStream source = getClass().getResourceAsStream(resourceName);
try {
dom = builder.build(source);
root = dom.getRootElement();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 遞歸查找. 在指定的父節點下查找葉子元素
private Element findRecursively(String name, Element parent) {
Element found = null;
List<Element> children = parent.getChildren();
if (children != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < children.size(); i++) {
Element element = children.get(i);
String tmpName = element.getName();
if ((name.equals(tmpName)) && (!hasChild(element))) {
return element;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < children.size(); i++) {
Element element = children.get(i);
if (hasChild(element)) {
found = findRecursively(name, element);
if (found != null) {
return found;
}
}
}
}
return found;
}
private boolean hasChild(Element element) {
boolean hasChild = false;
List children = element.getChildren();
if ((children != null) && (children.size() > 0)) {
hasChild = true;
}
return hasChild;
}
private void sync() throws IOException {
Format format = Format.getPrettyFormat();
XMLOutputter outputter = new XMLOutputter(format);
File file = null;
URL url = getClass().getResource(resourceName);
if (url == null) {
file = new File(resourceName);
} else {
file = new File(url.getPath());
OutputStream out = null;
try {
out = new FileOutputStream(file);
outputter.output(dom, out);
out.close();
out = null;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
if (out != null) {
out.close();
}
}
}
}
} |