用java實現中國移動WLAN業務PORTAL協議規范
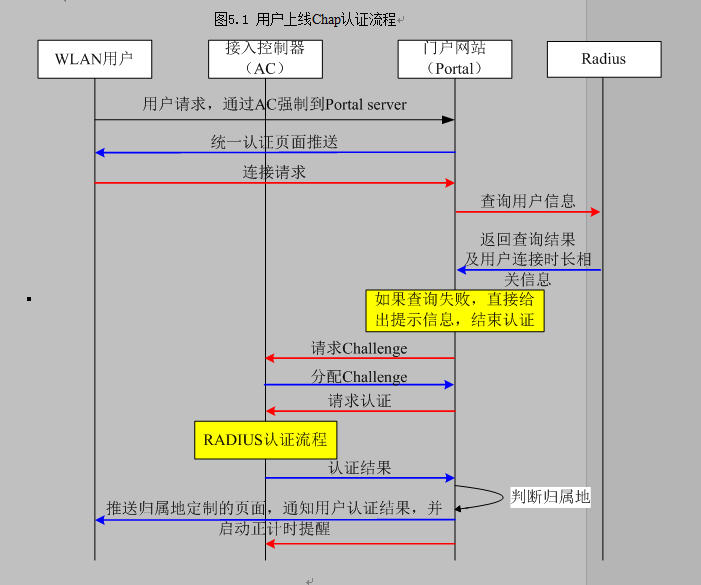
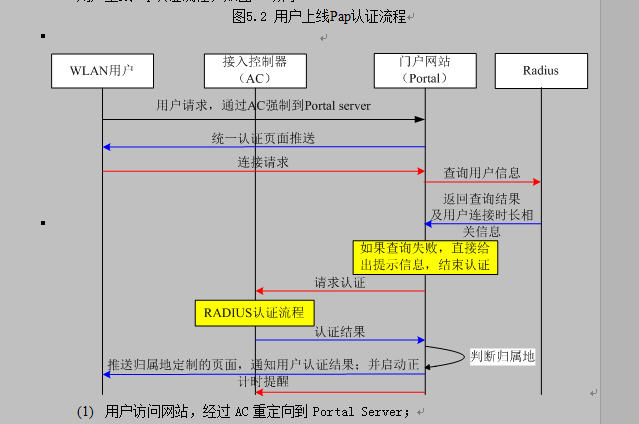
有需要代碼的可聯系本人。
QQ:316909543
Simple Network Management Protocol i.e. SNMP is a simple request/response protocol in which SNMP manager communicates with SNMP agents/managed devices using SNMP PDU’s (Packet Data Unit). These PDUs are encapsulated in SNMP Messages. An snmp message consists of a sequence that contains SNMP version, Community String, and SNMP PDU and an SNMP PDU forms the body of the message. Look here to read about seven types of SNMP PDUs.
We need to understand that SNMP Message is different from SNMP PDU and hence their formats. Let us now understand SNMP Message Format and SNMP PDUD Format for SNMPv1, SNMPv2 and SNMPv3.
SNMPv1 Message Format

- SNMP Version – It is an Integer that identifies the version of SNMP. For SNMPv1, it is 0.
- Community String – An Octet String that may contain a string used to add security to SNMP devices.
- SNMP PDU – The SNMP PDU (Protocol Data Unit) is used for communication between the SNMP entities.
SNMPv1 PDU Format
For SNMPv1, there are two pdu formats, one for Trap and other for rest of the pdu types.
Below PDU format is applicable for Get, GetNext, Set and Response PDUs:

- PDU Type – Specifies the type of PDU
- Request ID – Associates SNMP requests with responses.
- Error status – Indicates one of a number of errors and error types. It is set only in Response PDU, for rest it is set as 0.
- Error index – Associates an error with a particular object instance. It is set only in Response PDU, for rest it is set as 0.
- Variable bindings – Each variable binding associates a particular object instance with its current value. For Get and GetNext requests, the value is ignored.
Below PDU format is applicable for Trap PDU:

- PDU Type – Specifies the type of PDU as Trap
- Enterprise – Identifies the management enterprise under whose registration authority the trap was defined.
- Agent address – IP address of the agent
- Generic trap type – Used to identiy the generic trap. There are six types of generic traps.
- Specific trap type – Used to identify a specific trap.
- Time Stamp – Value of the sysUpTime mib object
SNMPv2 Message Format

- SNMP Version – It is an Integer that identifies the version of SNMP. For SNMPv2, it is 1.
- Community String – An Octet String that may contain a string used to add security to SNMP devices.
- SNMP PDU – The SNMP PDU (Protocol Data Unit) is used for communication between the SNMP entities.
SNMPv2 PDU Format
For SNMPv2, there are two pdu formats, one for GetBulk and other for rest of the pdu types.
Below PDU format is applicable for Get, GetNext, Set, Response, Trap and Inform PDUs:

- PDU Type- Specifies the type of PDU
- Request ID- Associates SNMP requests with responses.
- Error Status- Indicates one of a number of errors and error types. It is set only in Response PDU, for rest it is set as 0.
- Error Index- Associates an error with a particular object instance. It is set only in Response PDU, for rest it is set as 0.
- Variable Bindings- Each variable binding associates a particular object instance with its current value. For Get and GetNext requests, the value is ignored.
Below PDU format is applicable for GetBulk PDU:
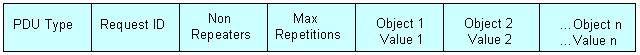
- PDU Type – Specifies the type of PDU as GetBulk
- Request ID- Associates SNMP requests with responses.
- Non repeaters- Specifies the number of object instances in the variable bindings field that should be retrieved no more than once from the beginning of the request.
- Max repetitions- Defines the maximum number of times that other variables beyond those specified by the Non repeaters field should be retrieved.
- Variable Bindings- Each variable binding associates a particular object instance with its current value.
SNMPv3 Message Format
SNMPv3 message format is very different from the above two because of lot of security parameters introduced in this version. Below is how it looks like:
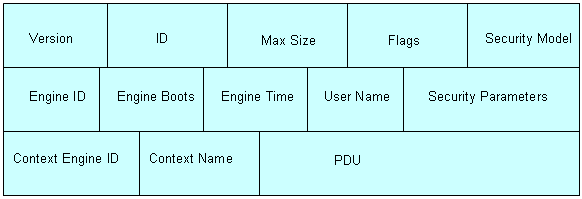
- Version – It is an Integer that identifies the version of SNMP. For SNMPv3, it is 3.
- ID – This field contains the SNMP message identifier which is a unique ID associated with the message. The msgID field is different from the reqID field available in the PDU.
- Max Size – This field represents the maximum size of message which the requesting SNMP entity can accept.
- Flags – This field contains the message security level. 0 – message is authenticated, 1 – message uses privacy, 2 – a report PDU is expected for the message
- Security Model – This field indicates the security model used to generate the message. When USM is used, it has a value of 3
- Engine ID – This field has the SNMPEngineID of the authoritative SNMP entity involved in the transaction. When a request PDU is generated from an SNMP engine, the remote peer (agent for Get request and manager for Trap request) is the authoritative SNMP entity.
- Engine Boots – This field has the snmpEngineBoots value of the authoritative SNMP entity involved in the transaction
- Engine Time – This field has the snmpEngineTime value of the authoritative SNMP entity involved in the transaction
- User Name – This field contains the principal who originated the request.
- Security Parameters – This field contains the security parameters that are security model dependent. It contains the authentication parameters and the privacy parameters for USM.
- Context Engine ID – Within an administrative domain, the contextEngineID uniquely identifies an SNMP entity that may realize an instance of a context with a particular contextName.
- Context Name – A contextName is used to name a context. Each contextName must be unique within an SNMP entity.
- PDU – The SNMP PDU (Protocol Data Unit) is used for communication between the SNMP entities.
SNMPv3 PDU Format
The PDU types for SNMPv3 are the same as the SNMPv2.
Thus, above are the message and pdu formats for SNMPv1, SNMPv2 and SNMPv3. Hope you find the information presented here useful. Feel free to leave your footprints for any queries, feedback or suggestions in the comments section below.