原文地址:http://linliangyi2007.javaeye.com/blog/166314
Web Service概述
Web Service的定義
W3C組織對(duì)其的定義如下,它是一個(gè)軟件系統(tǒng),為了支持跨網(wǎng)絡(luò)的機(jī)器間相互操作交互而設(shè)計(jì)。Web Service服務(wù)通常被定義為一組模塊化的API,它們可以通過(guò)網(wǎng)絡(luò)進(jìn)行調(diào)用,來(lái)執(zhí)行遠(yuǎn)程系統(tǒng)的請(qǐng)求服務(wù)。
這里我們從一個(gè)程序員的視角來(lái)觀察web service。在傳統(tǒng)的程序編碼中,存在這各種的函數(shù)方法調(diào)用。通常,我們知道一個(gè)程序模塊M中的方法A,向其發(fā)出調(diào)用請(qǐng)求,并傳入A方法需要的參數(shù)P,方法A執(zhí)行完畢后,返回處理結(jié)果R。這種函數(shù)或方法調(diào)用通常發(fā)生在同一臺(tái)機(jī)器上的同一程序語(yǔ)言環(huán)境下。現(xiàn)在的我們需要一種能夠在不同計(jì)算機(jī)間的不同語(yǔ)言編寫的應(yīng)用程序系統(tǒng)中,通過(guò)網(wǎng)絡(luò)通訊實(shí)現(xiàn)函數(shù)和方法調(diào)用的能力,而Web service正是應(yīng)這種需求而誕生的。
最普遍的一種說(shuō)法就是,Web Service = SOAP + HTTP + WSDL。其中,SOAP Simple Object Access Protocol)協(xié)議是web service的主體,它通過(guò)HTTP或者SMTP等應(yīng)用層協(xié)議進(jìn)行通訊,自身使用XML文件來(lái)描述程序的函數(shù)方法和參數(shù)信息,從而完成不同主機(jī)的異構(gòu)系統(tǒng)間的計(jì)算服務(wù)處理。這里的WSDL(Web Services Description Language)web 服務(wù)描述語(yǔ)言也是一個(gè)XML文檔,它通過(guò)HTTP向公眾發(fā)布,公告客戶端程序關(guān)于某個(gè)具體的 Web service服務(wù)的URL信息、方法的命名,參數(shù),返回值等。
下面,我們先來(lái)熟悉一下SOAP協(xié)議,看看它是如何描述程序中的函數(shù)方法、參數(shù)及結(jié)果對(duì)象的。
SOAP協(xié)議簡(jiǎn)介
什么是SOAP
SOAP 指簡(jiǎn)單對(duì)象訪問(wèn)協(xié)議,它是一種基于XML的消息通訊格式,用于網(wǎng)絡(luò)上,不同平臺(tái),不同語(yǔ)言的應(yīng)用程序間的通訊。可自定義,易于擴(kuò)展。一條 SOAP 消息就是一個(gè)普通的 XML 文檔,包含下列元素:
• Envelope 元素,標(biāo)識(shí)XML 文檔一條 SOAP 消息
• Header 元素,包含頭部信息的XML標(biāo)簽
• Body 元素,包含所有的調(diào)用和響應(yīng)的主體信息的標(biāo)簽
• Fault 元素,錯(cuò)誤信息標(biāo)簽。
以上的元素都在 SOAP的命名空間http://www.w3.org/2001/12/soap-envelope中聲明;
SOAP的語(yǔ)法規(guī)則
• SOAP 消息必須用 XML 來(lái)編碼
• SOAP 消息必須使用 SOAP Envelope 命名空間
• SOAP 消息必須使用 SOAP Encoding 命名空間
• SOAP 消息不能包含 DTD 引用
• SOAP 消息不能包含 XML 處理指令
SOAP 消息的基本結(jié)構(gòu)
<? xml version="1.0"?>
<soap:Envelope xmlns:soap="http://www.w3.org/2001/12/soap-envelope"
soap:encodingStyle="http://www.w3.org/2001/12/soap-encoding">
<soap:Header>


</soap:Header>
<soap:Body>


<soap:Fault>


</soap:Fault>
</soap:Body>
</soap:Envelope>
SOAP Envelope 元素
Envelope 元素是 SOAP 消息的根元素。它指明 XML 文檔是一個(gè)SOAP 消息。它的屬性 xmlns:soap的值必須是http://www.w3.org/2001/12/soap-envelope。
? encodingStyle 屬性,語(yǔ)法:soap:encodingStyle="URI"
encodingStyle 屬性用于定義文檔中使用的數(shù)據(jù)類型。此屬性可出現(xiàn)在任何 SOAP 元素中,并會(huì)被應(yīng)用到元素的內(nèi)容及元素的所有子元素上。
<? xml version="1.0"?>
<soap:Envelope
xmlns:soap="http://www.w3.org/2001/12/soap-envelope"
soap:encodingStyle="http://www.w3.org/2001/12/soap-encoding">

Message information goes here

</soap:Envelope>
SOAP Header 元素
- actor 屬性,語(yǔ)法soap:actor="URI"
通過(guò)沿著消息路徑經(jīng)過(guò)不同的端點(diǎn),SOAP 消息可從某個(gè)發(fā)送者傳播到某個(gè)接收者。并非 SOAP 消息的所有部分均打算傳送到 SOAP 消息的最終端點(diǎn),不過(guò),另一個(gè)方面,也許打算傳送給消息路徑上的一個(gè)或多個(gè)端點(diǎn)。SOAP 的 actor 屬性可被用于將 Header 元素尋址到一個(gè)特定的端點(diǎn)。
- mustUnderstand 屬性 ,語(yǔ)法soap:mustUnderstand="0|1"
SOAP 的 mustUnderstand 屬性可用于標(biāo)識(shí)標(biāo)題項(xiàng)對(duì)于要對(duì)其進(jìn)行處理的接收者來(lái)說(shuō)是強(qiáng)制的還是可選的。假如您向 Header 元素的某個(gè)子元素添加了 "mustUnderstand="1",則要求處理此頭部的接收者必須認(rèn)可此元素。
<? xml version="1.0"?>
<soap:Envelope xmlns:soap="http://www.w3.org/2001/12/soap-envelope"
soap:encodingStyle="http://www.w3.org/2001/12/soap-encoding">
<soap:Header>
<m:Trans xmlns:m="http://www.jsoso.net/transaction/" soap:mustUnderstand="1"
soap:actor="http://www.w3schools.com/appml/">234</m:Trans>
</soap:Header>


</soap:Envelope>
SOAP Body 元素
必需的 SOAP Body 元素可包含打算傳送到消息最終端點(diǎn)的實(shí)際 SOAP 消息。Body元素中既可以包含SOAP定義的命名空間中的元素,如Fault,也可以是用戶的應(yīng)用程序自定義的元素。以下是一個(gè)用戶定義的請(qǐng)求:
<? xml version="1.0"?>
<soap:Envelope
xmlns:soap="http://www.w3.org/2001/12/soap-envelope"
soap:encodingStyle="http://www.w3.org/2001/12/soap-encoding">
<soap:Body>
<m:GetPrice xmlns:m="http://www.jsoso.net/prices">
<m:Item>Apples</m:Item>
</m:GetPrice>
</soap:Body>
</soap:Envelope>
上面的例子請(qǐng)求蘋果的價(jià)格。請(qǐng)注意,上面的 m:GetPrice 和 Item 元素是應(yīng)用程序?qū)S玫脑亍K鼈儾⒉皇?SOAP 標(biāo)準(zhǔn)的一部分。而對(duì)應(yīng)的 SOAP 響應(yīng)應(yīng)該類似這樣:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<soap:Envelope
xmlns:soap="http://www.w3.org/2001/12/soap-envelope"
soap:encodingStyle="http://www.w3.org/2001/12/soap-encoding">
<soap:Body>
<m:GetPriceResponse xmlns:m="http://www.jsoso.net/prices">
<m:Price>1.90</m:Price>
</m:GetPriceResponse>
</soap:Body>
</soap:Envelope>
SOAP Fault 元素
Fault 元素表示 SOAP的錯(cuò)誤消息。它必須是 Body 元素的子元素,且在一條 SOAP 消息中,F(xiàn)ault 元素只能出現(xiàn)一次。Fault 元素?fù)碛邢铝凶釉兀?


常用的SOAP Fault Codes


 HTTP協(xié)議中的SOAP 實(shí)例
HTTP協(xié)議中的SOAP 實(shí)例
下面的例子中,一個(gè) GetStockPrice 請(qǐng)求被發(fā)送到了服務(wù)器。此請(qǐng)求有一個(gè) StockName 參數(shù),而在響應(yīng)中則會(huì)返回一個(gè) Price 參數(shù)。此功能的命名空間被定義在此地址中: "http://www.jsoso.net/stock"
- SOAP 請(qǐng)求:(注意HTTP的Head屬性)
POST /InStock HTTP/1.1
Host: www.jsoso.net
Content-Type: application/soap+xml; charset=utf-8
Content-Length: XXX
<? xml version="1.0"?>
<soap:Envelope
xmlns:soap="http://www.w3.org/2001/12/soap-envelope"
soap:encodingStyle="http://www.w3.org/2001/12/soap-encoding">
<soap:Body xmlns:m="http://www.jsoso.net/stock">
<m:GetStockPrice>
<m:StockName>IBM</m:StockName>
</m:GetStockPrice>
</soap:Body>
</soap:Envelope>
- SOAP 響應(yīng):(注意HTTP的Head屬性)
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/soap+xml; charset=utf-8
Content-Length: XXX
<? xml version="1.0"?>
<soap:Envelope
xmlns:soap="http://www.w3.org/2001/12/soap-envelope"
soap:encodingStyle="http://www.w3.org/2001/12/soap-encoding">
<soap:Body xmlns:m="http://www.jsoso.net/stock">
<m:GetStockPriceResponse>
<m:Price>34.5</m:Price>
</m:GetStockPriceResponse>
</soap:Body>
</soap:Envelope>
HTTP協(xié)議中的SOAP RPC工作流程

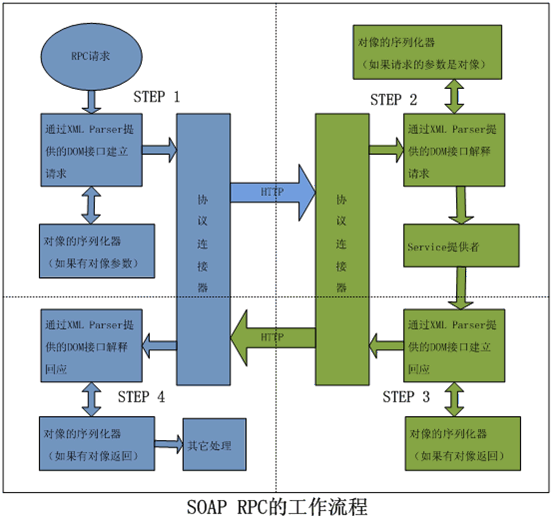 WSDL簡(jiǎn)介
WSDL簡(jiǎn)介
介紹過(guò)了SOAP,讓我們關(guān)注Web Service中另外一個(gè)重要的組成WSDL。
WSDL的主要文檔元素

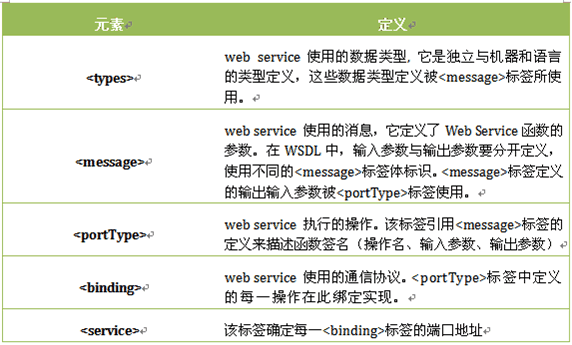
WSDL文檔可以分為兩部分。頂部分由抽象定義組成,而底部分則由具體描述組成。抽象部分以獨(dú)立于平臺(tái)和語(yǔ)言的方式定義SOAP消息,它們并不包含任何隨機(jī)器或語(yǔ)言而變的元素。這就定義了一系列服務(wù),截然不同的應(yīng)用都可以實(shí)現(xiàn)。具體部分,如數(shù)據(jù)的序列化則歸入底部分,因?yàn)樗唧w的定義。在上述的文檔元素中,<types>、<message>、<portType>屬于抽象定義層,<binding>、<service>屬于具體定義層。所有的抽象可以是單獨(dú)存在于別的文件中,也可以從主文檔中導(dǎo)入。
WSDL文檔的結(jié)構(gòu)實(shí)例解析
下面我們將通過(guò)一個(gè)實(shí)際的WSDL文檔例子來(lái)詳細(xì)說(shuō)明各標(biāo)簽的作用及關(guān)系。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<definitions
xmlns:soap="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/soap/"
xmlns:tns="http://www.jsoso.com/wstest"
xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
xmlns="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/"
targetNamespace="http://www.jsoso.com/wstest"
name="Example">
<types>
<xsd:schema>
<xsd:import
namespace="http://www.jsoso.com/wstest"
schemaLocation="http://localhost:8080/hello?xsd=1"></xsd:import>
</xsd:schema>
</types>
<message name="toSayHello">
<part name="userName" type="xsd:string"></part>
</message>
<message name="toSayHelloResponse">
<part name="returnWord" type="xsd:string"></part>
</message>
<message name="sayHello">
<part name="person" type="tns:person"></part>
<part name="arg1" type="xsd:string"></part>
</message>
<message name="sayHelloResponse">
<part name="personList" type="tns:personArray"></part>
</message>
<message name="HelloException">
<part name="fault" element="tns:HelloException"></part>
</message>
<portType name="Example">
<operation name="toSayHello" parameterOrder="userName">
<input message="tns:toSayHello"></input>
<output message="tns:toSayHelloResponse"></output>
</operation>
<operation name="sayHello" parameterOrder="person arg1">
<input message="tns:sayHello"></input>
<output message="tns:sayHelloResponse"></output>
<fault message="tns:HelloException" name="HelloException"></fault>
</operation>
</portType>
<binding name="ExamplePortBinding" type="tns:Example">
<soap:binding
transport="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/http"
style="rpc"></soap:binding>
<operation name="toSayHello">
<soap:operation soapAction="sayHello"></soap:operation>
<input>
<soap:body use="literal"
namespace="http://www.jsoso.com/wstest"></soap:body>
</input>
<output>
<soap:body use="literal"
namespace="http://www.jsoso.com/wstest"></soap:body>
</output>
</operation>
<operation name="sayHello">
<soap:operation soapAction="sayHello"></soap:operation>
<input>
<soap:body use="literal"
namespace="http://www.jsoso.com/wstest"></soap:body>
</input>
<output>
<soap:body use="literal"
namespace="http://www.jsoso.com/wstest"></soap:body>
</output>
<fault name="HelloException">
<soap:fault name="HelloException" use="literal"></soap:fault>
</fault>
</operation>
</binding>
<service name="Example">
<port name="ExamplePort" binding="tns:ExamplePortBinding">
<soap:address location="http://localhost:8080/hello"></soap:address>
</port>
</service>
</definitions>
由于上面的事例XML較長(zhǎng),我們將其逐段分解講解
WSDL文檔的根元素:<definitions>
<definitions
xmlns:soap="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/soap/"
xmlns:tns="http://www.jsoso.com/wstest"
xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
xmlns="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/"
targetNamespace="http://www.jsoso.com/wstest"
name="Example">
……
……
</definitions>
<definitions>定義了文檔中用到的各個(gè)xml元素的namespace縮寫,也界定了本文檔自己的targetNamespace="http://www.jsoso.com/wstest",這意味著其它的XML要引用當(dāng)前XML中的元素時(shí),要聲明這個(gè)namespace。注意xmlns:tns="http://www.jsoso.com/wstest"這個(gè)聲明,它標(biāo)示了使用tns這個(gè)前綴指向自身的命名空間。
引用
WSDL文檔數(shù)據(jù)類型定義元素:<types>
<types>
<xsd:schema>
<xsd:import
namespace="http://www.jsoso.com/wstest"
schemaLocation="http://localhost:8080/hello?xsd=1"></xsd:import>
</xsd:schema>
</types>
<types>標(biāo)簽定義了當(dāng)前的WSDL文檔用到的數(shù)據(jù)類型。要說(shuō)明的是,為了最大程度的平臺(tái)中立性,WSDL 使用 XML Schema 語(yǔ)法來(lái)定義數(shù)據(jù)類型。這些數(shù)據(jù)類型用來(lái)定義web service方法的參數(shù)和返回指。對(duì)于通用的原生數(shù)據(jù)類型如:integer , boolean , char , float等,在W3C的標(biāo)準(zhǔn)文檔http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema中已經(jīng)做了定義。這里我們要引入的schema定義schemaLocation="http://localhost:8080/hello?xsd=1"是我們自定義的Java對(duì)象類型。
WSDL文檔消息體定義元素:< message >
<message name="toSayHello">
<part name="userName" type="xsd:string"></part>
</message>
<message name="toSayHelloResponse">
<part name="returnWord" type="xsd:string"></part>
</message>
<message name="sayHello">
<part name="person" type="tns:person"></part>
<part name="arg1" type="xsd:string"></part>
</message>
<message name="sayHelloResponse">
<part name="personList" type="tns:personArray"></part>
</message>
<message name="HelloException">
<part name="fault" element="tns:HelloException"></part>
</message>
<message>元素定義了web service函數(shù)的參數(shù)。<message>元素中的每個(gè)<part>子元素都和某個(gè)參數(shù)相符。輸入?yún)?shù)在<message>元素中定義,與輸出參數(shù)相隔離,輸出參數(shù)有自己的<message>元素。兼作輸入、輸出的參數(shù)在輸入輸出的<message>元素中有它們相應(yīng)的<part>元素。輸出<message>元素以"Response"結(jié)尾,對(duì)Java而言方法得返回值就對(duì)應(yīng)一個(gè)輸出的<message>。每個(gè)<part>元素都有名字和類型屬性,就像函數(shù)的參數(shù)有參數(shù)名和參數(shù)類型。
在上面的文檔中有兩個(gè)輸入?yún)?shù)、兩個(gè)輸出參數(shù)和一個(gè)錯(cuò)誤參數(shù)(對(duì)應(yīng)Java中的Exception)。
? 輸入?yún)?shù)<message>的name屬性分別命名為toSayHello,sayHello。
toSayHello對(duì)應(yīng)輸入?yún)?shù)userName,參數(shù)類型為xsd:string,在Java語(yǔ)言中就是String;
sayHello對(duì)應(yīng)兩個(gè)輸入?yún)?shù)person和arg1,類型為tns:person和xsd:string。這里tns:person類型就是引用了< types >標(biāo)簽中的類型定義。
? 輸出參數(shù)<message>的name屬性分別命名為toSayHelloResponse和sayHelloResponse。
這個(gè)名稱和輸入?yún)?shù)的<message>標(biāo)簽name屬性對(duì)應(yīng),在其后面加上Response尾綴。
toSayHelloResponse對(duì)應(yīng)的返回值是returnWord,參數(shù)類型為xsd:string;
sayHelloResponse對(duì)應(yīng)的返回值是personList,參數(shù)類型為tns:personArray(自定義類型);
? 錯(cuò)誤參數(shù)<message>的name屬性為HelloException。
它的<part>子標(biāo)簽element而不是type來(lái)定義類型。
以上的message標(biāo)簽的name屬性通常使用web service函數(shù)方法名作為參照,錯(cuò)誤參數(shù)標(biāo)簽則使用異常類名為參照。標(biāo)簽中的參數(shù)名稱,即part子元素的name屬性是可自定義的(下一章節(jié)詳細(xì)說(shuō)明)。message標(biāo)簽的參數(shù)類型將引用types標(biāo)簽的定義。
WSDL文檔函數(shù)體定義元素:< portType >
<portType name="Example">
<operation name="toSayHello" parameterOrder="userName">
<input message="tns:toSayHello"></input>
<output message="tns:toSayHelloResponse"></output>
</operation>
<operation name="sayHello" parameterOrder="person arg1">
<input message="tns:sayHello"></input>
<output message="tns:sayHelloResponse"></output>
<fault message="tns:HelloException" name="HelloException"></fault>
</operation>
</portType>
<portType> 元素是最重要的 WSDL 元素。它可描述一個(gè) web service、可被執(zhí)行的操作,以及相關(guān)的消息。portType的name屬性對(duì)應(yīng)Java中的一個(gè)服務(wù)類的類名。<portType> 元素使用其子元素< operation>描述一個(gè)web service的服務(wù)方法。
在<operation>元素中,name屬性表示服務(wù)方法名,parameterOrder屬性表示方法的參數(shù)順序,使用空格符分割多個(gè)參數(shù),如:“parameterOrder="person arg1”。<operation>元素的子標(biāo)簽<input>表示輸入?yún)?shù)說(shuō)明,它引用<message>標(biāo)簽中的輸入?yún)?shù)。<output>表示輸出參數(shù)說(shuō)明,它引用<message>標(biāo)簽中的輸出參數(shù)。<fault>標(biāo)簽在Java方法中的特別用來(lái)表示異常(其它語(yǔ)言有對(duì)應(yīng)的錯(cuò)誤處理機(jī)制),它引用<message>標(biāo)簽中的錯(cuò)誤參數(shù)。
WSDL綁定實(shí)現(xiàn)定義元素:< binding >
<binding name="ExamplePortBinding" type="tns:Example">
<soap:binding
transport="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/http"
style="rpc"></soap:binding>
<operation name="toSayHello">
<soap:operation soapAction="sayHello"></soap:operation>
<input>
<soap:body use="literal"
namespace="http://www.jsoso.com/wstest"></soap:body>
</input>
<output>
<soap:body use="literal"
namespace="http://www.jsoso.com/wstest"></soap:body>
</output>
</operation>
<operation name="sayHello">
<soap:operation soapAction="sayHello"></soap:operation>
<input>
<soap:body use="literal"
namespace="http://www.jsoso.com/wstest"></soap:body>
</input>
<output>
<soap:body use="literal"
namespace="http://www.jsoso.com/wstest"></soap:body>
</output>
<fault name="HelloException">
<soap:fault name="HelloException" use="literal"></soap:fault>
</fault>
</operation>
/binding>
<binding>標(biāo)簽是完整描述協(xié)議、序列化和編碼的地方,<types>,<message>和<portType>標(biāo)簽處理抽象的數(shù)據(jù)內(nèi)容,而<binding>標(biāo)簽是處理數(shù)據(jù)傳輸?shù)奈锢韺?shí)現(xiàn)。
<binding>標(biāo)簽把前三部分的抽象定義具體化。
首先<binding>標(biāo)簽使用<soap:binding>的transport和style屬性定義了Web Service的通訊協(xié)議HTTP和SOAP的請(qǐng)求風(fēng)格RPC。其次<operation>子標(biāo)簽將portType中定義的operation同SOAP的請(qǐng)求綁定,定義了操作名稱soapAction,輸出輸入?yún)?shù)和異常的編碼方式及命名空間。
WSDL服務(wù)地址綁定元素:< service >
<service name="Example">
<port name="ExamplePort" binding="tns:ExamplePortBinding">
<soap:address location="http://localhost:8080/hello"></soap:address>
</port>
</service>
service是一套<port>元素。在一一對(duì)應(yīng)形式下,每個(gè)<port>元素都和一個(gè)location關(guān)聯(lián)。如果同一個(gè)<binding>有多個(gè)<port>元素與之關(guān)聯(lián),可以使用額外的URL地址作為替換。
一個(gè)WSDL文檔中可以有多個(gè)<service>元素,而且多個(gè)<service>元素十分有用,其中之一就是可以根據(jù)目標(biāo)URL來(lái)組織端口。在一個(gè)WSDL文檔中,<service>的name屬性用來(lái)區(qū)分不同的service。在同一個(gè)service中,不同端口,使用端口的"name"屬性區(qū)分。
這一章節(jié),我們簡(jiǎn)單的描述了WSDL對(duì)SOAP協(xié)議的支持,以及在Web Service中的作用。在接下來(lái)的章節(jié)中,我們將學(xué)習(xí)如何使用Java6.0的Annotation標(biāo)簽來(lái)定義和生成對(duì)應(yīng)的WSDL。
JavaSE6.0下的Web Service
從JavaSE6.0開始,Java引入了對(duì)Web Service的原生支持。我們只需要簡(jiǎn)單的使用Java的Annotation標(biāo)簽即可將標(biāo)準(zhǔn)的Java方法發(fā)布成Web Service。(PS:Java Annotation資料請(qǐng)參考
JDK5.0 Annotation學(xué)習(xí)筆記(一) )
但不是所有的Java類都可以發(fā)布成Web Service。Java類若要成為一個(gè)實(shí)現(xiàn)了Web Service的bean,它需要遵循下邊這些原則:
- ? 這個(gè)類必須是public類
- ? 這些類不能是final的或者abstract
- ? 這個(gè)類必須有一個(gè)公共的默認(rèn)構(gòu)造函數(shù)
- ? 這個(gè)類絕對(duì)不能有finalize()方法
下面我們將通過(guò)一個(gè)具體的Java Web Service代碼例子,配合上述的WSDL文件,講述如何編寫JavaSE6.0的原生Web Service應(yīng)用。
完整的Java Web Service類代碼
package org.jsoso.jws.server;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import javax.jws.WebMethod;
import javax.jws.WebParam;
import javax.jws.WebResult;
import javax.jws.WebService;
import javax.jws.WebParam.Mode;
import javax.jws.soap.SOAPBinding;
/
* 提供WebService服務(wù)的類
*/
@WebService(name="Example", targetNamespace="http://www.jsoso.com/wstest", serviceName="Example")
@SOAPBinding(style=SOAPBinding.Style.RPC)
public class Example {
private ArrayList<Person> persons = new ArrayList<Person>();;
/**
*
* 返回一個(gè)字符串
* @param userName
* @return
*/
@WebMethod(operationName="toSayHello",action="sayHello",exclude=false)
@WebResult(name="returnWord")//自定義該方法返回值在WSDL中相關(guān)的描述
public String sayHello(@WebParam(name="userName")String userName) {
return "Hello:" + userName;
}
/**
* web services 方法的返回值與參數(shù)的類型不能為接口
* @param person
* @return
* @throws HelloException
*/
@WebMethod(operationName="sayHello", action="sayHello")
@WebResult(partName="personList")
public Person[] sayHello(@WebParam(partName="person", mode=Mode.IN)Person person,
String userName) throws HelloException {
if (person == null || person.getName() == null) {
throw new HelloException("說(shuō)hello出錯(cuò),對(duì)像為空。。");
}
System.out.println(person.getName() + " 對(duì) " + userName + " 說(shuō):Hello,我今年" + person.getAge() + "歲");
persons.add(person);
return persons.toArray(new Person[0]);
}
}
Annotation 1@WebService(name="Example", targetNamespace="http://www.jsoso.com/wstest", serviceName="Example")
@WebService標(biāo)簽主要將類暴露為WebService,其中targetNamespace屬性定義了自己的命名空間,serviceName則定義了< definitions >標(biāo)簽和<service>標(biāo)簽的name屬性。
Annotation 2:@SOAPBinding(style=SOAPBinding.Style.RPC)
@SOAPBinding標(biāo)簽定義了WSDL文檔中SOAP的消息協(xié)議,其中style屬性對(duì)應(yīng)SOAP的文檔類型,可選的有RPC和DOCUMENT
Annotation 3:@WebMethod(operationName="toSayHello",action="sayHello",exclude=false)
@WebMethod定義Web Service運(yùn)作的方法,
屬性action 對(duì)應(yīng)操作的活動(dòng) ,如<soap:operation soapAction="sayHello" />
屬性operationName匹配的wsdl:operation 的名稱,如<operation name="toSayHello" parameterOrder="userName">
屬性exclude 用于阻止將某一繼承方法公開為web服務(wù),默認(rèn)為false
Annotation 4:@WebResult(name="returnWord")
@ WebResult定義方法返回值得名稱,如<part name="returnWord" type="xsd:string" />
Annotation 5:@WebParam(partName="person", mode=Mode.IN
@WebParam定義方法的參數(shù)名稱,如<part name="person" type="tns:person" />,其中mode屬性表示參數(shù)的流向,可選值有IN / OUT / INOUT
這里要著重說(shuō)明的是,上述Web Service類的sayHello方法中,帶有HelloException這個(gè)異常聲明,造成該服務(wù)類不能直接發(fā)布成Web Service。需要使用wsgen工具為其生存異常Bean。關(guān)于wsgen工具的使用,請(qǐng)參考wsgen與wsimport命令說(shuō)明
發(fā)布一個(gè)的Java Web Service
在完成了上述的Web Service Annotation注釋后,我們使用wsgen工具為其進(jìn)行服務(wù)資源文件的構(gòu)造(這里主要是生成一個(gè)名為org.jsoso.jws.server.jaxws.HelloExceptionBean的異常bean類),最后使用以下的類發(fā)布Web 服務(wù):
package org.jsoso.jws.server;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import javax.xml.ws.Binding;
import javax.xml.ws.Endpoint;
import javax.xml.ws.handler.Handler;
/**
* @author zsy 啟動(dòng)web services服務(wù)
*/
public class StartServer {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
* 生成Example 服務(wù)實(shí)例
*/
Example serverBean = new Example();
/*
* 發(fā)布Web Service到http://localhost:8080/hello地址
*/
Endpoint endpoint =
Endpoint.publish("http://localhost:8080/hello", serverBean);
Binding binding = endpoint.getBinding();
/*
* 設(shè)置一個(gè)SOAP協(xié)議處理?xiàng)?nbsp;
* 這里就簡(jiǎn)單得打印SOAP的消息文本
*/
List<Handler> handlerChain = new LinkedList<Handler>();
handlerChain.add(new TraceHandler());
binding.setHandlerChain(handlerChain);
System.out.println("服務(wù)已啟動(dòng) http://localhost:8080/hello");
}
}
在控制臺(tái)運(yùn)行這個(gè)類,就可以使用URL :http://localhost:8080/hello?wsdl 瀏覽到上文所描述的WSDL的全文了。這說(shuō)明您的第一個(gè)Web Service應(yīng)用發(fā)布成功!
構(gòu)建Web Service客戶端
使用JavaSE6.0構(gòu)建Web Service的客戶端是一件相當(dāng)簡(jiǎn)單的事。這里我們要使用到JDK中的另一個(gè)命令行工具wsimport。在控制臺(tái)下輸入以下命令:
引用
wsimport -d ./bin -s ./src -p org.jsoso.jws.client.ref http://localhost:8080/hello?wsdl
即可在包org.jsoso.jws.client.ref中生成客戶端的存根及框架文件。其中我們要使用的類只有兩個(gè):服務(wù)類Example_Service和本地接口Example。編寫如下客戶端,即可調(diào)用Web Service服務(wù):
package org.jsoso.jws.client;
import org.jsoso.jws.client.ref.*;
public class RunClient {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
//初始化服務(wù)框架類
Example_Service service = new Example_Service();
//或者本地服務(wù)借口的實(shí)例
Example server = (Example) service.getExamplePort();
try {
//調(diào)用web service的toSayHello方法
System.out.println("輸入toSayHello的返回值——" + server.toSayHello("阿土"));
Person person = new Person();
person.setName("阿土");
person.setAge(25);
//調(diào)用web service的sayHello方法
server.sayHello(person, "機(jī)器人");
person = new Person();
person.setName("aten");
person.setAge(30);
//調(diào)用web service的sayHello方法
PersonArray list = server.sayHello(person, "機(jī)器人");
//輸出返回值
System.out.println("\n以下輸入sayHello的返回值——");
for (Person p : list.getItem()) {
System.out.println(p.getName() + ":" + p.getAge());
}
} catch (HelloException_Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
屆此,本次Web Service的學(xué)習(xí)暫告一個(gè)段落。Java Web Service是一個(gè)相當(dāng)龐大的知識(shí)體系,其中涉及的相關(guān)技術(shù)較多,這里無(wú)法一一道來(lái),我們將會(huì)在今后的開發(fā)和使用中,同大家做進(jìn)一步深入的探討和學(xué)習(xí)。
附錄:wsgen與wsimport命令說(shuō)明
wsgen
wsgen是在JDK的bin目錄下的一個(gè)exe文件(Windows版),該命令的主要功能是用來(lái)生成合適的JAX-WS。它讀取Web Service的終端類文件,同時(shí)生成所有用于發(fā)布Web Service所依賴的源代碼文件和經(jīng)過(guò)編譯過(guò)的二進(jìn)制類文件。這里要特別說(shuō)明的是,通常在Web Service Bean中用到的異常類會(huì)另外生成一個(gè)描述Bean,如果Web Service Bean中的方法有申明拋出異常,這一步是必需的,否則服務(wù)器無(wú)法綁定該對(duì)像。此外,wsgen還能輔助生成WSDL和相關(guān)的xsd文件。wsgen從資源文件生成一個(gè)完整的操作列表并驗(yàn)證web service是否合法,可以完整發(fā)布。
命令參數(shù)說(shuō)明:
- ? -cp 定義classpath
- ? -r 生成 bean的wsdl文件的存放目錄
- ? -s 生成發(fā)布Web Service的源代碼文件的存放目錄(如果方法有拋出異常,則會(huì)生成該異常的描述類源文件)
- ? -d 生成發(fā)布Web Service的編譯過(guò)的二進(jìn)制類文件的存放目錄(該異常的描述類的class文件)
命令范例:wsgen -cp ./bin -r ./wsdl -s ./src -d ./bin -wsdl org.jsoso.jws.server.Example
wsimport
wsimport也是在JDK的bin目錄下的一個(gè)exe文件(Windows版),主要功能是根據(jù)服務(wù)端發(fā)布的wsdl文件生成客戶端存根及框架,負(fù)責(zé)與Web Service 服務(wù)器通信,并在將其封裝成實(shí)例,客戶端可以直接使用,就像使用本地實(shí)例一樣。對(duì)Java而言,wsimport幫助程序員生存調(diào)用web service所需要的客戶端類文件.java和.class。要提醒指出的是,wsimport可以用于非Java的服務(wù)器端,如:服務(wù)器端也許是C#編寫的web service,通過(guò)wsimport則生成Java的客戶端實(shí)現(xiàn)。
命令參數(shù)說(shuō)明:
- ? -d 生成客戶端執(zhí)行類的class文件的存放目錄
- ? -s 生成客戶端執(zhí)行類的源文件的存放目錄
- ? -p 定義生成類的包名
命令范例:wsimport -d ./bin -s ./src -p org.jsoso.jws.client.ref http://localhost:8080/hello?wsdl