Directory類系
綜述:Directory類系可以被理解成是一個文件夾,它提供些對文件夾內容及本身的一些操作。比如:
1.建立/讀取/刪除/重命名文件;
2.復制文件夾;
3.查尋是否存在某文件;
4.設置/獲取某文件最后訪問時間;
5.查尋文件夾大小;
6.查看文件列表
1.Directory類系層次圖
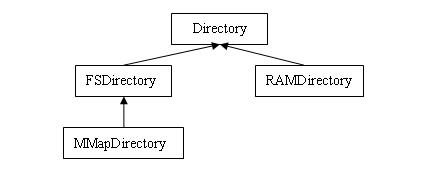
2. 部分代碼說明
Directory類
Directory是所有文件夾類的父類。它規定了所有子類必須提供的操作,但它本身只實現了部分,其中比較重要的就是文件夾間的拷貝操作copy()方法。
1 public static void copy(Directory src, Directory dest, boolean closeDirSrc)
public static void copy(Directory src, Directory dest, boolean closeDirSrc)
2
 throws IOException
throws IOException  { // 文件夾之間的的復制
{ // 文件夾之間的的復制
3 final String[] files = src.list(); // 獲取源文件夾文件列表
final String[] files = src.list(); // 獲取源文件夾文件列表
4
5 if (files == null)
if (files == null)
6 throw new IOException("cannot read directory " + src
throw new IOException("cannot read directory " + src
7 + ": list() returned null");
+ ": list() returned null");
8
9 byte[] buf = new byte[BufferedIndexOutput.BUFFER_SIZE]; // 建立緩沖buf
byte[] buf = new byte[BufferedIndexOutput.BUFFER_SIZE]; // 建立緩沖buf
10
 for (int i = 0; i < files.length; i++)
for (int i = 0; i < files.length; i++)  { // 對每個文件進行復制操作
{ // 對每個文件進行復制操作
11 IndexOutput os = null; // 寫通道
IndexOutput os = null; // 寫通道
12 IndexInput is = null; // 讀通道
IndexInput is = null; // 讀通道
13
 try
try  {
{
14 // create file in dest directory
// create file in dest directory
15 os = dest.createOutput(files[i]); // 創建對file[i]的寫通道
os = dest.createOutput(files[i]); // 創建對file[i]的寫通道
16 // read current file
// read current file
17 is = src.openInput(files[i]); // 讀通道
is = src.openInput(files[i]); // 讀通道
18 // and copy to dest directory
// and copy to dest directory
19 long len = is.length(); // 文件總長度
long len = is.length(); // 文件總長度
20 long readCount = 0; // 已讀取長度
long readCount = 0; // 已讀取長度
21
 while (readCount < len)
while (readCount < len)  { // 循環讀取文件數據
{ // 循環讀取文件數據
22 int toRead = readCount + BufferedIndexOutput.BUFFER_SIZE > len ? (int) (len - readCount)
int toRead = readCount + BufferedIndexOutput.BUFFER_SIZE > len ? (int) (len - readCount)
23 : BufferedIndexOutput.BUFFER_SIZE; // 實際一次讀取長度
: BufferedIndexOutput.BUFFER_SIZE; // 實際一次讀取長度
24 is.readBytes(buf, 0, toRead); // 讀取
is.readBytes(buf, 0, toRead); // 讀取
25 os.writeBytes(buf, toRead); // 寫入
os.writeBytes(buf, toRead); // 寫入
26 readCount += toRead; // 記錄已寫入數量
readCount += toRead; // 記錄已寫入數量
27 }
}
28
 } finally
} finally  { // 關閉操作
{ // 關閉操作
29 // graceful cleanup
// graceful cleanup
30
 try
try  {
{
31 if (os != null)
if (os != null)
32 os.close();
os.close();
33
 } finally
} finally  {
{
34 if (is != null)
if (is != null)
35 is.close();
is.close();
36 }
}
37 }
}
38 }
}
39 if (closeDirSrc)
if (closeDirSrc)
40 src.close();
src.close();
41 }
}
FSDirectory類
FSDirectory是基于硬盤的Directory。
FSDirectory中最重要的實例生成方法就是getFSDirectory(File, LockFactory)了。
1 public static FSDirectory getDirectory(File file, LockFactory lockFactory)
public static FSDirectory getDirectory(File file, LockFactory lockFactory)
2
 throws IOException
throws IOException  {
{
3 file = new File(file.getCanonicalPath()); // 獲得file
file = new File(file.getCanonicalPath()); // 獲得file
4
5 if (file.exists() && !file.isDirectory()) // file存在但不是文件夾
if (file.exists() && !file.isDirectory()) // file存在但不是文件夾
6 throw new IOException(file + " not a directory");
throw new IOException(file + " not a directory");
7
8 if (!file.exists()) // file不存在
if (!file.exists()) // file不存在
9 if (!file.mkdirs()) // 試圖創建file文件夾,失敗則拋出異常
if (!file.mkdirs()) // 試圖創建file文件夾,失敗則拋出異常
10 throw new IOException("Cannot create directory: " + file);
throw new IOException("Cannot create directory: " + file);
11
12 FSDirectory dir;
FSDirectory dir;
13
 synchronized (DIRECTORIES)
synchronized (DIRECTORIES)  { // 同步訪問DIRECTORIES
{ // 同步訪問DIRECTORIES
14 dir = (FSDirectory) DIRECTORIES.get(file); // 試圖從DIRECTORIES中獲取
dir = (FSDirectory) DIRECTORIES.get(file); // 試圖從DIRECTORIES中獲取
15
 if (dir == null)
if (dir == null)  { // 獲取失敗
{ // 獲取失敗
16
 try
try  {
{
17 dir = (FSDirectory) IMPL.newInstance(); // 創建一個新實例
dir = (FSDirectory) IMPL.newInstance(); // 創建一個新實例
18
 } catch (Exception e)
} catch (Exception e)  {
{
19 throw new RuntimeException(
throw new RuntimeException(
20 "cannot load FSDirectory class: " + e.toString(), e);
"cannot load FSDirectory class: " + e.toString(), e);
21 }
}
22 dir.init(file, lockFactory); // 初始化dir
dir.init(file, lockFactory); // 初始化dir
23 DIRECTORIES.put(file, dir); // 把dir放入DIRECTORIES
DIRECTORIES.put(file, dir); // 把dir放入DIRECTORIES
24
 } else
} else  {
{
25 // Catch the case where a Directory is pulled from the cache,
// Catch the case where a Directory is pulled from the cache,
26 // but has a
// but has a
27 // different LockFactory instance.
// different LockFactory instance.
28
 if (lockFactory != null && lockFactory != dir.getLockFactory())
if (lockFactory != null && lockFactory != dir.getLockFactory())  {
{
29 throw new IOException(
throw new IOException(
30 "Directory was previously created with a different LockFactory instance; please pass null as the lockFactory instance and use setLockFactory to change it");
"Directory was previously created with a different LockFactory instance; please pass null as the lockFactory instance and use setLockFactory to change it");
31 }
}
32 }
}
33 }
}
34
 synchronized (dir)
synchronized (dir)  {
{
35 dir.refCount++; // refCount++
dir.refCount++; // refCount++
36 }
}
37 return dir;
return dir;
38 }
}
init(File, LockFactory)為初始化FSDirectory實例的方法,只能內部調用。
1
 private void init(File path, LockFactory lockFactory) throws IOException
private void init(File path, LockFactory lockFactory) throws IOException  {
{
2
3 // Set up lockFactory with cascaded defaults: if an instance was passed
// Set up lockFactory with cascaded defaults: if an instance was passed
4 // in,
// in,
5 // use that; else if locks are disabled, use NoLockFactory; else if the
// use that; else if locks are disabled, use NoLockFactory; else if the
6 // system property org.apache.lucene.store.FSDirectoryLockFactoryClass
// system property org.apache.lucene.store.FSDirectoryLockFactoryClass
7 // is set,
// is set,
8 // instantiate that; else, use SimpleFSLockFactory:
// instantiate that; else, use SimpleFSLockFactory:
9
10 directory = path;
directory = path;
11
12 boolean doClearLockID = false;
boolean doClearLockID = false;
13
14
 if (lockFactory == null)
if (lockFactory == null)  {
{
15
16
 if (disableLocks)
if (disableLocks)  {
{
17 // Locks are disabled:
// Locks are disabled:
18 lockFactory = NoLockFactory.getNoLockFactory();
lockFactory = NoLockFactory.getNoLockFactory();
19
 } else
} else  {
{
20 String lockClassName = System
String lockClassName = System
21 .getProperty("org.apache.lucene.store.FSDirectoryLockFactoryClass");
.getProperty("org.apache.lucene.store.FSDirectoryLockFactoryClass");
22
23
 if (lockClassName != null && !lockClassName.equals(""))
if (lockClassName != null && !lockClassName.equals(""))  { // 系統設置了默認lockFactory
{ // 系統設置了默認lockFactory
24 Class c;
Class c;
25
26
 try
try  {
{
27 c = Class.forName(lockClassName);
c = Class.forName(lockClassName);
28
 } catch (ClassNotFoundException e)
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e)  {
{
29 throw new IOException("unable to find LockClass "
throw new IOException("unable to find LockClass "
30 + lockClassName);
+ lockClassName);
31 }
}
32
33
 try
try  {
{
34 lockFactory = (LockFactory) c.newInstance(); // 實例化系統默認的lockFactory
lockFactory = (LockFactory) c.newInstance(); // 實例化系統默認的lockFactory
35
 } catch (IllegalAccessException e)
} catch (IllegalAccessException e)  {
{
36 throw new IOException(
throw new IOException(
37 "IllegalAccessException when instantiating LockClass "
"IllegalAccessException when instantiating LockClass "
38 + lockClassName);
+ lockClassName);
39
 } catch (InstantiationException e)
} catch (InstantiationException e)  {
{
40 throw new IOException(
throw new IOException(
41 "InstantiationException when instantiating LockClass "
"InstantiationException when instantiating LockClass "
42 + lockClassName);
+ lockClassName);
43
 } catch (ClassCastException e)
} catch (ClassCastException e)  {
{
44 throw new IOException("unable to cast LockClass "
throw new IOException("unable to cast LockClass "
45 + lockClassName + " instance to a LockFactory");
+ lockClassName + " instance to a LockFactory");
46 }
}
47
48
 if (lockFactory instanceof NativeFSLockFactory)
if (lockFactory instanceof NativeFSLockFactory)  { // 根據lockFactory的類型各自調用setLockDir()
{ // 根據lockFactory的類型各自調用setLockDir()
49 ((NativeFSLockFactory) lockFactory).setLockDir(path);
((NativeFSLockFactory) lockFactory).setLockDir(path);
50
 } else if (lockFactory instanceof SimpleFSLockFactory)
} else if (lockFactory instanceof SimpleFSLockFactory)  {
{
51 ((SimpleFSLockFactory) lockFactory).setLockDir(path);
((SimpleFSLockFactory) lockFactory).setLockDir(path);
52 }
}
53
 } else
} else  { // 使用lucene默認的lockFactory: SimpleFSLockFactory
{ // 使用lucene默認的lockFactory: SimpleFSLockFactory
54 // Our default lock is SimpleFSLockFactory;
// Our default lock is SimpleFSLockFactory;
55 // default lockDir is our index directory:
// default lockDir is our index directory:
56 lockFactory = new SimpleFSLockFactory(path);
lockFactory = new SimpleFSLockFactory(path);
57 doClearLockID = true; // 設置為true, 不懂!!!!!!
doClearLockID = true; // 設置為true, 不懂!!!!!!
58 }
}
59 }
}
60 }
}
61
62 setLockFactory(lockFactory); // 設置lockFactory
setLockFactory(lockFactory); // 設置lockFactory
63
64
 if (doClearLockID)
if (doClearLockID)  {
{
65 // Clear the prefix because write.lock will be
// Clear the prefix because write.lock will be
66 // stored in our directory:
// stored in our directory:
67 lockFactory.setLockPrefix(null);
lockFactory.setLockPrefix(null);
68 }
}
69 }
}
MMapDirectory類
MMapDirectory是FSDirectory的子類,它重寫了FSDirectory的openInput()方法。他們的區別是,在讀取文件時,FSDirectory在底層用BufferedIndexInput(把文件部分讀入內存),而MMapDirectory則用MMapDirectory/MultiMMapDirectory(把文件一次性全部讀入內存)。
openInput(String)功能為打開某文件的讀取通道。
1
 public IndexInput openInput(String name) throws IOException
public IndexInput openInput(String name) throws IOException  {
{
2 File f = new File(getFile(), name);
File f = new File(getFile(), name);
3 RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile(f, "r");
RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile(f, "r");
4
 try
try  { // 根據文件的大小選擇適當的IndexInput
{ // 根據文件的大小選擇適當的IndexInput
5 return (raf.length() <= MAX_BBUF) ? (IndexInput) new MMapIndexInput(
return (raf.length() <= MAX_BBUF) ? (IndexInput) new MMapIndexInput(
6 raf)
raf)
7 : (IndexInput) new MultiMMapIndexInput(raf, MAX_BBUF);
: (IndexInput) new MultiMMapIndexInput(raf, MAX_BBUF);
8
 } finally
} finally  {
{
9 raf.close();
raf.close();
10 }
}
11 }
}
RAMDirectory類
RAMDirectory與FSDirectory不同,它是基于內存的。它在內存中劃出一個區域,用來存放文件,在性能上肯定要比FSDirectory快的多。當然它也有它的局限性,比如,文件過大,內存小放不下,呵呵。
RAMDirectory里定義了變量:HashMap fileMap = new HashMap()用來存放文件名及與之對應得文件在內存中的指針。還有一個變量long sizeInBytes:文件夾總字節數。
當通過Directory來創建RAMDirectory時,RAMDirectory需要把Directory中的數據拷貝到RAMDirectory中來。
1
 private RAMDirectory(Directory dir, boolean closeDir) throws IOException
private RAMDirectory(Directory dir, boolean closeDir) throws IOException  {
{
2 this();
this();
3 Directory.copy(dir, this, closeDir); // 拷貝數據
Directory.copy(dir, this, closeDir); // 拷貝數據
4 }
}
list()用來列出RAMDirectory中的所有文件,也就是fileMap中的所有文件名。
1
 public synchronized final String[] list()
public synchronized final String[] list()  { // 列出fileMap中的文件清單
{ // 列出fileMap中的文件清單
2 ensureOpen(); // 確保fileMap不為空
ensureOpen(); // 確保fileMap不為空
3 Set fileNames = fileMap.keySet(); // 返回文件名set
Set fileNames = fileMap.keySet(); // 返回文件名set
4 String[] result = new String[fileNames.size()];
String[] result = new String[fileNames.size()];
5 int i = 0;
int i = 0;
6 Iterator it = fileNames.iterator();
Iterator it = fileNames.iterator();
7 while (it.hasNext())
while (it.hasNext())
8 // 遍歷文件名
// 遍歷文件名
9 result[i++] = (String) it.next();
result[i++] = (String) it.next();
10 return result; // 返回文件名數組
return result; // 返回文件名數組
11 }
}
在查詢某文件是否存在時,只需要到fileMap中看下對應的文件名是否存在。
1
 public final boolean fileExists(String name)
public final boolean fileExists(String name)  { // 查詢是否存在名為name的文件
{ // 查詢是否存在名為name的文件
2 ensureOpen();
ensureOpen();
3 RAMFile file;
RAMFile file;
4
 synchronized (this)
synchronized (this)  {
{
5 file = (RAMFile) fileMap.get(name); // 從fileMap中取name文件
file = (RAMFile) fileMap.get(name); // 從fileMap中取name文件
6 }
}
7 // file != null 說明文件存在;反之,不存在
// file != null 說明文件存在;反之,不存在
8 return file != null;
return file != null;
9 }
}
touchFile(String)功能是修改給定文件名的文件的最近修改時間。方法本身并不是同步方法,因此在方法體內部需要考慮同步的問題。
1
 public void touchFile(String name) throws IOException
public void touchFile(String name) throws IOException  {
{
2 // 修設置最近修改時間為當前時間
// 修設置最近修改時間為當前時間
3 ensureOpen();
ensureOpen();
4 RAMFile file;
RAMFile file;
5
 synchronized (this)
synchronized (this)  {
{
6 file = (RAMFile) fileMap.get(name);
file = (RAMFile) fileMap.get(name);
7 }
}
8 if (file == null)
if (file == null)
9 throw new FileNotFoundException(name);
throw new FileNotFoundException(name);
10
11 long ts2, ts1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
long ts2, ts1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
12
 do
do  { // 這個循環的用意是什么?????有人告訴我不????
{ // 這個循環的用意是什么?????有人告訴我不????
13
 try
try  {
{
14 Thread.sleep(0, 1); // 睡 1ns
Thread.sleep(0, 1); // 睡 1ns
15
 } catch (InterruptedException e)
} catch (InterruptedException e)  {
{
16 }
}
17 ts2 = System.currentTimeMillis(); // 獲取當前時間
ts2 = System.currentTimeMillis(); // 獲取當前時間
18 } while (ts1 == ts2);
} while (ts1 == ts2);
19
20 file.setLastModified(ts2); // 同步修改最近修改時間
file.setLastModified(ts2); // 同步修改最近修改時間
21 }
}
deleteFile(String)功能為刪除給定文件名的文件,不存在則拋出異常。
1
 public synchronized void deleteFile(String name) throws IOException
public synchronized void deleteFile(String name) throws IOException  { // 刪除name文件
{ // 刪除name文件
2 ensureOpen();
ensureOpen();
3 RAMFile file = (RAMFile) fileMap.get(name);
RAMFile file = (RAMFile) fileMap.get(name);
4
 if (file != null)
if (file != null)  {
{
5 fileMap.remove(name); // 從fileMap中刪除此文件,也就是刪掉該文件的相關記錄:名字和buffer地址
fileMap.remove(name); // 從fileMap中刪除此文件,也就是刪掉該文件的相關記錄:名字和buffer地址
6 file.directory = null; // 設置file的所屬文件夾為null,即它不再屬于任何文件夾
file.directory = null; // 設置file的所屬文件夾為null,即它不再屬于任何文件夾
7 sizeInBytes -= file.sizeInBytes; // updates to RAMFile.sizeInBytes synchronized on directory
sizeInBytes -= file.sizeInBytes; // updates to RAMFile.sizeInBytes synchronized on directory
8 } else
} else
9 throw new FileNotFoundException(name);
throw new FileNotFoundException(name);
10 }
}
createOutput()創建一個新文件并返回其寫通道。若同名文件已存在,則刪除之。

 public IndexOutput createOutput(String name) throws IOException
public IndexOutput createOutput(String name) throws IOException  { // 新建給定名字的文件并返回它的寫通道
{ // 新建給定名字的文件并返回它的寫通道
 ensureOpen(); // 確保fileMap不為null
ensureOpen(); // 確保fileMap不為null
 RAMFile file = new RAMFile(this); // 創建一個內存文件,參數為當前文件夾
RAMFile file = new RAMFile(this); // 創建一個內存文件,參數為當前文件夾

 synchronized (this)
synchronized (this)  { // 獲取同步鎖
{ // 獲取同步鎖
 RAMFile existing = (RAMFile) fileMap.get(name);
RAMFile existing = (RAMFile) fileMap.get(name);

 if (existing != null)
if (existing != null)  { // 存在同名文件,則刪除之
{ // 存在同名文件,則刪除之
 sizeInBytes -= existing.sizeInBytes; // 更改文件夾大小
sizeInBytes -= existing.sizeInBytes; // 更改文件夾大小
 existing.directory = null; // 設置其directory為null
existing.directory = null; // 設置其directory為null
 }
}
 fileMap.put(name, file);
fileMap.put(name, file);
 }
}
 return new RAMOutputStream(file); // 返回該文件的寫通道
return new RAMOutputStream(file); // 返回該文件的寫通道
 }
}