AIX下用nmon進行監控和分析實戰
nmon從這里下載:
http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/wikis/display/Wikiptype/nmonanalyser
1、準備:
1)用root用戶登錄到系統中
2)建目錄:#mkdir /nmon/script
3)確定版本:#oslevel,以便確定用哪個腳本,我是用530
# oslevel -s
5300-09-01-0847
4)把nmon12e_aix530用ftp上傳到/nmon/script
5)執行授權命令:#chmod +x nmon12e_aix530
2、使用:
1)直接使用:
./nmon/nmon12e_aix536 -f -N -m /nmon/log -s 30 -c 2880
表示:
-f 按標準格式輸出文件:<hostname>_YYYYMMDD_HHMM.nmon
-N include NFS sections
-m 切換到路徑去保存日志文件
-s 每隔n秒抽樣一次,這里為30
-c 取出多少個抽樣數量,這里為2880,即監控=2880*(30/60/60)=24小時
根據小時計算這個數字的公式為:c=h*3600/s,比如要監控10小時,每隔30秒采樣一次,則c=10*3600/30=1200
2)用crontab定期使用:
A、執行命令:#crontab -e
B、在最后一行添加如下命令:
0 8 * * 1,2,3,4,5 /nmon/script/nmon12e_aix530 -f -N -m /nmon/log -s 30 -c 1200
表示:
周一到周五,從早上08點開始,監控10個小時(到18:00整為止),輸出到/nmon/log
3、分析
1)會在/tmp/nmon生成*.nmon的文件把它下載到你的電腦上
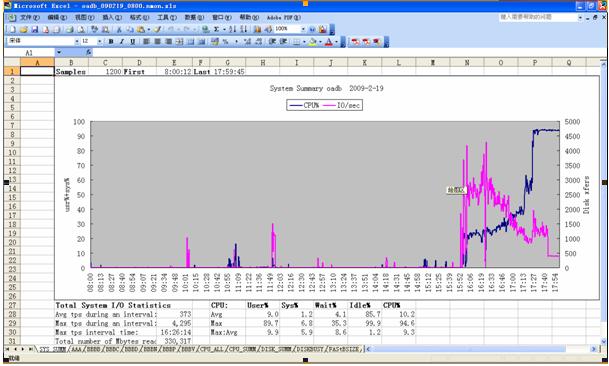
2)打開nmon analyser v339.xls,把宏的安全性設成最低,打開下載好的*.nmon文件。
并且保存為一個文件,生成的是視圖模式的,非常直觀!
參考:
附錄一:crontab參數:
參考:http://tech.ddvip.com/2008-11/122629526990895.html
f1 f2 f3 f4 f5 program
minute hour day_of_month month weekday command這些字段接收以下值:
minute 0 到 59
hour 0 到 23
day_of_month 1 到 31
month 1 到 12
weekday 0 到 6(星期天到星期六)
其中f1 是表示分鐘,f2 表示小時,f3 表示一個月份中的第幾日,f4 表示月份,f5 表示一個星期中的第幾天。program 表示要執行的程序。
當 f1 為 * 時表示每分鐘都要執行 program,f2 為 * 時表示每小時都要執行程序,其馀類推
當 f1 為 a-b 時表示從第 a 分鐘到第 b 分鐘這段時間內要執行,f2 為 a-b 時表示從第 a 到第 b 小時都要執行,其馀類推
當 f1 為 */n 時表示每 n 分鐘個時間間隔執行一次,f2 為 */n 表示每 n 小時個時間間隔執行一次,其馀類推
當 f1 為 a, b, c,... 時表示第 a, b, c,... 分鐘要執行,f2 為 a, b, c,... 時表示第 a, b, c...個小時要執行,其馀類推
附錄二:nmon參數:
參考http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/wikis/display/Wikiptype/nmonanalyser
nmon:
-f spreadsheet output format [note: default -s300 -c288]
Output file is <hostname>_YYYYMMDD_HHMM.nmon
-F <filename> same as -f but user supplied filename
-c <number> number of snapshots
-d requests disk service and wait times (DISKSERV and DISKWAIT)
-i <percent> Ignore processes using less than this amount of CPU when generating TOP section – useful for reducing data volumes
-g <filename> file containing disk group definitions
-l <dpl> number of hdisks per sheet - defaults to 150, maximum 250. See notes
-m <dir> NMON changes to this directory before saving the file
-r <runname> goes into spreadsheet file [default hostname]
-s <seconds> interval between snap shots
-x capacity planning (15 mins for 1 day = -fdt -s900 -c96)
-t include top processes in the output
-T as –t plus saves command line arguments in UARG section
-A include data for async I/O (PROCAIO) sections
-D prevents DISK sections being produced (useful when Disk Groups are being used because there are too many hdisks to process)
-E stops ESS sections being produced (necessary when Disk Groups are being used because there are too many vpaths to process)
-J prevents JFS sections being produced (prevents Excel errors when you have more than 255 filesystems)
-L includes LARGEPAGE section
-N include NFS sections
-S include WLM sections with subclasses
-W include WLM sections without subclasses
-Y include SUMMARY section (very efficient alternative to –t if PID level data is not required)
example: nmon_aix51 -F asterix.nmon -r Test1 -s6 -c12